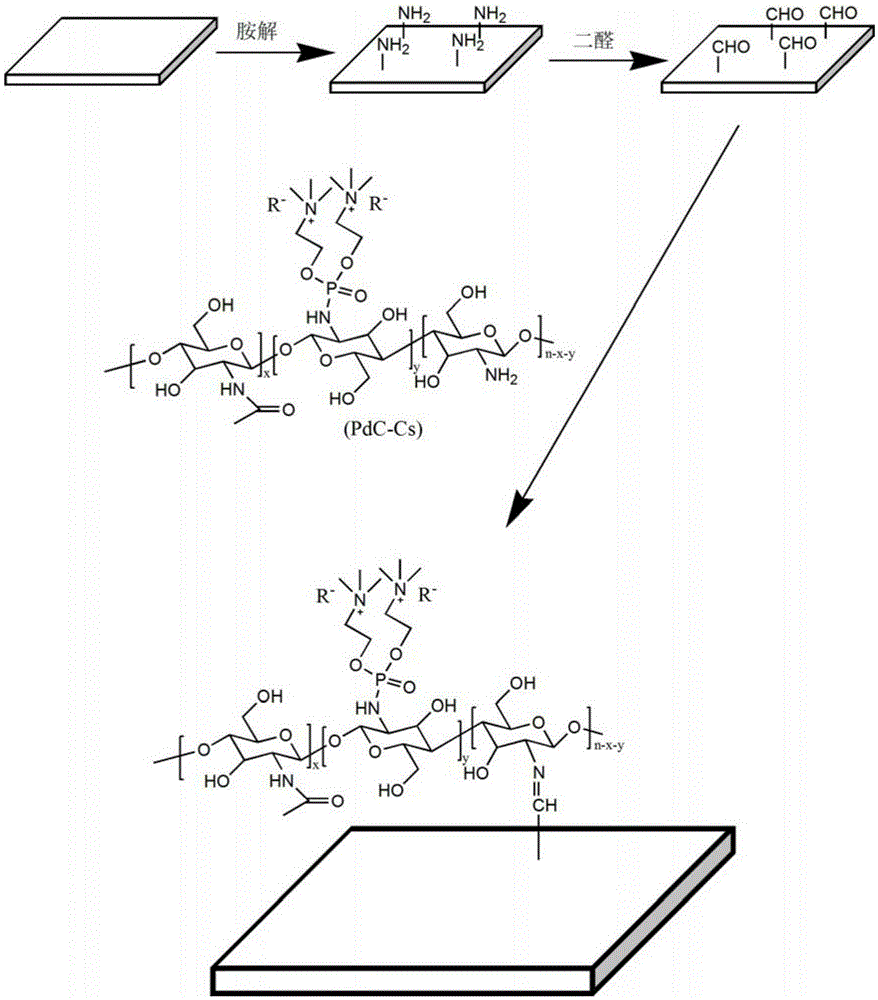
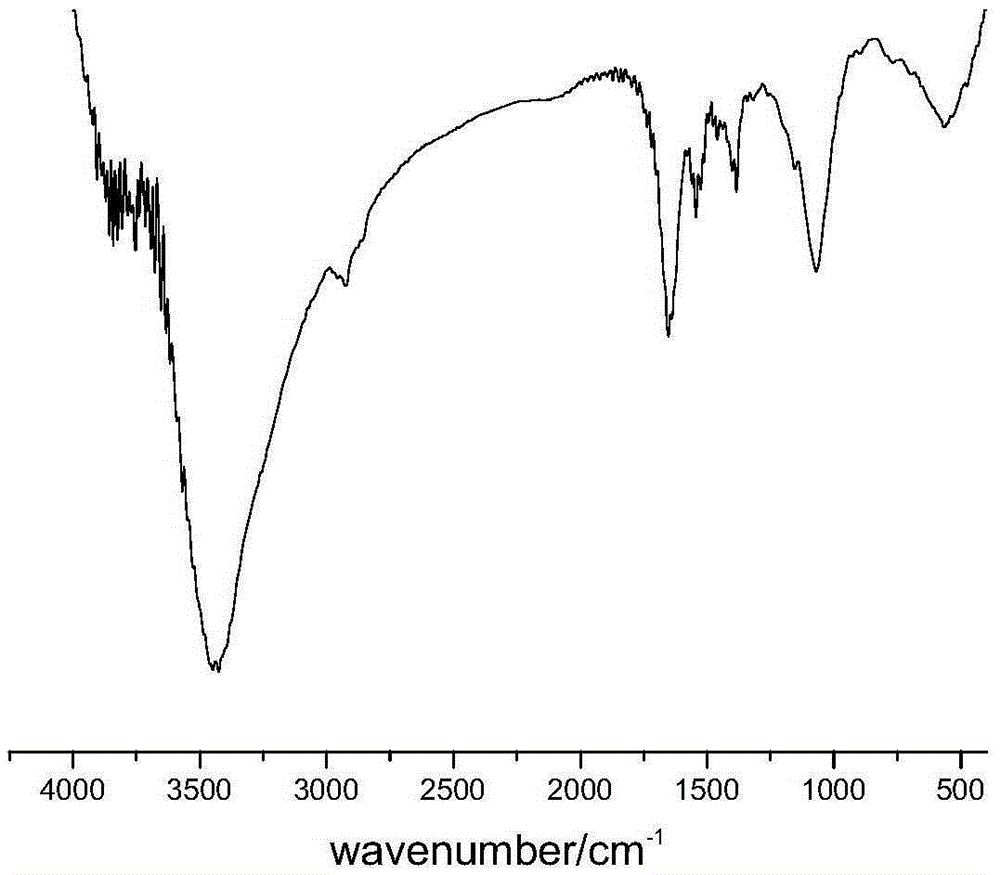
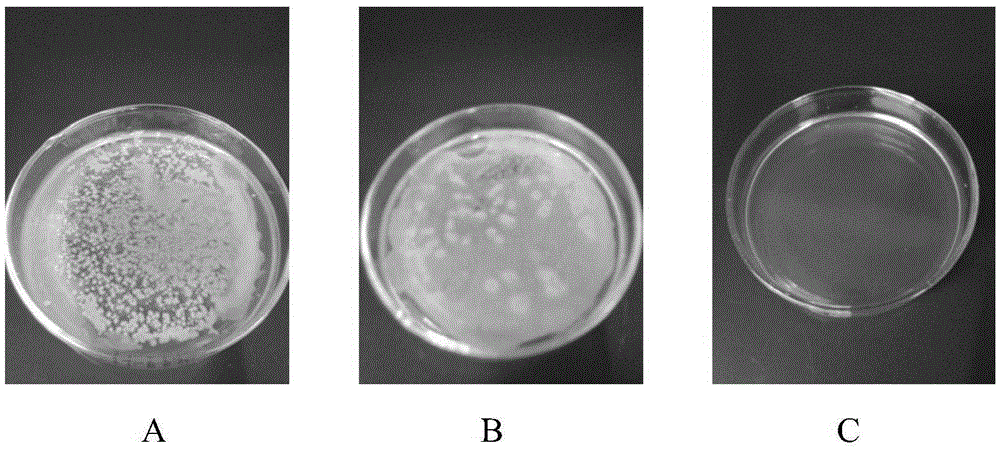
Polyester material with antibacterial and biocompatible surface and preparing method and application thereof
A biocompatible, polyester material technology, applied in the field of polymer material surface modification, can solve the problems of poor biocompatibility, toxic effects on cells, etc., and achieve good cell compatibility, easy operation, technical mild effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] The preparation of embodiment 1 phosphoric acid dicholine chitosan hydrochloride
[0040] Take 200mg of 6-O-triphenyl methyl etherified chitosan (CsTr) modified by chitosan (x / n=0) and dissolve it in 15mL of anhydrous dimethylacetamide, and add 0.42mL of Tris Ethylamine and 0.19mL of carbon tetrachloride; slowly add 0.46g of disubstituted choline phosphonate, wherein the molar ratio of the amino group in CsTr to phosphonate is 1:3, stir and react at 0°C for 6 hours; spin to dry the solvent , add formic acid, stir at room temperature for 1 hour; spin dry formic acid, dialyze with physiological saline and deionized water for 3 days, and freeze-dry to obtain phosphoric acid dicholine chitosan hydrochloride. Wherein the degree of substitution of the phosphoric acid dicholine group is 30%.
Embodiment 2
[0041] The preparation of embodiment 2 phosphoric acid dicholine chitosan hydrochloride
