A method for improving the stress resistance of Clostridium beijerinckii to 4-hydroxycinnamic acid
A technology of hydroxycinnamic acid and Clostridium beijerinckii is applied in the field of genetic engineering to achieve the effects of high butanol yield, improved stress resistance and high efficiency stress resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1: the construction method of Clostridium beijerinckii Cbei_2996 gene inactivation mutant
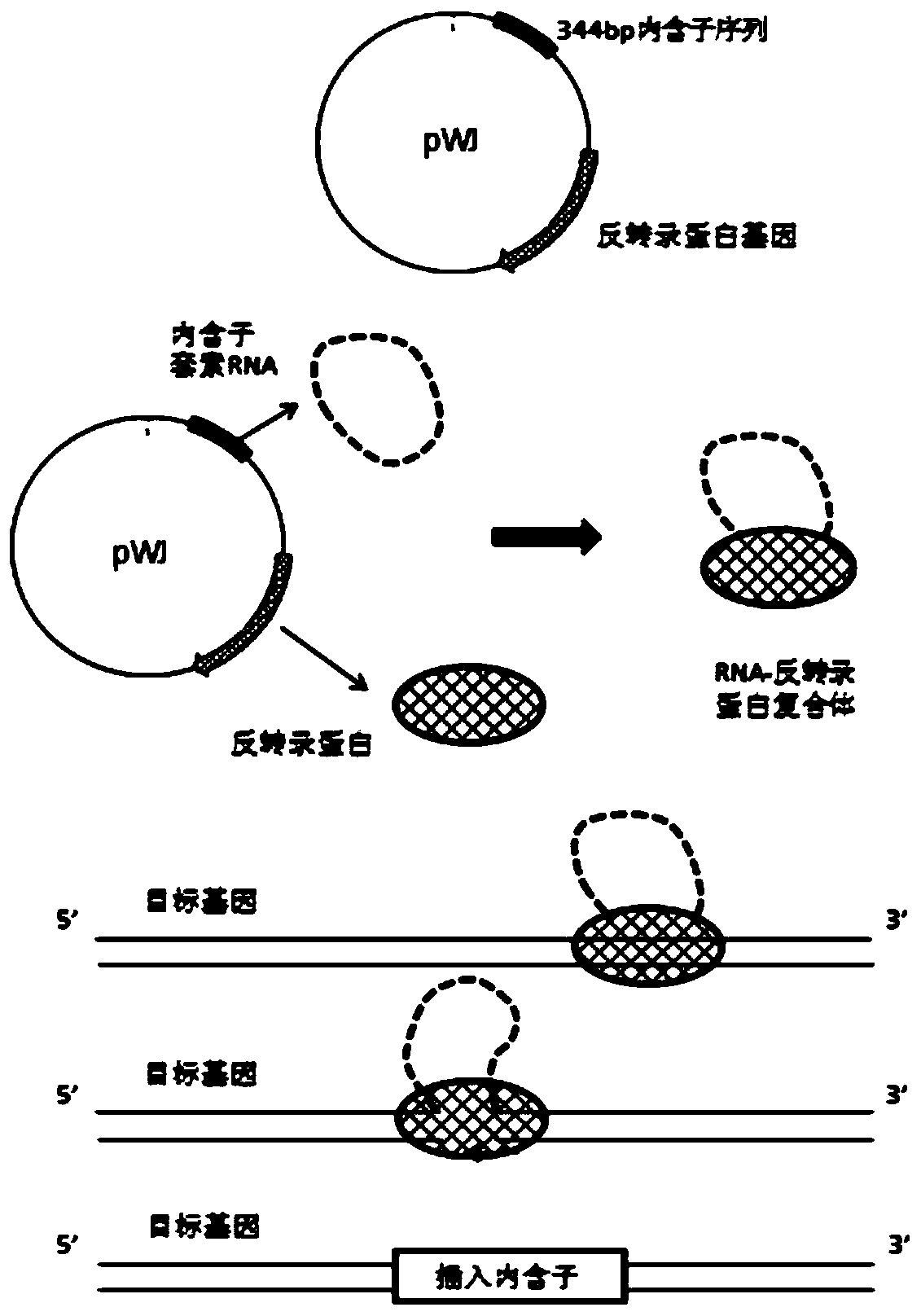
[0047] (1) Design introns:
[0048] According to the Cbei_2996 gene sequence of Clostridium beijerinckii included in the NCBI database (as shown in SEQ ID No: 1), that is, the base sequence encoding coenzyme Q oxidoreductase subunit A ( nuo A), with the help of software to design a suitable insertion gene site (http: / / www.clostron.com), through the previous experimental screening and verification, select the insertion between the 62nd and 63rd bases of the Cbei_2996 gene sequence, and generate Intron sequence, the synthetic intron is S-62, and its sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:2.
