A Microbiological Method for Detecting Heavy Metal Copper in Water
A water body and copper ion technology, applied in the field of environmental biology, can solve the problems of poor stability of fluorescence detection signals and poor repeatability of independent experiments, slow development of heavy metal microbial detection technology, uneven plasmid copy number, etc., and achieve short detection time, Fluorescence intensity value deviation is small, and the effect of improving sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Embodiment 1. Detect the preparation of heavy metal copper Escherichia coli strain:
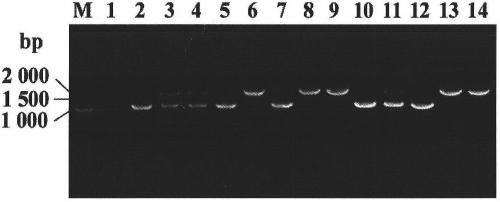
[0065] 1. Construction of Escherichia coli mutant strain E.coli copA sensitive to copper ion by using Red recombination system - cueO - cusA -
[0066] Using pKD3 as a template, the chloramphenicol resistance gene with FRT site (FLP recombinase recognition site) was amplified by PCR, and it was electrotransformed into MC4100 electroporation-competent cells containing pKD46 plasmid. pKD46 / MC4100 bacteria were induced by 30mmol / L arabinose during the competent preparation, so that the pKD46 plasmid expressed Gam, Bet and Exo three lambda phage recombinases in the bacteria, and the Gam recombinase inhibited the RecBCD exonuclease of Escherichia coli Enzyme V activity, so that the chloramphenicol gene electrotransferred into the bacteria will not be degraded immediately. At the same time, Exo and Bet recombinase guide the recombination and replacement of the chloramphenicol gene and the...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Example 2. Determination and parameter optimization of the performance of detecting heavy metal copper Escherichia coli strains
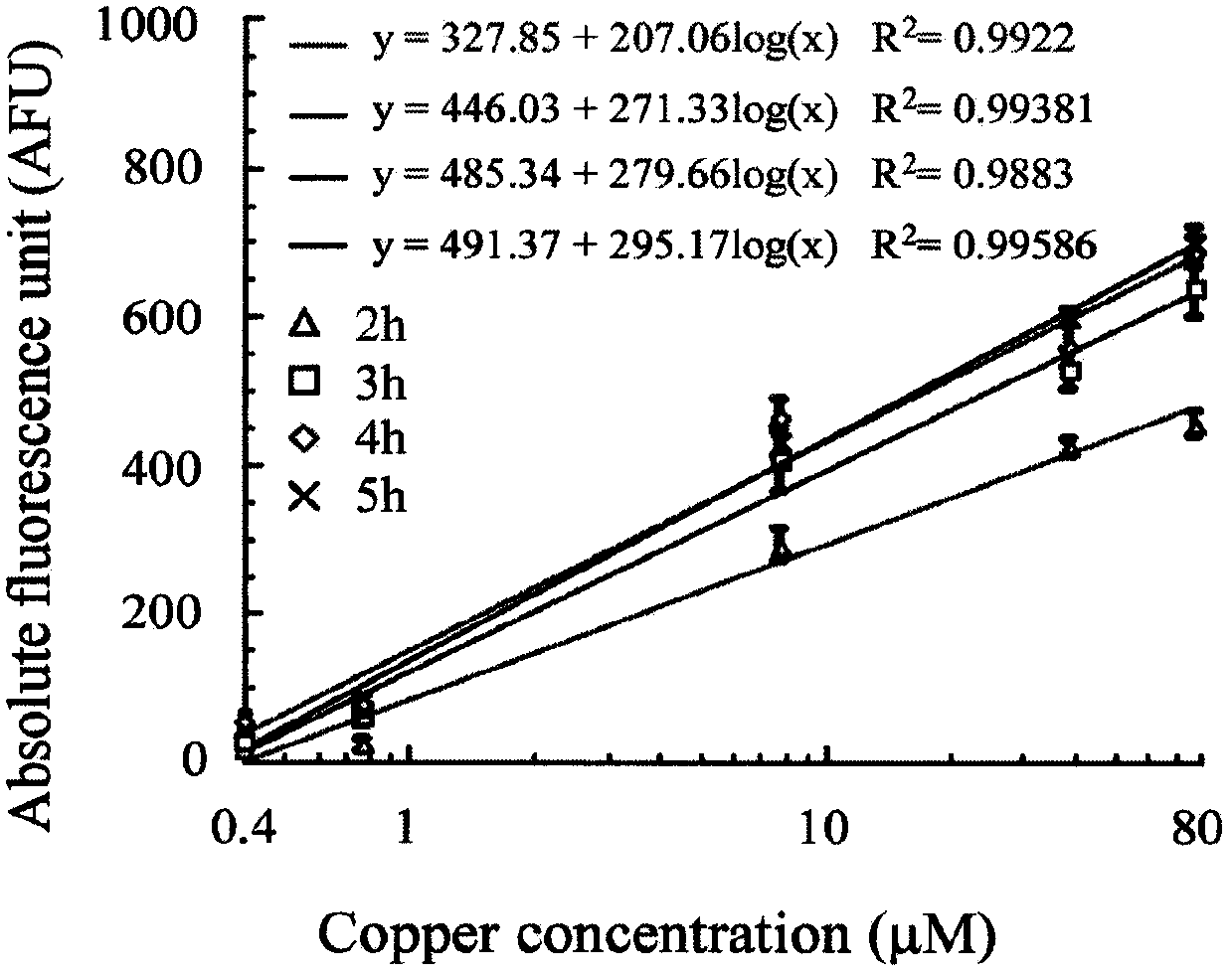
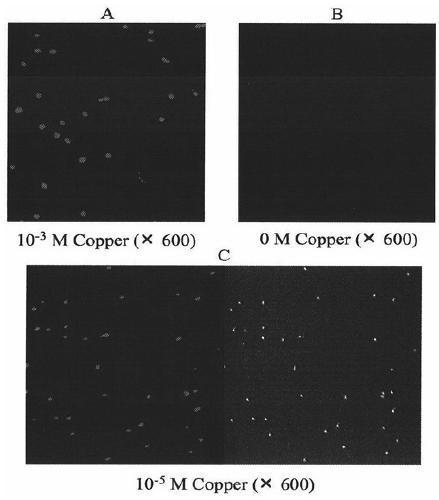
