Biological modification method for sludge deep dewatering
A biological modification and deep dewatering technology, applied in water/sludge/sewage treatment, sludge treatment, sludge treatment, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the content of persistent organic pollutants and heavy metals in sludge, No degradation, low temperature operation limited sludge and other problems, to achieve the effect of short biological modification time, low cost and reducing toxic effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Preparation of enrichment, domestication and inoculum of complex microbial flora
[0044] The microorganisms adopted in the method of the present invention are two kinds of composite microbial flora, which are respectively composite flora 1 and composite flora 2. Both of these two flora are micro-organisms that have been acclimatized at low temperature, and the acclimation temperature is 10-35°C, and they can reproduce and grow rapidly at 10-35°C.
[0045] Composite flora 1 includes Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, white rot fungi and Alteromonas, and was purchased from the German Culture Collection. Above-mentioned bacterial strain is inoculated in respective culture medium, and the formula of the culture medium of Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, white rot fungus and alteromonas is respectively as follows (g / L):
[0046] The culture medium of Bacillus subtilis is: 20g glucose, 15g peptone, 5g sodium chloride, 5g beef extract;
[0047] ...
Embodiment 2
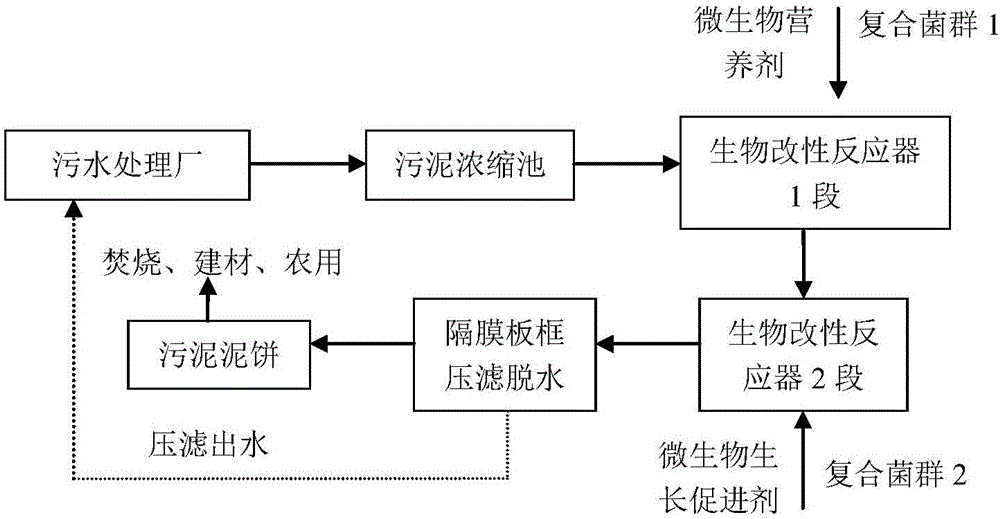
[0056] The invention discloses a biological modification method for deep dehydration of sludge, which adopts the method of biological modification combined with plate and frame filter press to perform rapid deep dehydration treatment on sludge. The method adopts two kinds of composite microbial flora (composite flora 1 and composite flora 2), and adopts two-stage biomodification technology to carry out biological modification treatment to the sludge, and the described method comprises the following steps:
[0057] (1) Enrichment, domestication and preparation of inoculum of complex microbial flora
[0058] With embodiment 1.
[0059] (2) Biological modification of sludge
[0060] According to the 10%-30% of the fresh sludge volume ratio, add the described composite flora 1 sludge inoculum to the biological modification reactor equipped with fresh sludge, and according to the 3%-8% of the dry matter mass of the sludge Add microbial modified nutrients at a ratio of %, and reac...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3 Biological modification of sludge from a sewage treatment plant in Nanjing
[0070] According to the process method mentioned in the present invention, according to figure 1 The process flow shown is for biomodification of sludge from an urban sewage treatment plant in Nanjing. The sewage treatment of the waterworks adopts the activated sludge method, and the sludge has not undergone anaerobic or aerobic treatment. About 10 tons of concentrated sludge containing 3% solids were taken, the organic matter content was determined to be 45%, and the pH value was 7.6. The enrichment, acclimation and inoculum preparation of the complex microbial flora are the same as in Example 1, but in this example the acclimatization temperature is 30°C.
[0071] Biomodification stage:
[0072] Add the complex flora 1 sludge inoculum to the bio-modification reactor equipped with fresh sludge according to 10% of the fresh sludge volume ratio, and add microbial modified nutrients ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com