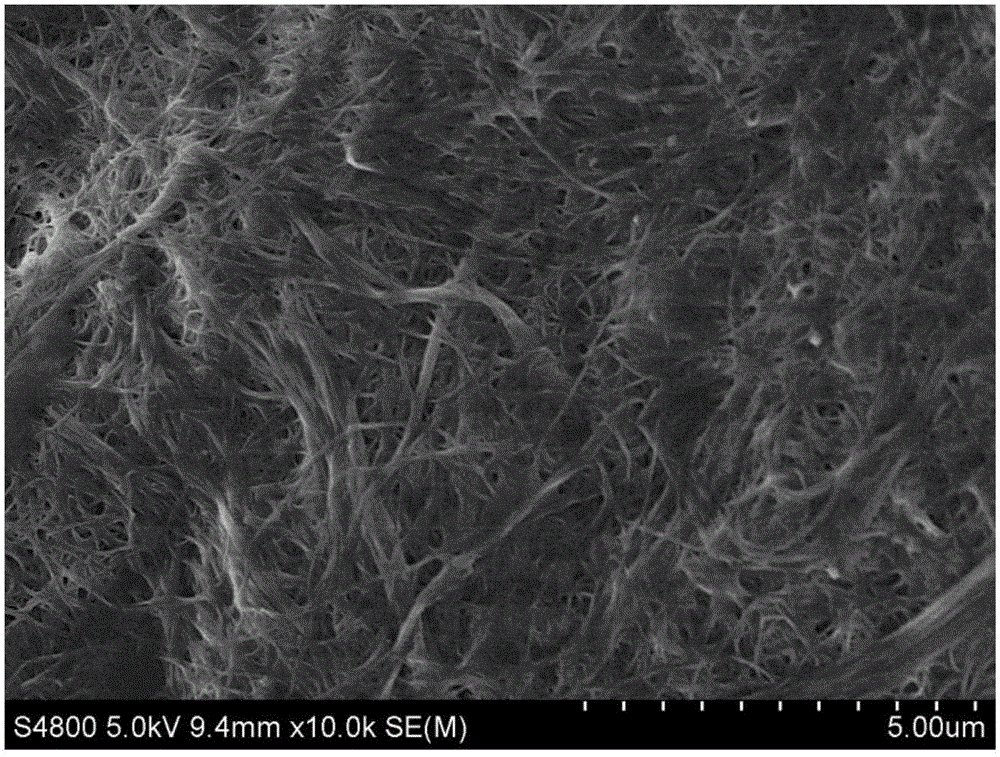
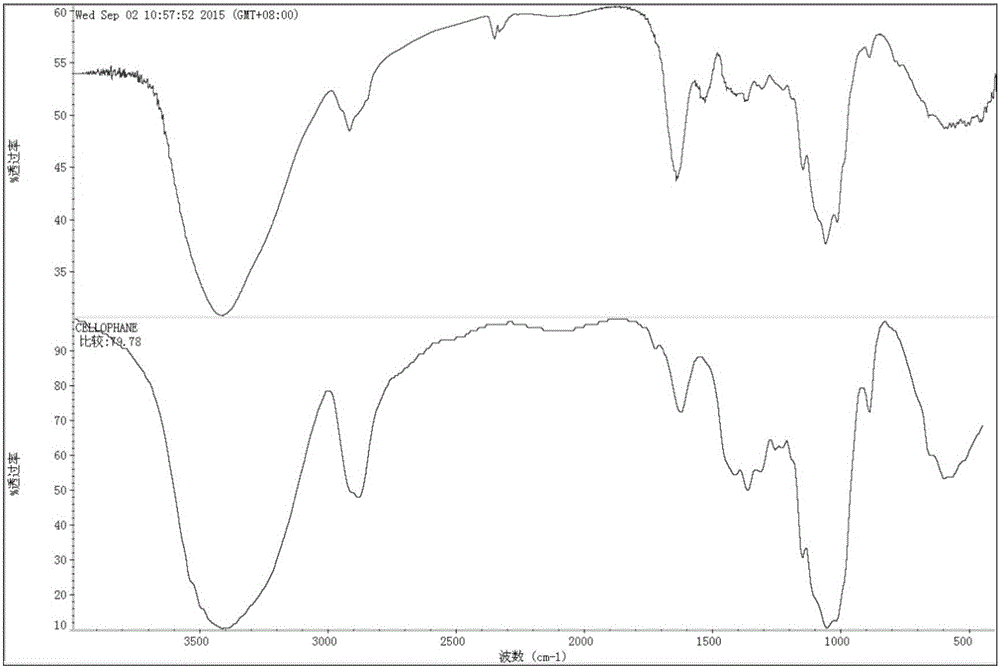
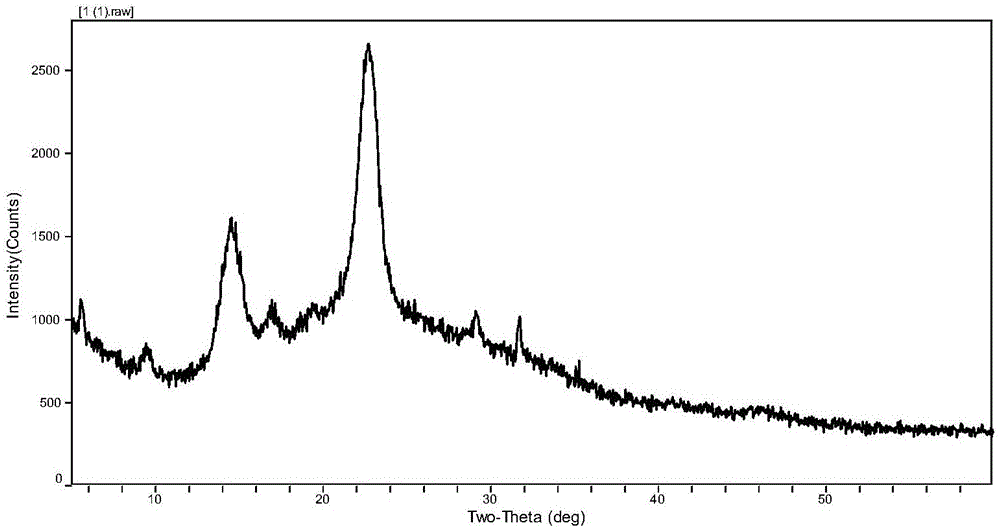
Preparation method and application of nanoscale bacterial cellulose membrane
A bacterial cellulose membrane and nano-scale technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, skin care preparations, etc., can solve the problems of long fermentation cycle, low degree of mechanization, and reduced price of end products. Achieve the effect of lower production cost, better effect and strong market competitiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0042] Preparation of seed solution:
[0043] a. The formula of nutrients required for seed cultivation is as follows:
[0044] In terms of mass ratio (w / v), glucose 5-20%, peptone 0.5-2%, yeast extract 0.5-2%, citric acid 0.01-0.1%, Na 2 HPO 4 0.2~0.5%, KH 2 PO 4 0.1~0.2%, MgSO 4 0.025~0.05%, pH4.8~6.8, sterilized at 121℃ for 20min.
[0045] b. Seed activation method is as follows:
[0046] Pick a single colony on the plate and inoculate it in a fresh medium, add 0.01% cellulase, and culture on a shaker at 180 rpm at 30°C for 48 hours. Centrifuge at 5000rpm for 10min to obtain bacterial cell sedimentation, wash with sterile normal saline water 3 times to remove cellulase in the system, and finally dissolve the cleaned bacterial cells with the same volume of sterile water for use.
Embodiment 1
[0047] Embodiment 1: Synthesize bacterial cellulose with pullulan polysaccharide fermentation waste water as raw material
