Short wave optical thermal detector and focal plane array device thereof
A thermal detector and photothermal detection technology, applied in the field of photoelectric detectors, can solve the problems of no application, poor detection rate and response time, low electromagnetic radiation absorption, etc., to achieve strong versatility, fast response speed, and low thermal mass. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
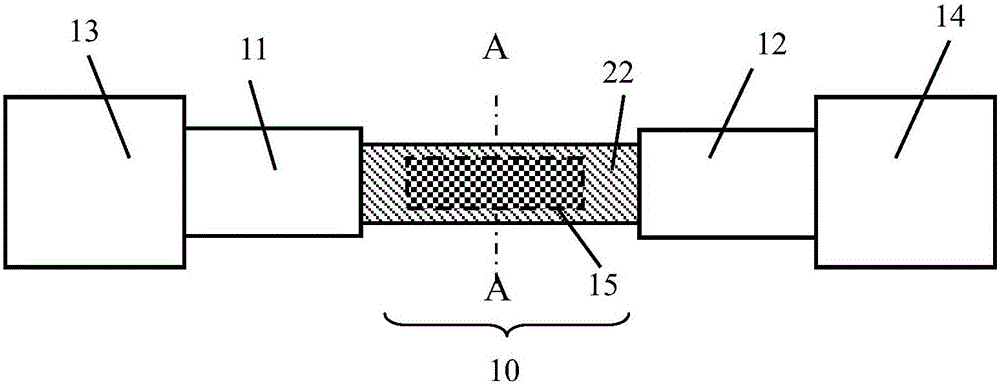
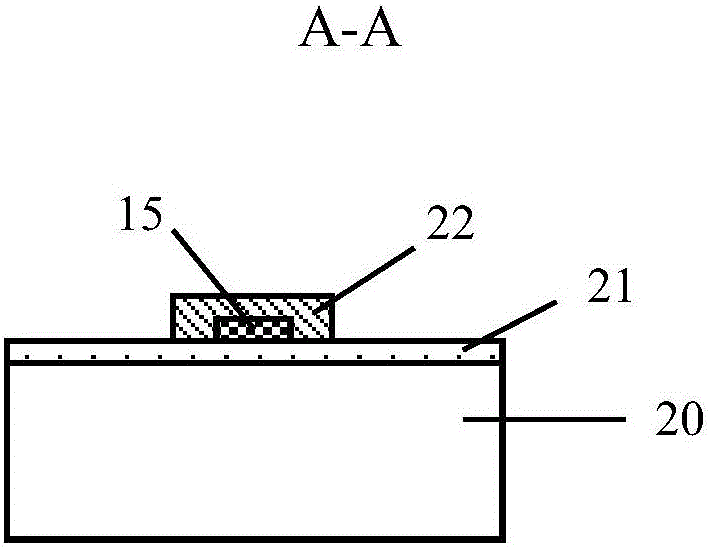
[0023] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the short-wave optical thermal detector in this embodiment includes a photothermal detection structure 10, two electrodes 11, 12, two electrical contacts or metal pads 13 and 14, and a silicon substrate 20, wherein the two electrodes 11, Both ends of 12 are respectively connected to photothermal detection structure 10 and electrical contact points or metal pads 13 and 14 . The photothermal detection structure 10 is at least composed of heat-sensitive wires 22 and conductive nanoparticles 15 , and an insulating medium layer 21 is placed between the heat-sensitive wires 22 and the substrate 20 . Electrical contacts or metal pads 13 and 14 are interconnected with readout circuitry on substrate 20 or external circuitry (not shown). The insulating dielectric layer 21 is preferably silicon dioxide.