[0049] (2) Construction of Cbei_2996 insertion inactivation vector:
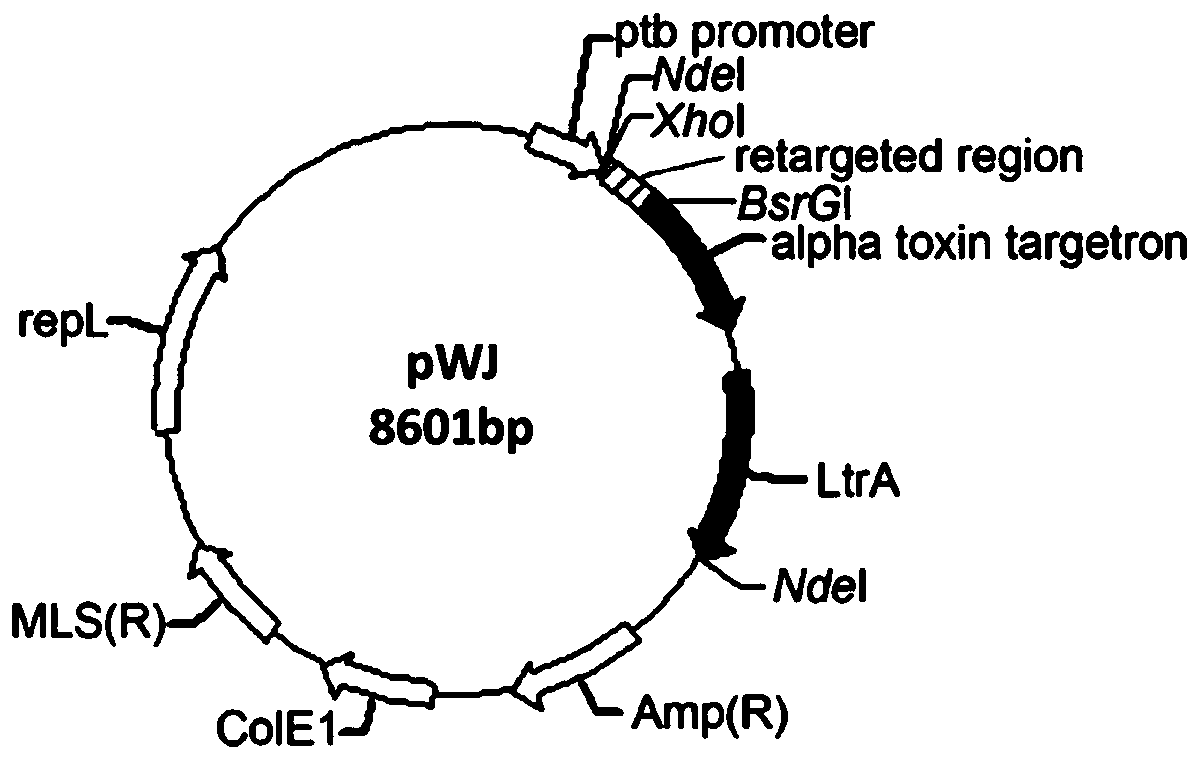
[0050] Use XhoI and BsrGI to double-enzyme-cut the vector pWJ (provided by Yang Sheng, Shanghai Academy of Biological Sciences, its sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 5, and the plasmid map of pWJ is shown in figure 1 sho...
Embodiment 2
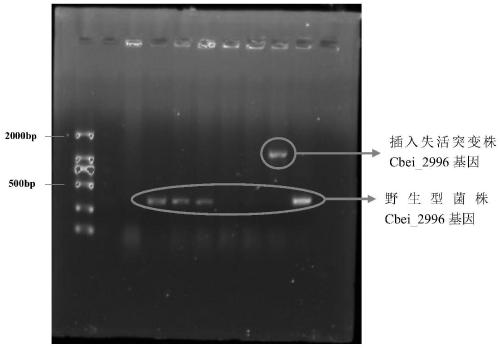
[0061] Embodiment 2: the passage stability of the recombinant bacterium of Cbei_2996 gene inactivation
[0062] The culture medium formula described in the present embodiment:
[0063] Plate medium: yeast powder 3 g / L, peptone 5 g / L, soluble starch 10 g / L, ammonium acetate 2 g / L, sodium chloride 3 g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 3 g / L, diphosphate Potassium hydrogen 1 g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 1 g / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.1 g / L, agar 15 g / L, the rest is water, pH 6.
[0064] Seed medium: yeast powder 3 g / L, peptone 5 g / L, soluble starch 10 g / L, ammonium acetate 2 g / L, sodium chloride 3 g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 3 g / L, diphosphate Potassium hydrogen 1 g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 1 g / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.1 g / L, the rest is water, pH 6.
[0065] Fermentation medium: glucose 30 g / L, ammonium acetate 2.2 g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.5 g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.5 g / L, sodium chloride 0.01 g / L, magnesium sul...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Embodiment 3: Recombinant bacteria and departure bacterial strains are investigated to the stress resistance of 4-hydroxycinnamic acid
[0072] Plate medium: yeast powder 3 g / L, peptone 5 g / L, soluble starch 10 g / L, ammonium acetate 2 g / L, sodium chloride 3 g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 3 g / L, diphosphate Potassium hydrogen 1 g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 1 g / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.1 g / L, agar 15 g / L, the rest is water, pH 6.
[0073] Seed medium: yeast powder 3 g / L, peptone 5 g / L, soluble starch 10 g / L, ammonium acetate 2 g / L, sodium chloride 3 g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 3 g / L, diphosphate Potassium hydrogen 1 g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 1 g / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.1 g / L, the rest is water, pH 6.
[0074] Fermentation medium: glucose 30 g / L, ammonium acetate 2.2 g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.5 g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.5 g / L, sodium chloride 0.01 g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2 g / L L, ferro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com