Moving bed methanol-to-hydrocarbon method
A technology for producing hydrocarbons from methanol and moving bed is applied in chemical instruments and methods, producing hydrocarbons from oxygen-containing organic compounds, and preparing liquid hydrocarbon mixtures, etc., and can solve the problems of wear, difficulty in maintaining the thermal balance of the reaction regeneration system, and economic losses.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
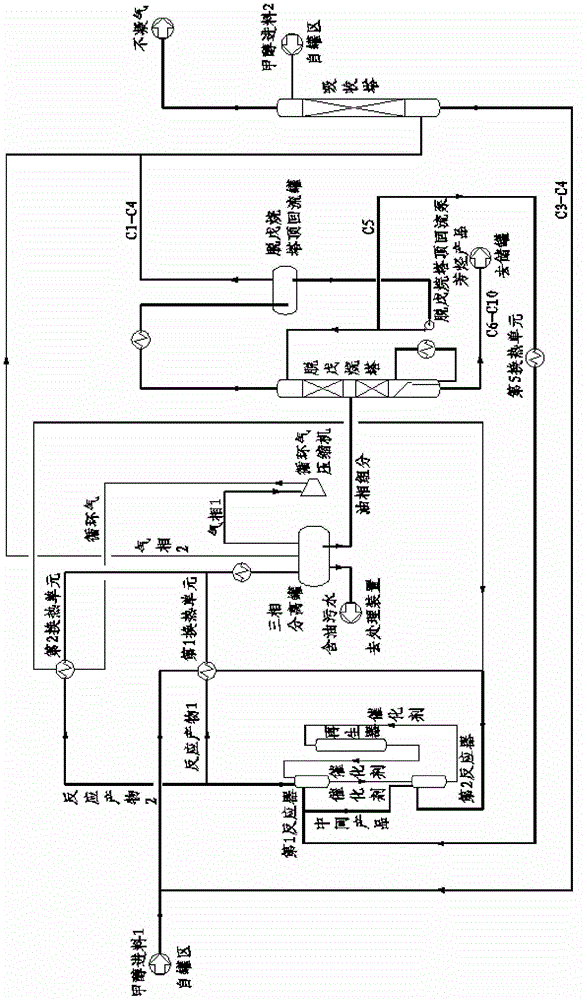
[0044] Embodiment one (see figure 1 ): Containing the first and second two reactors, the separation step adopts depentanizer fractionation.
[0045] The fresh methanol feed is pumped outside the boundary area, the pressure is increased to 0.5MPaG, and the temperature is 25°C. The fresh methanol feed 1 first enters the second reactor (equivalent to the last reactor) after heat exchange with the reaction product, and passes through the pre-passivated catalyst from the first reactor (equivalent to the initial end reactor). To the moving bed contact reaction, the liquid hourly space velocity is 1.0h -1 , to generate an intermediate product (ie, the reaction product of the second reactor), with a pressure of 0.45MPaG and a temperature of 520°C. After leaving the second reactor, the intermediate product enters the first reactor, and conducts a radial moving bed contact reaction with the high-activity catalyst from the regenerator. The liquid hourly space velocity is 1.0h -1 , to ...
Embodiment 2
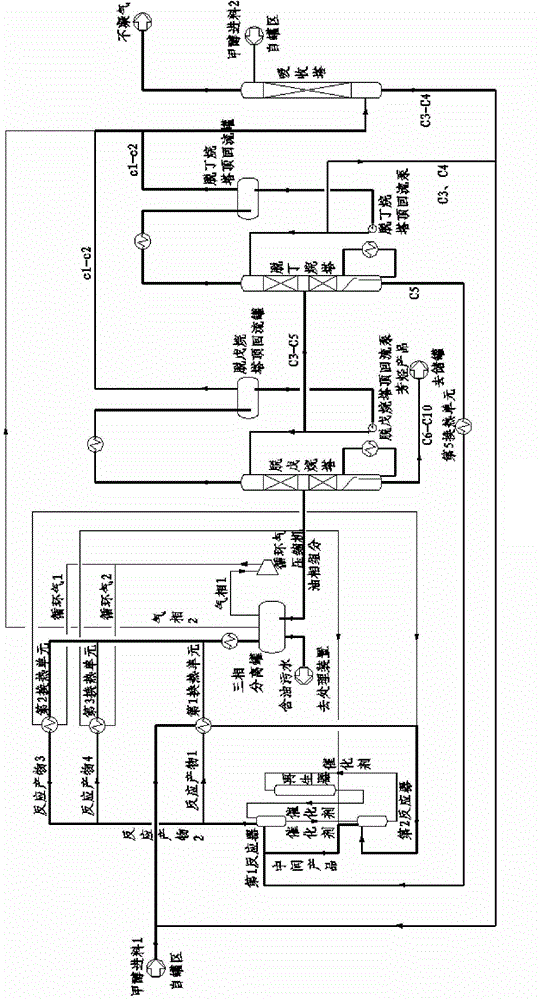
[0050] Embodiment two (see figure 2 ): Containing the first and second two reactors, the separation step adopts two-stage fractionation of a depentanizer and a debutanizer.