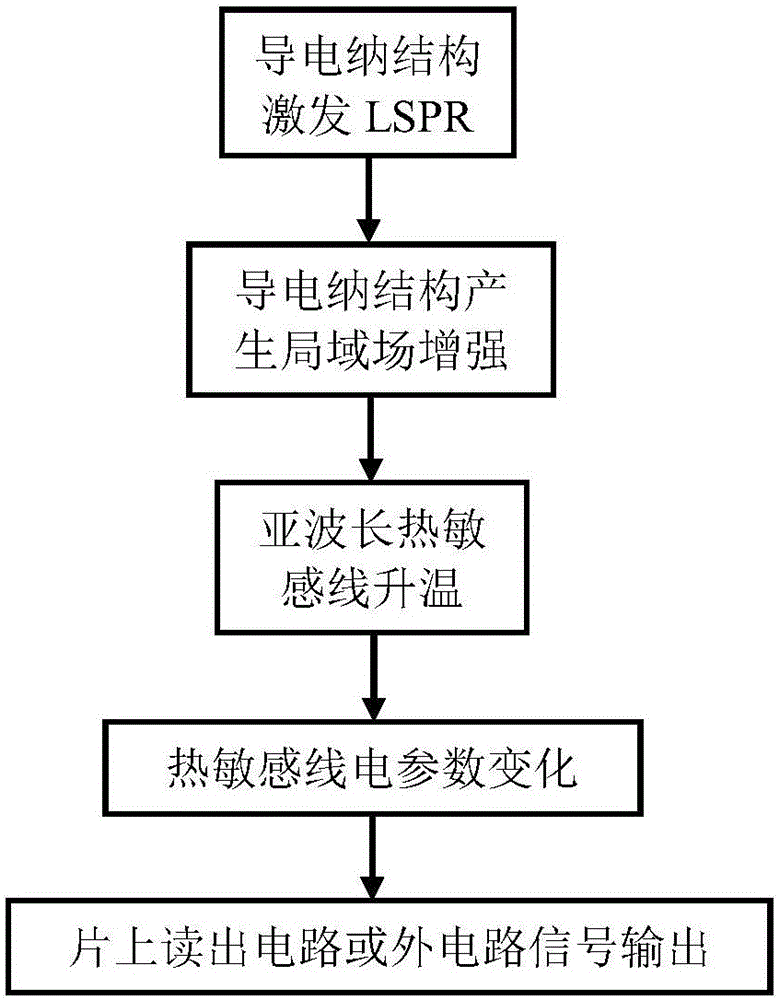
[0024] The operating principle of the short-wave optical thermal detector in this embodiment is as follows: image 3 As shown, the in...
Embodiment 2
[0031] In order to further improve the absorption efficiency and reduce the loss of light energy caused by the scattering of nanoparticles, such as Figure 6 As shown, the present invention also provides a preferred embodiment of a short-wave optical thermal detector. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that: the conductive nanoparticle 15 is embedded in the heat sensitive wire 22, and the heat sensitive wire 22 A metal reflective layer 25 is added below, and there is an insulating medium layer 21 with low thermal conductivity between the metal reflective layer 25 and the heat-sensitive wire 22, and the material of the insulating medium layer 21 is preferably silicon dioxide. In addition, the surface of the heat sensitive line 22 also contains a passivation protection layer 23 . The improved structure reflects the incident or scattered electromagnetic radiation reaching the reflective layer back to the photothermal detection structure, which can enhance ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] The further improvement of this embodiment relative to Embodiment 2 is that there is a cavity 26 and a metal reflective layer 25 etched by the isolation layer 27 under the photothermal detection structure, such as Figure 7 shown. The cavity 26 is used to block the thermal conduction loss of the thermal detection structure through the substrate below it, and plays a role of thermal isolation. At the same time, when its height meets a quarter of the detection wavelength, it will also form resonance absorption, which can significantly enhance the wavelength. nearby absorptivity. The material used for the isolation layer 27 can be selected from inorganic media such as silicon oxide, silicon nitride or organic polymers such as polyimide or BCB. The medium of the cavity 26 is inert gas or vacuum. In this embodiment, the insulating dielectric layer 21 is located between the isolation layer 27 and the heat sensitive wire 22 .
[0034] Investigate the thermal conductance and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com