Substrate treatment method for phytosterol side chain degradation reaction
A technology for phytosterol and degradation reaction, which is applied in the field of substrate treatment of phytosterol side chain degradation reaction, can solve the problems of poor contact between the substrate and microbial cells, easy aggregation on the surface of the water phase, prolonged transformation time, etc. Achieving the effect of sufficient raw material sources, low price and improved conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0023] 1 Preparation of co-modified attapulgite-phytosterols:
[0024] (1) Acid co-modified attapulgite-phytosterol: add phytosterol and attapulgite to 100mL of 4mol / L acid solution in a mass ratio of 1:0.1~5, wherein the total mass of phytosterol and attapulgite does not exceed 5g, the acid solution is one of sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid or phosphoric acid, ultrasonically oscillated for 30min, centrifuged and washed until neutral, dried at 60°C for 8h, and ground into fine powder.
[0025] (2) Silane coupling agent co-modified attapulgite-phytosterol: add phytosterol and attapulgite to 100mL of acetic acid aqueous solution with pH 3.5 according to the mass ratio of 1:0.1~5, the total mass of phytosterol and attapulgite is not More than 5g, then add 0.1mL of silane coupling agent, the silane coupling agent is 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane KH550, ultrasonic vibration for 30min, centrifugal washing until no silane coupling agent, dry at 60℃ for 8h, grind into po...
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1: silane coupling agent co-modifies attapulgite-phytosterol
[0037] 1 Modification of the substrate:
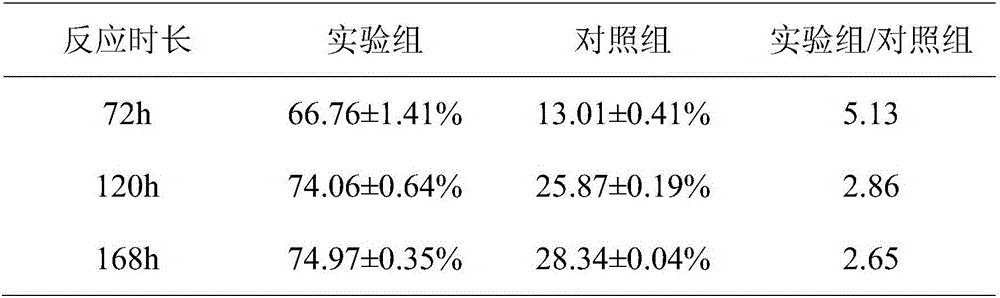
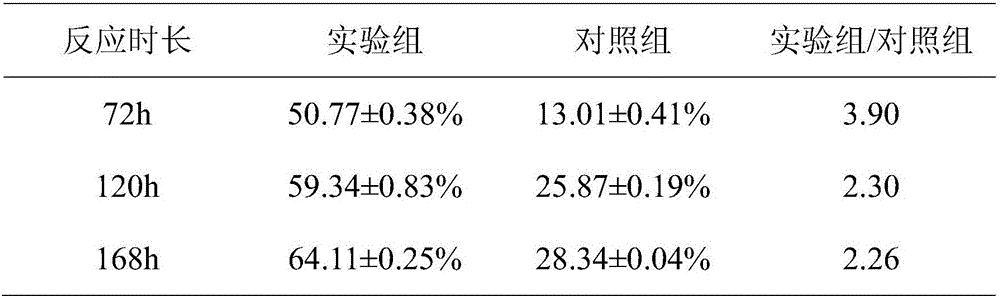
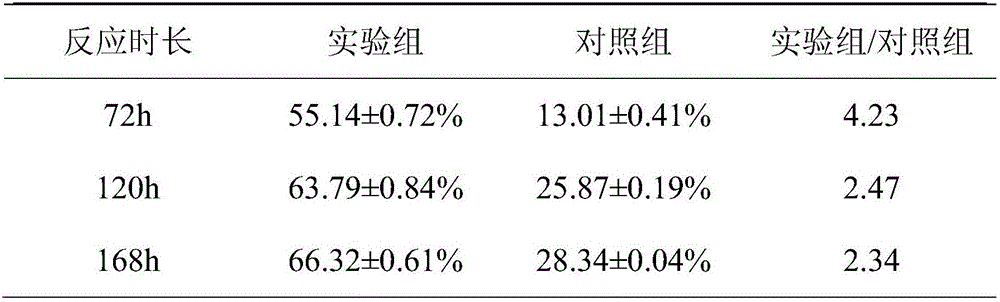
[0038] Add 1g phytosterol PS and 3g attapulgite AT to 100mL acetic acid solution (pH3.5), then add 0.1mL 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane KH550, ultrasonically shake for 30min, centrifuge at 5000r / min for 10min, deionize Wash with water until there is no KH550, dry at 60°C for 8 hours, and grind into a fine powder, which is silane coupling agent co-modified attapulgite-phytosterol KH550-AT-PS.
[0039] 2 Degradation reactions of phytosterol side chains
[0040] The silane coupling agent co-modified attapulgite-phytosterol KH550-AT-PS was added to the mycobacterium fermentation medium for reaction.
[0041] The components of the fermentation medium are: glucose 10g / L, citric acid 2g / L, ferric ammonium citrate 0.05g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.5g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.5g / L, diammonium hydrogen phosphate 3.5g / L L, pH 7.2.
[0042] The inoculum amount...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2: Co-modification of attapulgite-phytosterols with acid
[0054] 1 Modification of the substrate:
[0055] Add 1g of phytosterol PS and 3g of attapulgite AT into 100mL of 4mol / L sulfuric acid solution, ultrasonically oscillate for 30min, centrifuge at 5000r / min for 10min, wash with deionized water until neutral, dry at 60°C for 8h, and grind into fine powder. Sulfuric acid co-modified attapulgite-phytosterol H 2 SO 4 -AT-PS.
[0056] 2 Degradation reactions of phytosterol side chains
[0057] co-modified attapulgite-phytosterol H with sulfuric acid 2 SO 4 -AT-PS was added to the mycobacterial fermentation medium for reaction.
[0058] The components of the fermentation medium are: glucose 10g / L, citric acid 2g / L, ferric ammonium citrate 0.05g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.5g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.5g / L, diammonium hydrogen phosphate 3.5g / L L, pH 7.2.
[0059] The inoculum amount of mycobacteria was 7% (v / v).
[0060] The fermentation system of ad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com