Method for accelerating biological production of 5-aminovaleric acid
A kind of aminovaleric acid, biological method, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and method, using carrier to introduce foreign genetic material, peptide, etc., to achieve the effect of low cost and simple operation of product separation and purification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
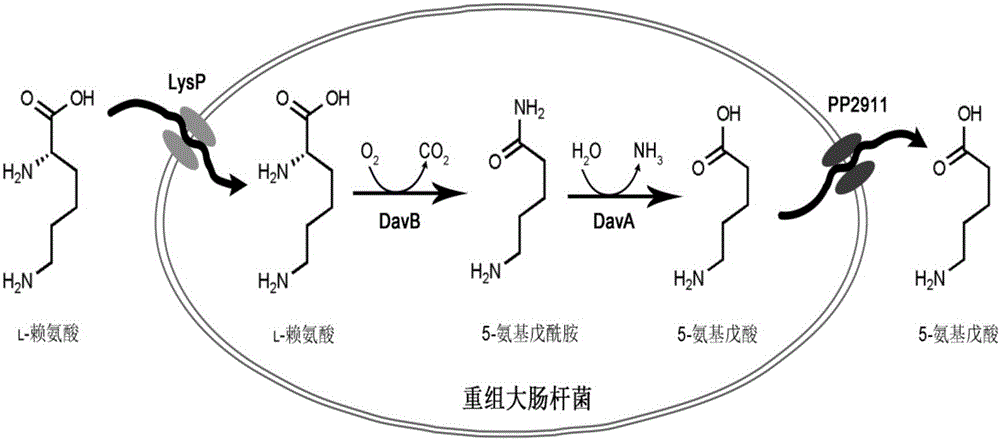
[0051] Example 1: Construction of a 5-aminovaleric acid production strain co-expressing the 4-aminobutyric acid transporter gene pp2911 and the lysine-specific permease gene lysP
[0052] (1) Cloning of gene davAB: Genomic DNA of strain Pseudomonas putida KT2440 was prepared by a conventional method, and the process referred to the method for small-scale genome preparation in "Guidelines for Molecular Biology" published by Science Press. The gene davAB was amplified by PCR from the genomic DNA of Pseudomonas putida KT2440 using synthetic primers;
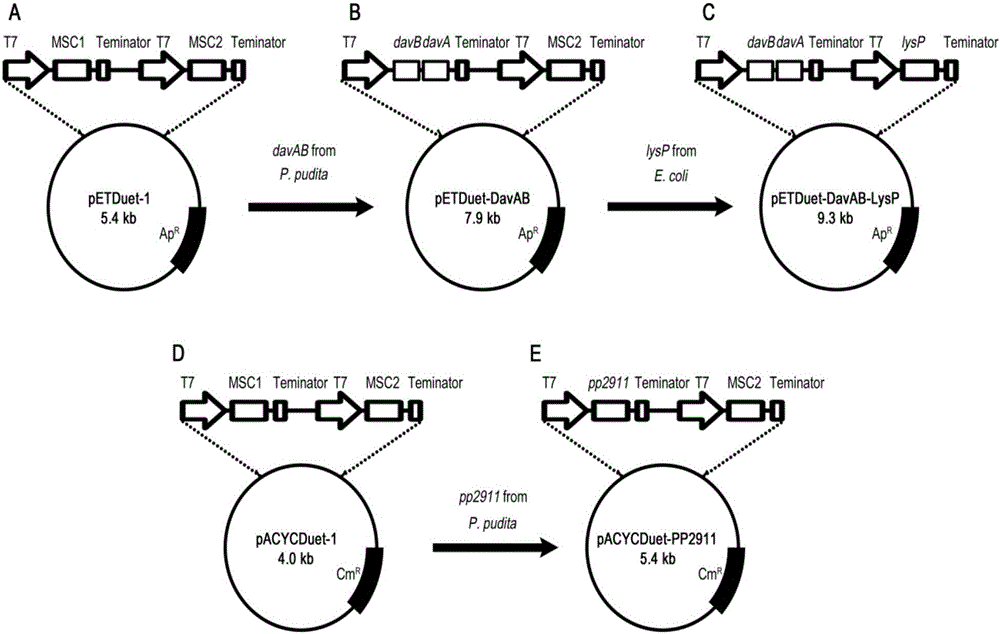
[0053] Pseudomonas putida KT2440 was used as the source of the davAB gene. According to the sequenced genome sequence of the bacteria, primers were designed to introduce BamHI and HindIII restriction enzyme sites that could be inserted into the multiple cloning site 1 (MCS1) of the plasmid pETDute-1. point, wherein the primer sequences are as follows:
[0054] Upstream primer: 5'- GGATCCG ATGAACAAGAAGAACCGCCAC-3', carrying a BamH...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2: Preparation of Whole Cell Catalyst
[0070] (1) Plate culture: Streak Escherichia coli BL21 / pETDuet-DavAB-LysP / pACYCDuet-PP2911 on an LB plate containing 1.5-1.8% agar with a mass volume ratio of 100 μg / mL ampicillin and 40 μg / mL chloramphenicol on, cultured at 37°C for 12 hours;
