Electrochemical pre-reduction method and device for mercury speciation analysis by HPLC-AFS (high performance liquid chromatography and atomic fluorescence spectroscopy)
A HPLC-AFS, speciation analysis technology, applied in electrochemical variables of materials, measuring devices, analytical materials, etc., can solve the problems of low detection limit of organic mercury, low analysis efficiency, low efficiency of ultraviolet digestion, etc., and achieve the detection limit obvious effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
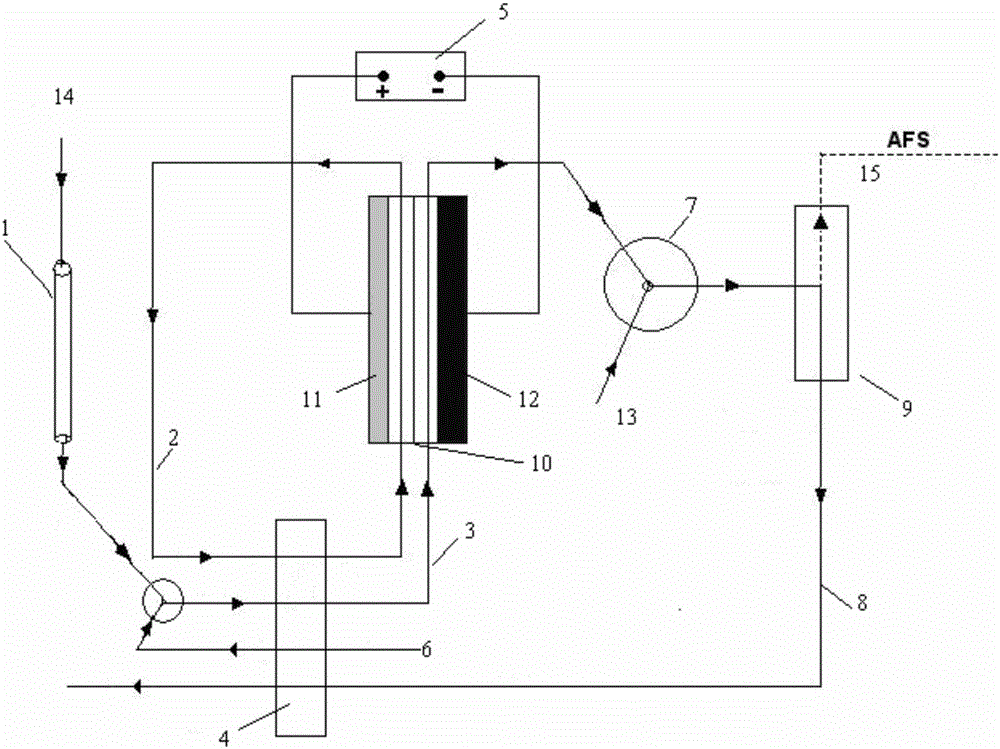
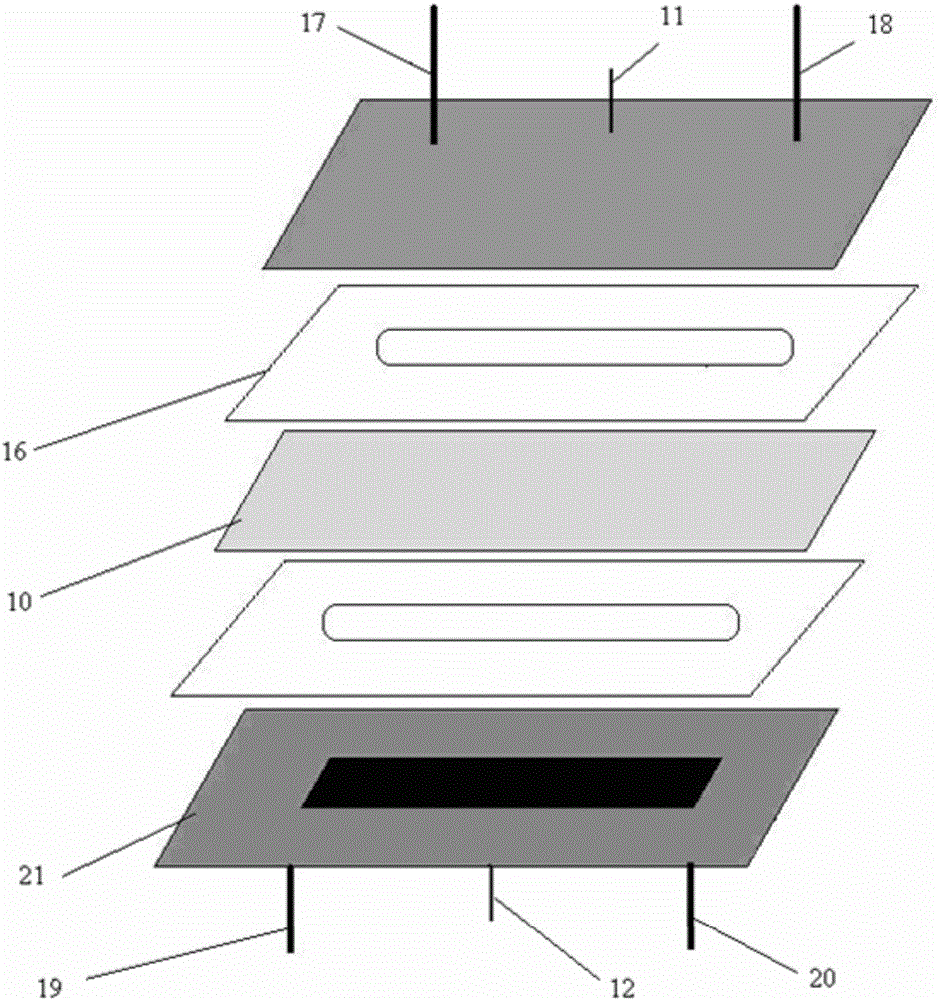
[0037] Such as figure 1 with figure 2 , an electrochemical pre-reduction device for HPLC-AFS mercury speciation analysis, which is connected with the outflow pipeline of C18 high performance liquid chromatography column (ZORBAXXDB-C18 column), and this electrochemical pre-reduction device is made of PTFE matrix 21, silicon An electrochemical flow cell assembled from a rubber sheet 16 and an ion-exchange membrane 10 (Nafion membrane), specifically including PTFE anode substrates and cathode substrates with the same shape, an ion-exchange membrane 10 is arranged between the anode substrate and the cathode substrate, and the ion-exchange membrane An anode gasket made of silicon rubber sheet 16 is placed between 10 and the anode substrate, and a rectangular hole is opened in the middle of the silicon rubber sheet 16 to form an anode chamber; an anode gasket is placed between the ion exchange membrane 10 and the cathode substrate, and the middle of the gasket is The opening const...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The influence of embodiment 2 electrolytic current on sensitivity
