High-strength and heat-resistant polylactic acid material for 3D printing
A polylactic acid material and 3D printing technology, applied in the field of 3D printing materials, can solve the problems of uneven structure of polylactic acid, affecting product printing and unusable industrial production, etc., to improve practicability and scope of application, reduce heat The effect of warping, increasing crystallization rate and crystallinity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
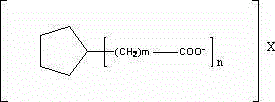
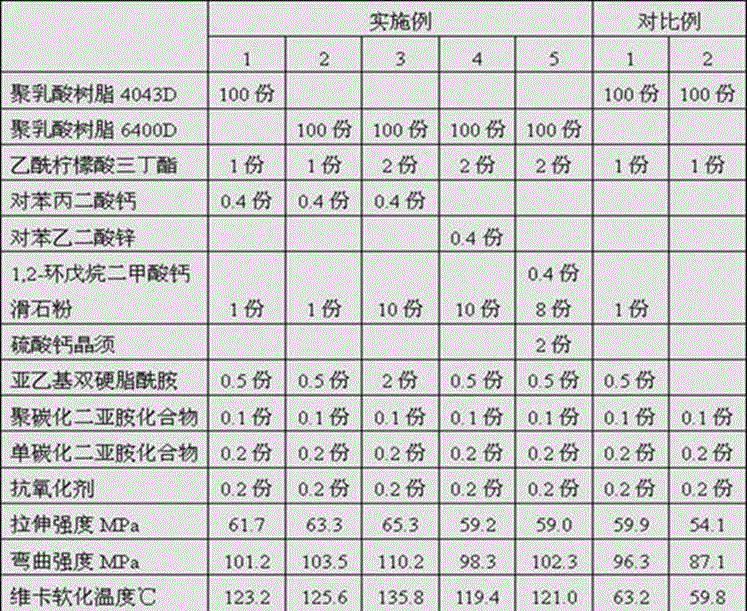
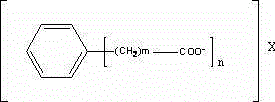
[0039] Example: 100 parts by mass of polylactic acid, 0.01 to 5 parts by mass of a nucleating agent, 0.1 to 2 parts by mass of a water resistant agent, 0.1 to 5 parts by mass of a nucleating aid, and 0.1 to 5 parts by mass of a plasticizer, 0.1-20 parts by mass of filler and 0.1-1 part by mass of antioxidant are uniformly mixed, melt-blended, extruded and granulated at 180-205°C. Dry the polylactic acid modified material obtained above and add it to the FDM 3D printing filament extruder. The extrusion temperature is 180-210°C. Control the water temperature, extrusion volume and traction speed, and control the diameter of the filament to be 1.75±0.03mm. . Control the printing temperature of the 3D printer to 200-210°C, and the temperature of the hot bed to 30-90°C. Control the 3D printer to print Type 1B samples that meet the requirements of GB / T 1040.2-2006. The tensile strength, flexural strength and Vicat softening temperature of the material were tested according to the s...
specific Embodiment approach
[0043] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with embodiment:
Synthetic example 1
[0044] Synthesis Example 1: Synthesis of Calcium Terephenylmalonate
[0045] Add 11.11 grams (0.05mol) of terephthalic acid (4251-21-2) and 250ml of water into a round bottom flask with a mechanical stirring bar, heat to 80°C, and stir for 30 minutes to fully dissolve it. Dissolve 3.70 grams (0.05mol) of Ca(OH)2 powder in 500ml of water, and the dissolution temperature is 100°C. Add the Ca(OH)2 aqueous solution to the terephthalic acid solution, and stir for 45 minutes until no white flocs or precipitates are formed. Suction filter the reactant, wash, dry, and pulverize to obtain calcium terephthalate. 12.01 g of the product was obtained with a yield of 92.3%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com