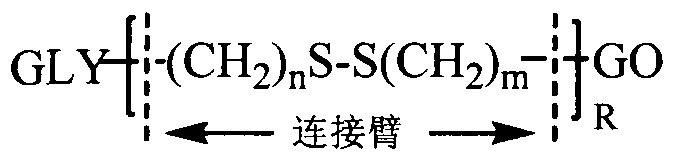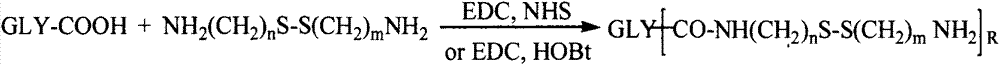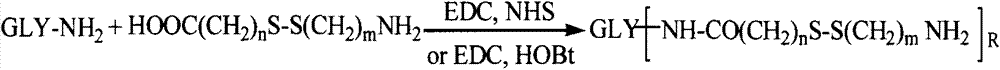Preparation and application of polysaccharide-modified graphene oxide carrier and its pharmaceutical composition for triggering drug release at the focus of organisms
A technology of graphene and organisms, applied in the field of preparation of the carrier, can solve the problems of slow polysaccharide degradation and shedding, hindering drug release, steric hindrance, etc., and achieve good redispersibility, increased biocompatibility, and good uniformity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Embodiment 1: the preparation of hyaluronic acid graphene oxide
[0055] 0.1mmol of hyaluronic acid, 1mmol of cystamine, 0.2mmol of EDC and 0.2mmol of NHS were dissolved in formamide. After 24 hours of reaction, the hyaluronic acid intermediate was precipitated with acetone, suction filtered and dialyzed with distilled water for 3 days (MWCO=3500) , to obtain a hyaluronic acid intermediate with a free one-terminal amino group.
[0056] 0.1 mmol of graphene oxide and 0.1 mmol of intermediates were dissolved in water, 0.4 mmol of EDC was used as an activator, and reacted for 24 hours. After the reaction, use a dialysis bag (MWCO 20000, 25000, 50000) to dialyze in distilled water at room temperature for 48 hours, filter and freeze-dry to obtain hyaluronic acid-modified graphene oxide.
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2: the preparation of chitosan graphene oxide
[0058] 0.1mmol chitosan was dissolved in a mixed solvent of water and dimethyl sulfoxide (v / v=1:1), adding 2mmol S-aminoethyl, 3,4-dithiopropionic acid, 0.4mmol EDC and 0.4mmol NHS, reacted for 24 hours, and dialyzed in distilled water for 3 days (MWCO=3500) to obtain a chitosan intermediate with a free terminal amino group.
[0059] 0.1 mmol of graphene oxide and 0.1 mmol of intermediates were dissolved in water, 0.4 mmol of EDC was used as an activator, and reacted for 24 hours. After the reaction, use a dialysis bag (MWCO 20000, 25000, 50000) to dialyze in distilled water at room temperature for 48 hours, filter and freeze-dry to obtain chitosan-modified graphene oxide.
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3: Preparation of low molecular weight heparin graphene oxide
[0061] 0.1mmol of low molecular weight heparin, 1mmol of cystamine, 0.2mmol of EDC and 0.2mmol of NHS were dissolved in formamide. After 24 hours of reaction, the hyaluronic acid intermediate was precipitated with acetone, suction filtered and dialyzed with distilled water for 3 days (MWCO=3500) , to obtain a low-molecular-weight heparin intermediate with a free one-terminal amino group.
[0062] 0.1 mmol of graphene oxide and 0.1 mmol of intermediates were dissolved in water, 0.4 mmol of EDC was used as an activator, and reacted for 24 hours. After the reaction, use a dialysis bag (MWCO 20000, 25000, 50000) to dialyze in distilled water at room temperature for 48 hours, filter and freeze-dry to obtain low molecular weight heparin-modified graphene oxide.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com