[0048] 1) Collect the pullulan fermentation broth, add 2 times the volume of ethanol to precipitate the polysaccharide in the fermentation broth, centrifuge at 5000rpm for 10min to obtain a mixture of fermentation broth and ethanol. The above mixture was transferred to a rotary evaporator to remove ethanol. The temperature of the water bath in the rotary evaporator was 40°C. An appropriate amount of distilled water was added to the alcohol-free fermentation broth obtained by rotary evaporation to make up for the water lost due to rotary evaporation.
[0049] 2) Use a biosensor analyzer to detect the sugar content in the fermentation medium, and adjust the sugar content of the fermentation broth to 2%. If it is lower than 2% (w / v), you need to add an appropriate amount of sucrose to ensure the normal growth of the bacteria; if it is higher than 2%, you nee...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2: Synthesizing bacterial cellulose with pullulan polysaccharide fermentation waste cells as raw material
[0056] Pullulan polysaccharide is a polysaccharide obtained by fermentation of Aureobasidium pullulans. Aureobasidium pullulans, also known as Pullulan yeast, has its own cell wall, and the cells need to be fully broken to dissolve the nutrients. Example The method of ultrasonic crushing is used for wall breaking treatment.
[0057] 1) Collect the fermentation waste bacterial liquid, and centrifuge to obtain bacterial sediment. Add an appropriate amount of distilled water, mix well, and prepare a 10-20% bacterial suspension. As for the ultrasonic breaker, the cells are physically crushed, the crushing power is 400w, the crushing time is 30s, and the interval is 5s. Repeat 20 cycles. For foam, it is necessary to add an appropriate amount of defoamer to improve the crushing effect. The bacterial suspension obtained after ultrasonic crushing was placed in a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com