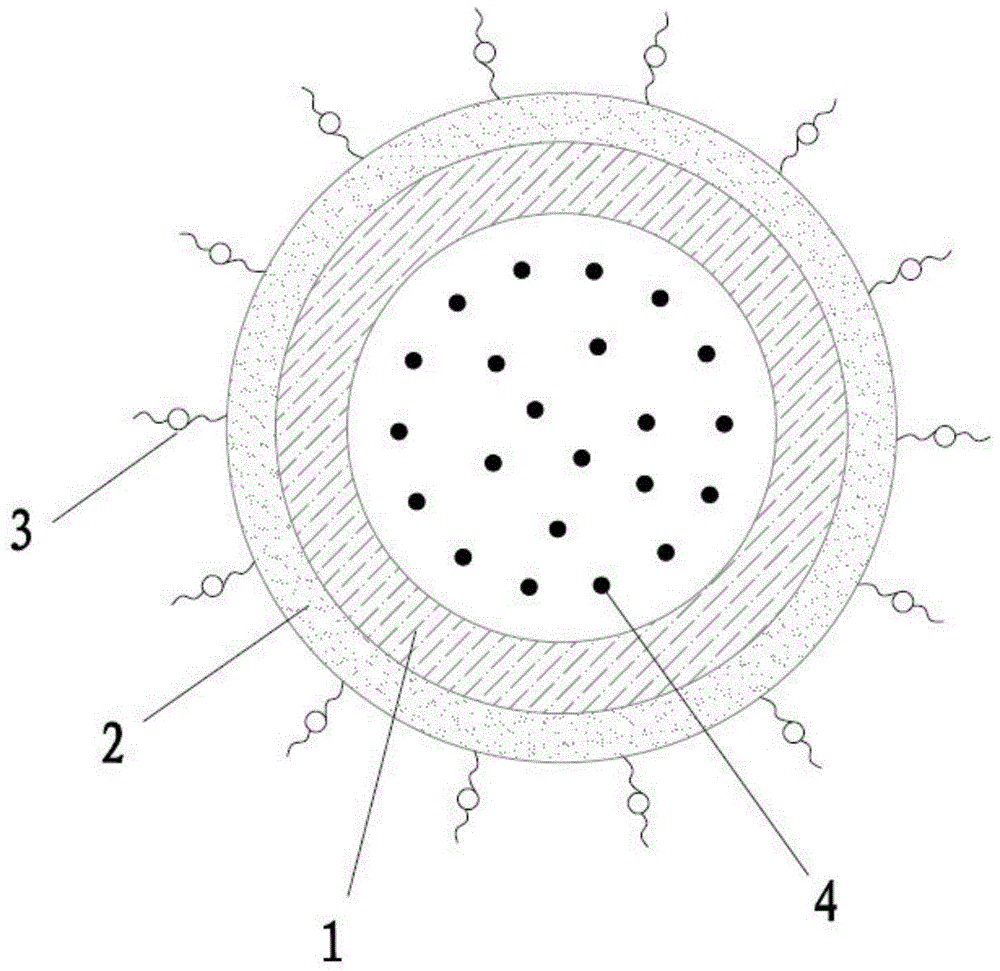
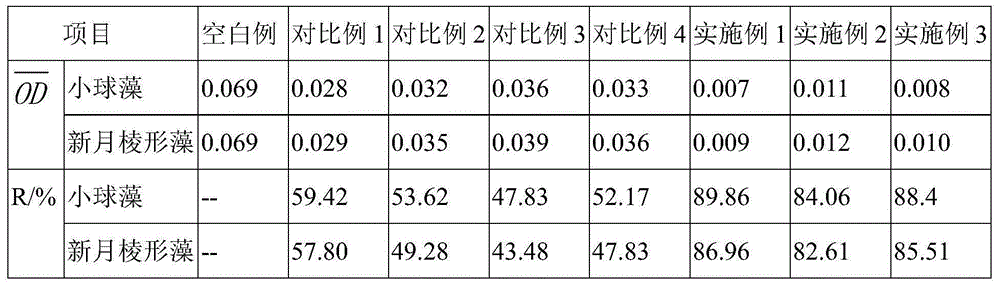
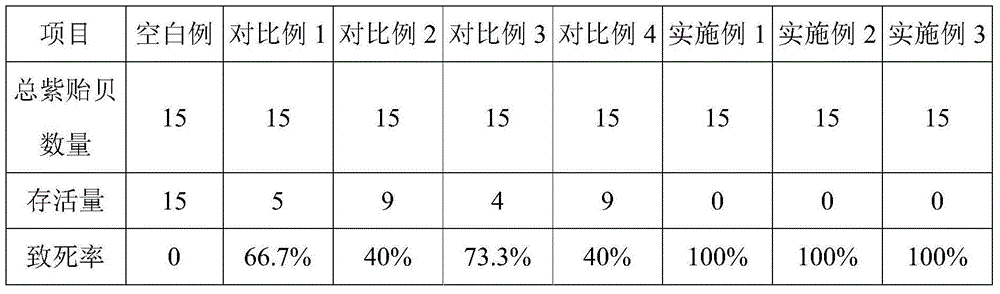
Antifouling biological adhesive agent and antifouling biological adhesive coating
A bio-fouling and anti-fouling technology, applied in anti-fouling/underwater coatings, anti-corrosion coatings, paints containing biocides, etc., can solve marine concrete structure fouling, economic loss, marine concrete structure safety and durability hazards and other problems, to achieve good biocompatibility, enhance antibacterial and antifouling, and improve antibacterial and anti-biological fouling performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Step1. Preparation of polyaspartic acid ester, code PAE-a
[0054] The amino-terminated polyether JeffamineD-2000 and diethyl maleate are in the ratio n(—NH 2 ): n(—C=C—)=1:1 metering. Add JeffamineD-2000 into the reaction kettle equipped with agitator and heating temperature control device, pass nitrogen gas and raise the temperature to 40°C, add diethyl maleate dropwise at a rate of one drop every two seconds, after the addition is completed, nitrogen protection Stir and heat to 80°C, keep warm for 24 hours, cool down and discharge to obtain polyaspartic acid ester.
[0055] Step2. Preparation of component A of polyaspartic ester coating
[0056] The amount of 2,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate MDI-50 and polyoxypropylene diol PPG2000 is measured according to NCO%=15% in the prepolymer produced. Add 2,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate MDI-50 into a reaction kettle equipped with a stirrer and a heating temperature control device, blow nitrogen gas and raise the tempera...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Step1. Preparation of polyaspartic acid ester, code PAE-b
