Bacillus aceticus and application of bacillus aceticus in coffee cherry peel and pulp fermentation vinegar
An acetic acid fermentation, Acetobacter pasteurian technology, applied in the preparation of vinegar, bacteria, microorganism-based methods, etc., to achieve the effects of good alcohol resistance, good passage stability, and strong acid production ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0043] (1) Preparation of coffee rind juice: crushing and homogenizing the rind to obtain coffee rind juice;
[0044] (2) Cellulase treatment of coffee peel juice: adding cellulase to the coffee peel juice obtained in step (1);
[0045] (3) sugar content adjustment: adding sugar to the coffee peel gravy after step (2) enzymolysis to adjust the initial sugar content of its fermentation;
[0046] (4) Sterilization treatment: the coffee peel meat juice obtained in step (3) is sterilized;
[0047] (5) Alcoholic fermentation: adding yeast to the coffee rind meat juice through step (4) sterilization and carrying out alcoholic fermentation;
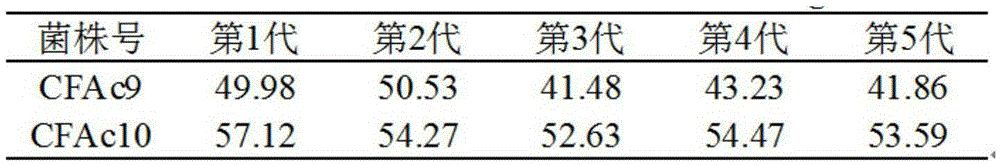
[0048] (6) Acetic acid fermentation: use the Acetobacter pasteurianum strain CFAc10 of the present invention to carry out acetic acid fermentation to step (5) through alcoholic fermentation coffee peel juice.
[0049] In step (1), conventional equipment such as a beater can be used to crush and homogenize the coffee berries, in order to obtain...
Embodiment 1
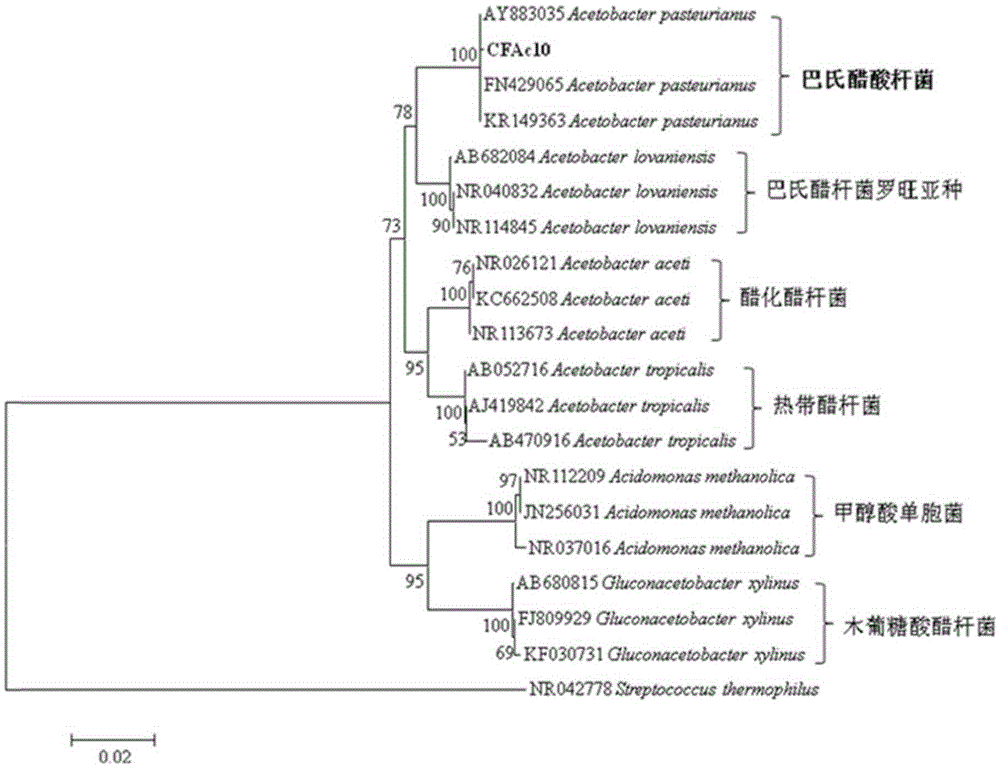
[0068] The isolation and identification of embodiment 1 acetic acid bacteria
[0069] The isolation and identification steps of acetic acid bacteria are as follows:
[0070] Sample (coffee wine)→enrichment culture of acetic acid bacteria→dilution coating separation→qualitative test of acetic acid bacteria→acid production of acetic acid bacteria→screening excellent strains→passage stability test→physiological and biochemical identification→identification by molecular biology methods
[0071] Sample: The acetic acid bacteria is isolated from the coffee fruit wine brewed by the inventor using the coffee fruit skin and flesh. For the method of brewing coffee fruit wine, refer to steps (1), (2), (3), and (5), that is, without sterilizing treatment. The coffee cherries are picked from coffee trees planted in Simao District, Pu'er City, Yunnan Province.
[0072]Enrichment culture of acetic acid bacteria: take 10ml of the above-mentioned coffee fruit wine and add it into a triangula...
Embodiment 2
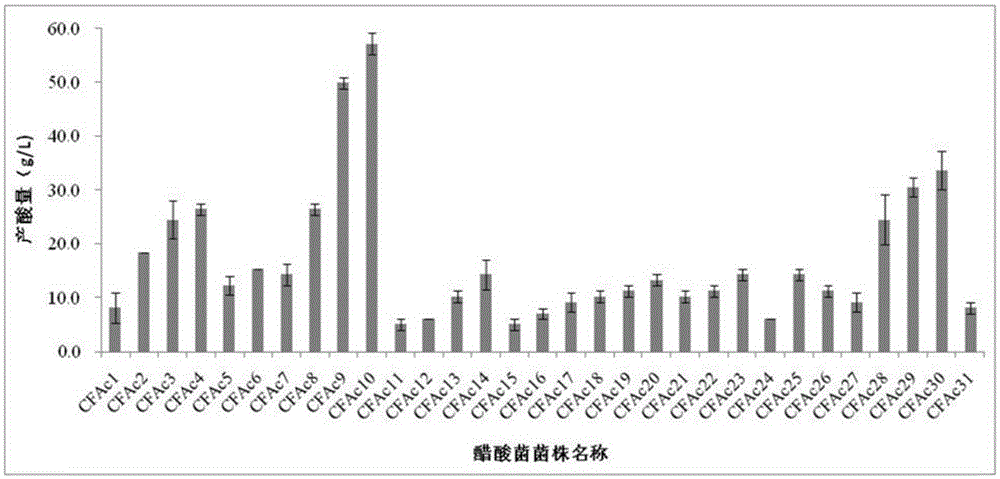
[0075] The acid production test of embodiment 2 acetic acid bacteria strain
[0076] Inoculate 1 ring of each of the screened acetic acid bacteria into 100ml of acetic acid bacteria liquid culture medium, culture at 30°C with shaking at 150r / min for 3 days, and then measure the amount of acid produced by alkaline titration. The strains with high acid production were screened for re-screening.
[0077] Take 2ml of the above culture solution, add 50ml of distilled water, add 2-3 drops of 1% phenolphthalein reagent, and titrate with 0.1mol / L NaOH until the pink color does not fade for 30s as the end point. The acid content (as acetic acid) in the sample was calculated from the amount of NaOH consumed. Parallel operation in the same way 3 times.
[0078] Acid production (g / L) = (V-V 0 )×C NaOH ×60 / V 样
[0079] In the formula: v is the volume number (ml) of the NaOH that fermented liquid sample titration consumes;
[0080] V 0 is the volume number (ml) of NaOH consumed by t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com