[0071] (2) First-class seeds: under sterile conditions, use a sterile toothpick to pick a single colony on the plate of step (1), and then inoculate it into 5 mL of 100 μg / mL ampicillin and 40 μg / mL chloramphenicol In the LB liquid medium, shake culture at 37°C for 12 hours;
[0072] (3) Secondary seeds: under aseptic conditions, take the bacterium solution cultivated in step (2) with an inoculum volume ratio of 1%, and inoculate into 100 mL of 100 μg / mL ampicillin and 40 μg / mL chloramphenicol In the LB liquid medium, shake culture at 37°C for 12 hours;
[0073] (4) Shake flask culture: under aseptic conditions, take the bacterial solution obtained in step (3) and inoculate 1 L ...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Embodiment 3: utilize the biocatalyst that embodiment 2 obtains to prepare 5-aminovaleric acid
[0076] Transformation experiment: take cell concentration as OD 600nm =60 of the whole cell catalyst, under the conditions of 30°C and pH 7.0, the conversion concentration is 40g / L of L-lysine, and after shaking and reacting at 120 rpm for 48 hours, the conversion solution containing 5-aminovaleric acid is obtained.
[0077] Collect the transformation solution at the end of the reaction, centrifuge at 13,000±500 rpm for 10-15 minutes to remove the added biocatalyst, derivate the supernatant by PITC method, and measure L-lysine and 5-aminovaleric acid in the transformation solution concentration.
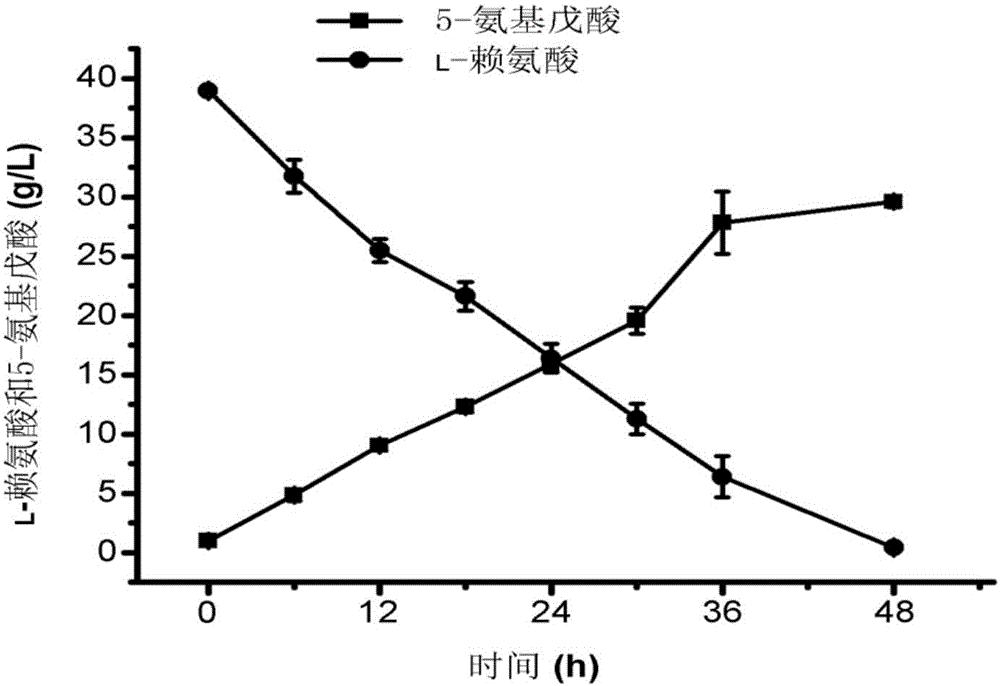
[0078] The conversion result is as image 3 Shown: 38.6g / L of L-lysine is finally consumed, 29.6g / L of 5-aminovaleric acid is produced, and the conversion rate reaches 0.96mol / mol.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com