[0051] The fresh methanol feed is pumped outside the boundary area, the pressure is increased to 1.76MPaG, and the temperature is 30°C. The fresh methanol feed 1 first enters the second reactor (equivalent to the last reactor) after heat exchange with the reaction product, and passes through the pre-passivated catalyst from the first reactor (equivalent to the initial end reactor). To the moving bed contact reaction, the liquid hourly space velocity is 4.8h -1 , can also be 5.0h -1 , to generate an intermediate product (ie the reaction product of the second reactor), the pressure is 1.74MPaG or 1.75MPaG, and the temperature is 350°C or 320°C. After leaving the second reactor, the product enters the first reactor, and conducts a radial moving bed contact reaction with the high-activity catalyst from th...
Embodiment 3
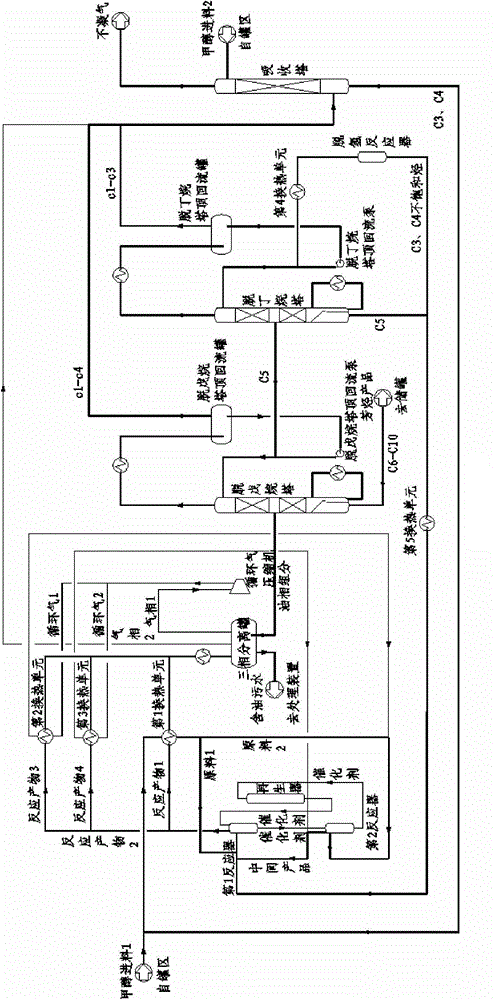
[0057] Embodiment three (see image 3 ): Contains the first and second two reactors. The separation step adopts depentanizer and debutanizer two-stage fractional distillation, and uses a dehydrogenation reactor to dehydrogenate C3~C4. The methanol raw material is divided into two stocks and enters two a reactor.
[0058] The fresh methanol feed is pumped through the boundary area, the pressure is increased to 0.3MPaG, and the temperature is 30°C. The fresh methanol feed 1 is divided into two stocks after heat exchange with the reaction product: raw material 1 and raw material 2, which are respectively used as the first reactor (equivalent to the initial reactor), the second reactor (equivalent to the final reactor) ) feed, the flow ratio is 1:9. Raw material 2 enters the second reactor, and conducts a radial moving bed contact reaction with the pre-passivated catalyst from the first reactor, and the liquid hourly space velocity is 2.5h -1 , generate an intermediate product ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com