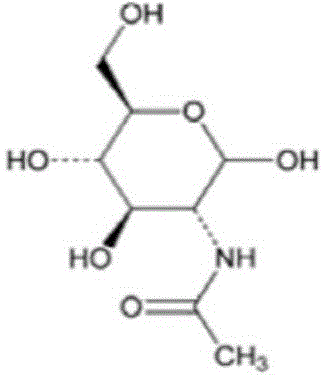
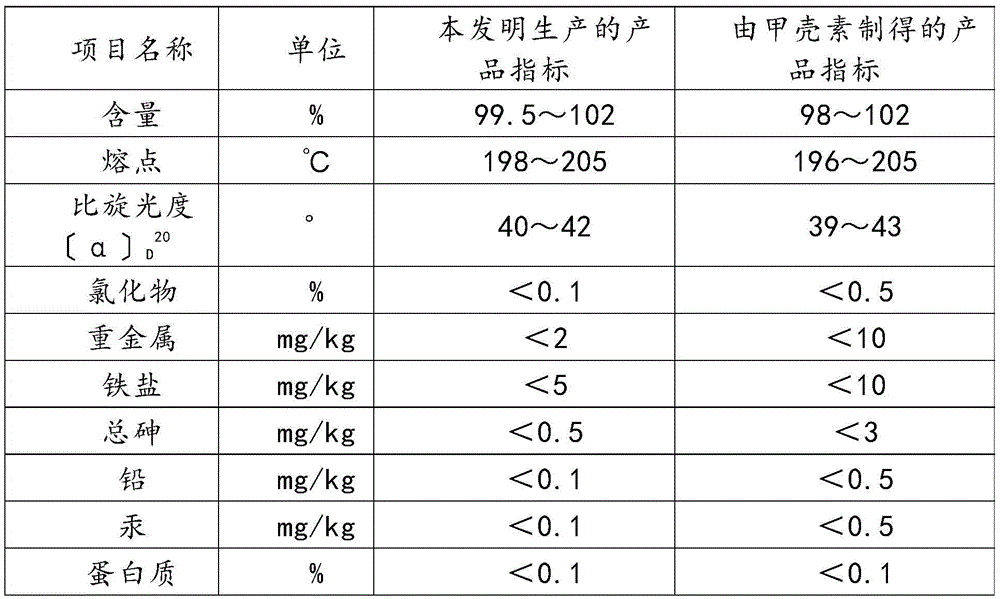
Preparation method of microbial fermentation-based N-acetyle-D-glucosamine
A technology of glucosamine and microbial fermentation, applied in the field of preparation of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, can solve the problems of reduced product yield, high price of chitinase, product oxidative denaturation, etc., and achieves reduction of the probability of other impurities, The effect of protecting from oxidation discoloration and reducing impurities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
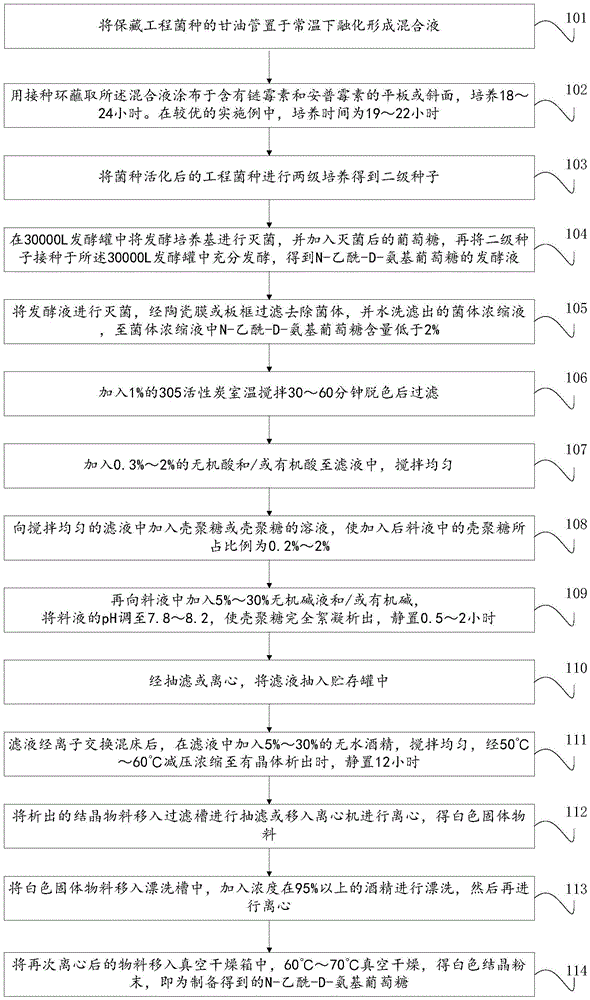
[0051] The preparation method that the embodiment of the present invention provides comprises the following steps:
[0052] S101, melting the glycerol tube for preserving the engineered bacteria at room temperature to form a mixed solution;
[0053] Specifically, the engineering strain is N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-producing Brevibacterium metabolizing.
[0054] S102, use an inoculation loop to dip the mixed solution onto a plate or slope containing streptomycin and apramycin, and incubate at 37°C for 18-24 hours. In a preferred embodiment, the incubation time is 19 to 22 hours;
[0055] Of course, before the activation of the strain, the strain needs to be preserved, and the preservation can be carried out at -80°C or -20°C.
[0056] Preservation methods specifically include: picking single colonies of engineering bacteria grown on resistant plates, adding them to resistant LB medium to form bacterial liquid, and culturing at 37°C for 8 to 12 hours; the culture time is preferab...
example 1
[0101] 1) Take the glycerol tube with bacteria stored at -20°C, melt it at room temperature, then use an inoculation loop to dip some into a plate or slope containing streptomycin and apramycin, and incubate at 37°C for 20 hours;