[0043] If the electrolytic current is too small, it is not conducive to the electrolysis of different forms of mercury into atomic states, which will reduce the steam generation efficiency of mercury; if the electrolytic current is too large, a large amount of hydrogen gas will be generated in the cathode chamber, and if the hydrogen gas production is too large, it will affect the stability of the detection device, making the Measurement deviations increase and at the same time there is a possibility of overheating of the electrolytic cell. This embodiment adopts the device of embodiment 1, HPLC mobile phase: 3% acetonitrile + 0.5% ammonium acetate + 0.03% 2-mercaptoethanol, the influence of the current on the sensitivity in the range of 0.3 ~ 1.5A electrolysis current is investigated, Fig. 7 (a), (b) are 2ppb inorganic mercury (Hg 2+ ) 6 measurements and standard curves under different currents, Figur...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3 Electrolyte flow rate optimization
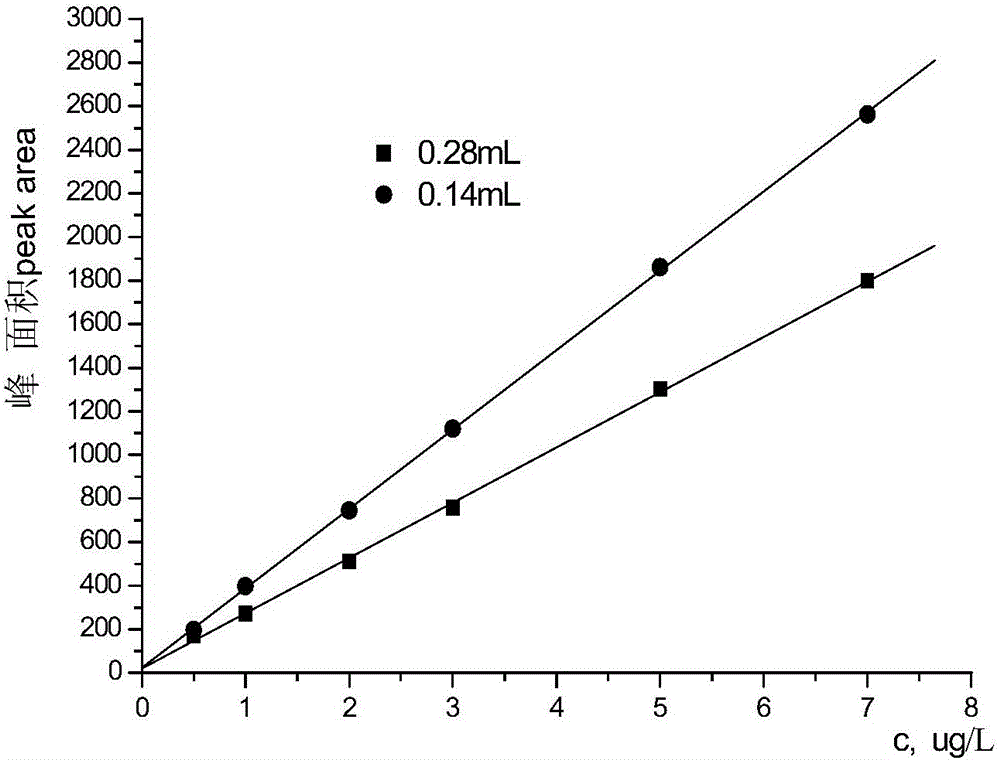
[0046] Choose 0.5mol.L -1 Sulfuric acid is used as the supporting electrolyte solution of the anode and cathode, and the 0.005-0.012m.s -1 The relationship between the fluorescence intensity of 2 μg / L methylmercury and the flow rate of the electrolyte solution within the flow rate range. The test device is as in Example 1, and the electrolytic current density is 0.54A / cm 2 . HPLC mobile phase: 5% methanol 0.5% ammonium acetate + 0.03% 2-mercaptoethanol. As shown in Fig. 5(a), within the tested concentration range, the fluorescence intensity decreases with the increase of electrolyte flow rate.
[0047] On the one hand, under a certain injection volume, the increase of the flow rate of the electrolyte solution is conducive to the mass transfer process of the sample to the electrode surface, and at the same time accelerates the rate of electrolysis products detaching from the electrode surface. This is conducive to th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com