Ethanol-tolerant bifunctional enzyme capable of degrading carbamide and ethyl carbamate (EC) and application of ethanol-tolerant bifunctional enzyme
A technology of urethane and bifunctional enzymes, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of poor ethanol tolerance, far-fetched, limited production capacity, etc., and achieve the effect of high ethanol tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Cloning of gene ureBL encoding ethanol-resistant and efficient degradation of EC urease
[0039] Genomic DNA of Bacillus licheniformis (Bacillus licheniformis 9945A) was extracted according to the instructions of the Bacterial Genome Extraction Kit (OMEGA). According to the urease gene sequence published by NCBI (GenBank: CP005965.1, GI: 521287266-521287273), design forward primer F and reverse primer R (sequences are shown in SEQ ID NO.5 and SEQ ID NO.6 respectively), Forward primer plus BamH I restriction site and its protective base, reverse primer plus Xho I restriction site and its protective base, as follows:
[0040] Forward primer F: 5'-CGCGGATCCGATGCAACTATTACCGCGTGAAGTAG-3'
[0041] Reverse primer R: 5'-CCGCTCGAGTTAAATCCAAAGGTTAAATAAACCC-3'
[0042] The ureBL gene (nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1) is amplified by using the Bacillus licheniformis genomic DNA as a template and the above-mentioned specific primer as a primer. Amplification s...
Embodiment 2
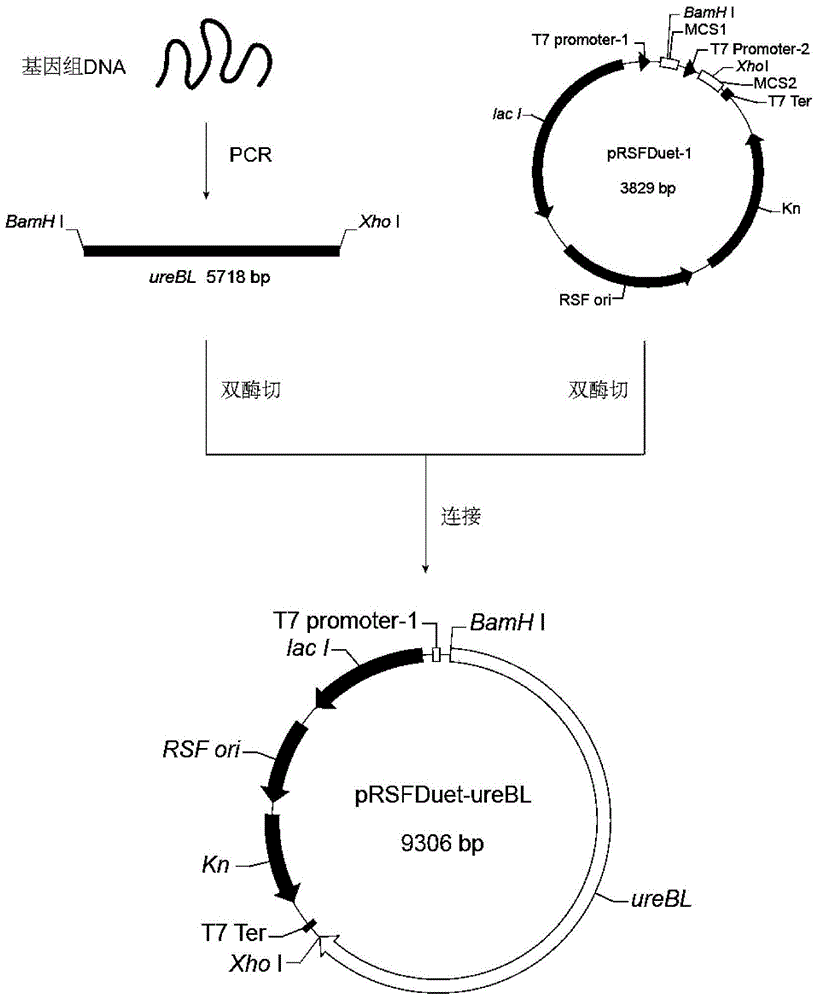
[0043] Embodiment 2: Construction of expression vector and expression system
[0044] The PCR product obtained by the method in Example 1 was digested with BamH I and Xho I, recovered after gel cutting, ligated with the pRSFDuet-1 plasmid digested with BamH I and Xho I, and transformed into E.coli BL21DE3 competent cells , spread on LB solid plates containing 50 μg / ml kanamycin, culture at 37°C for 12 hours, use forward primer F and reverse primer R, and identify positive clones by PCR. The positive clones identified correctly by colony PCR were cultured in LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / ml kanamycin, the plasmid was extracted, and the plasmid was double-enzymatically digested for verification. The correct plasmid was verified by BamH I and Xho I double digestion (such as figure 2 shown) were sent to Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for sequencing. Thus, the exogenous expression system BL21(DE3) / pRSFDuet-ureBL of recombinant urease was obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3: Recombinant expression of ethanol-resistant and efficient degradation of urethane urease
[0046] Pick a single colony of genetically engineered bacteria BL21(DE3) / pRSFDuet-ureBL, inoculate it in 25 mL of LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin, and culture it overnight at 37°C with shaking. The next day, transfer to TB medium containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin according to 1% inoculum, and cultivate to bacterial concentration OD 600 When = 0.6, add IPTG to a final concentration of 1 mmol / L for induction, culture at 30°C for 10 h, collect the bacteria by centrifugation, resuspend the cells with 20 mM pH4.5 citric acid-citric acid buffer, break the wall by ultrasonication, and centrifuge to get the supernatant , Determination of enzyme activity, and detection of protein expression by SDS-PAGE. from Figure 4 It can be seen that, compared with the empty vector lane without the target band connected, the induced lane has target bands at 62kDa and 14KDa that ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com