[0042] Get 500mg of 6-O-triphenyl methyl etherified chitosan (CsTr) modified by chitosan (x / n=0.2) and dissolve it in 40mL of anhydrous dimethylacetamide, add 1.05mL of Tris Ethylamine and 0.49mL of carbon tetrachloride; slowly add 2.3g of disubstituted choline phosphonate, wherein the molar ratio of the amino group in CsTr to phosphonate is 1:6, stir and react at 25°C for 12 hours; spin to dry the solvent , add formic acid, stir at room temperature for 3 hours; spin dry formic acid, dialyze with normal saline and deionized water for 3 days, and freeze-dry to obtain phosphoric acid dicholine chitosan hydrochloride. Wherein the degree of substitution of the phosphoric acid dicholine group is 50%.
Embodiment 3
[0043] The preparation of embodiment 3 phosphoric acid dicholine chitosan hydrochloride
[0044] Get 300mg of 6-O-triphenyl methyl etherified chitosan (CsTr) modified by chitosan (x / n=0.1) and dissolve it in 20mL of anhydrous dimethylacetamide, add 0.63mL of Tris Ethylamine and 0.29mL of carbon tetrachloride; slowly add 1.84g of disubstituted choline phosphonate, wherein the molar ratio of the amino group in CsTr to phosphonate is 1:8, stir and react at 40°C for 24 hours; spin to dry the solvent , add formic acid, stir at room temperature for 6 hours; spin dry formic acid, dialyze with normal saline and deionized water for 3 days, and freeze-dry to obtain phosphoric acid dicholine chitosan hydrochloride. Wherein the degree of substitution of the phosphoric acid dicholine group is 75%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of substitution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com