[0102] 2) Pick a single colony and place it in a 100mL Erlenmeyer flask with a liquid volume of 10ml LB (including streptomycin 50mg / L and apramycin 50mg / L), and shake and culture at 37°C for 8 hours;
[0103] 3) Inoculate 10ml of primary seeds in a 5L shake flask with 1L of secondary seed medium (comprising streptomycin 50mg / L and apramycin 50mg / L), culture with shaking at 34°C for 18 hours, OD600= 3, and 5 bottles are put into a 3000L seed tank, and the formula is shown in Table 1. Only streptomycin was added, not apramycin. Stirring speed 220rpm, ventilation ratio 1:0.8;
[0104] basic salt medium
Content (g / L)
Remark
K H 2 PO 4
14
CaCl 2
0.02
K H 2 PO 4 .3H 2 o
21
...
example 2
[0130] 1) Take the glycerol tube with strains preserved at -20°C, melt at room temperature, then use an inoculation loop to dip some into a plate or slope containing streptomycin and apramycin, and incubate at 37°C for 21 hours;
[0131] 2) Pick a single colony and place it in a 100 mL Erlenmeyer flask with a liquid volume of 10 ml LB (containing 50 mg / L streptomycin and 50 mg / L apramycin), and culture it with shaking at 37° C. for 8 hours.
[0132] 3) Inoculate 10 ml of primary seeds in a 5L shake flask with 1L of secondary seed medium (containing 50 mg / L streptomycin and 50 mg / L apramycin), and culture with shaking at 34°C for 17 hours, OD600= 4, and 4 bottles are inserted into a 3000L seed tank, and the formula is shown in Table 4. Only streptomycin was added, not apramycin. The stirring speed is 220rpm, and the ventilation ratio is 1:0.8.
[0133]
[0134] Sterilization: 121°C 20min
[0135] Table 4
[0136] 4) Prepare the fermentation medium, add various ingredient...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com