[0077] The amino-terminated polyether JeffamineT-5000 and diethyl maleate are in the ratio n(—NH 2 ): n(—C=C—)=1:1 metering. Add JeffamineT-5000 into a reaction kettle equipped with a stirrer and a heating temperature control device, pass nitrogen gas and raise the temperature to 40°C, add diethyl maleate dropwise at a rate of one drop every two seconds, after the addition is completed, nitrogen protection Stir and heat to 80°C, keep warm for 24 hours, cool down and discharge to obtain polyaspartic acid ester.
[0078] Step2. Preparation of component A of polyaspartic ester coating
[0079]The amount of 2,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate MDI-50 and polyoxypropylene diol PPG2000 is measured according to NCO%=15% in the prepolymer produced. Add 2,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate MDI-50 into a reaction kettle equipped with a stirrer and a heating temperature control device, blow nitrogen and raise the temperature...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Step1. Preparation of polyaspartic acid ester, code PAE-c
[0100] The amino-terminated polyether JeffamineT-403 and diethyl maleate are in the ratio n(—NH 2 ): n(—C=C—)=1:1 metering. Add JeffamineT-403 into a reaction kettle equipped with a stirrer and a heating temperature control device, blow nitrogen and raise the temperature to 40°C, add diethyl maleate dropwise at a rate of one drop every two seconds, after the addition is completed, nitrogen protection Stir and heat to 80°C, keep warm for 24 hours, cool down and discharge to obtain polyaspartic acid ester.
[0101] Step2. Preparation of component A of polyaspartic ester coating
[0102] The amount of 2,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate MDI-50 and polyoxypropylene diol PPG2000 is measured according to NCO%=15% in the prepolymer produced. Add 2,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate MDI-50 into a reaction kettle equipped with a stirrer and a heating temperature control device, blow nitrogen and raise the temperature to 4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com