[0084] Optimize the measurement conditions and determine the relevant parameters for the constructed Escherichia coli strains to determine a set of stable, sensitive and accurate experimental measurement conditions, including induction kinetic experiments, determination of response curves, specificity and selectivity experiments , characterization analysis, determination of the optimum detection range, determination of the lowest detection limit, etc.
[0085] 1. Optimization of incubation time of Escherichia coli strain E.coli WMC-007 with copper ions
[0086] 1.1 On fixing Cu 2+ Kinetic analysis of induction of GFPmut2 expression by E. coli WMC-007 under concentration conditions.
[0087] Use a pipette gun to draw a certain volume of E.coli WMC-007 overnight bacterial seed solution and add it to 50ml of fresh LB liquid medium, so that the...
Embodiment 3
[0126] Example 3. Establishment of a methodology for the detection of heavy metal copper in water by Escherichia coli strain E.coli WMC-007 and its application implementation
[0127] 1. Preparation of medium: 1g / L tryptone, 0.5g / L yeast extract, 1g / L NaCl, first add 50ml MilliQH 2 O, add MilliQ H after shaking until completely melted 2 O was adjusted to 80ml, autoclaved (121°C, 30min), then added 10ml of 400mM sterile MOPS buffer (pH 7.2), and mixed.
[0128] 2. Establishment of standard curve:
[0129] Use a pipette gun to draw a certain volume of E.coli WMC-007 overnight bacterial seed solution and add it to 50ml of fresh LB liquid medium (containing MOPS with a final concentration of 40mmol / L), so that the OD600 value of the initial bacterial solution is about 0.02, Aliquot (1ml / tube), add an equal volume of Cu with different concentrations 2+ Solution to each tube of bacteria solution, so that the final concentration is 0.16, 0.39, 0.78, 1.56, 7.81, 15.63, 31.25, 39.06...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com