Straw-based selective mercury removal material, preparation method and applications thereof
A selective, straw technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory adsorption effect, difficult mercury-containing waste liquid treatment, poor selectivity, etc. Low preparation cost, effective utilization, and the effect of solving disposal problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] 1. The straw with a length of 3-5 cm is subjected to steam explosion treatment at 1.5 MPa and 210° C., and then cracked in vacuum and nitrogen at 600° C. to obtain an adsorption carrier for future use.
[0035] 2. Immerse the adsorption carrier in 1 into a mixed solution of reducing sulfur-containing groups (thioglycolic acid 0.5 mol / L, ammonium thiocyanate 1.0 mol / L, ammonium thiosulfate 2.0 mol / L), at 50°C Under stirring for 1h, filtered and dried at room temperature. The dried impregnated material is mixed according to the ratio of carbon-sulfur mass ratio (C / S) 1:1, heated to 450°C under vacuum and nitrogen, and maintained for 2 hours, and the temperature is programmed to 600°C, and vacuum and nitrogen are maintained. 2h. Cool to room temperature and grind to obtain a sulfur load of 4.6wt% and a specific surface area of 398m 2 / g of selective mercury removal material.
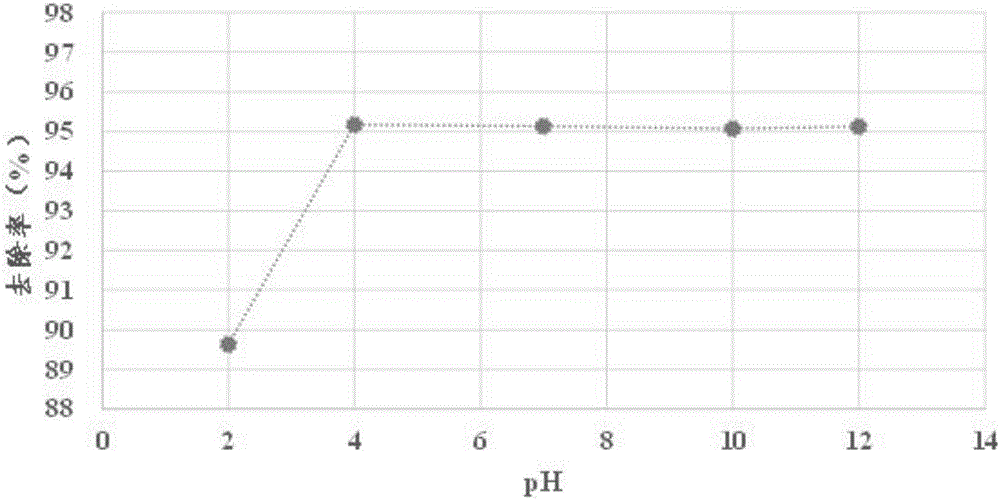
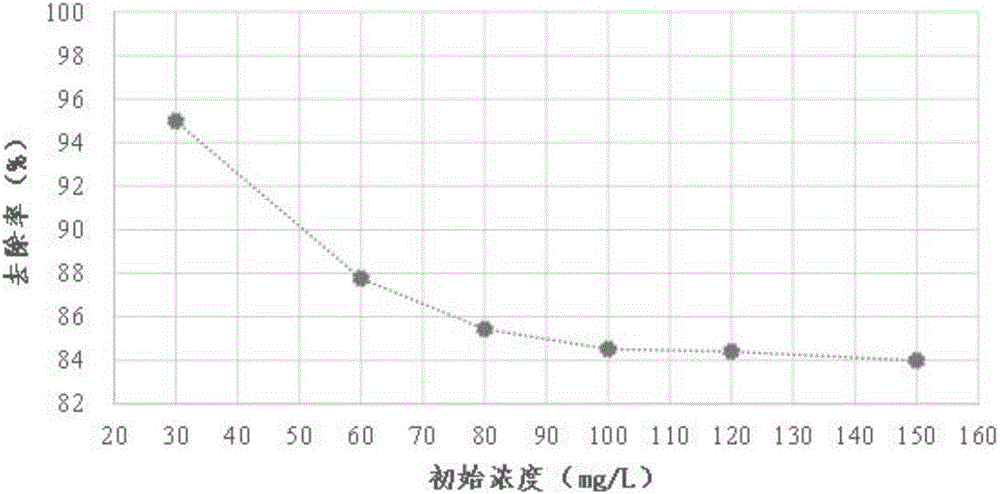
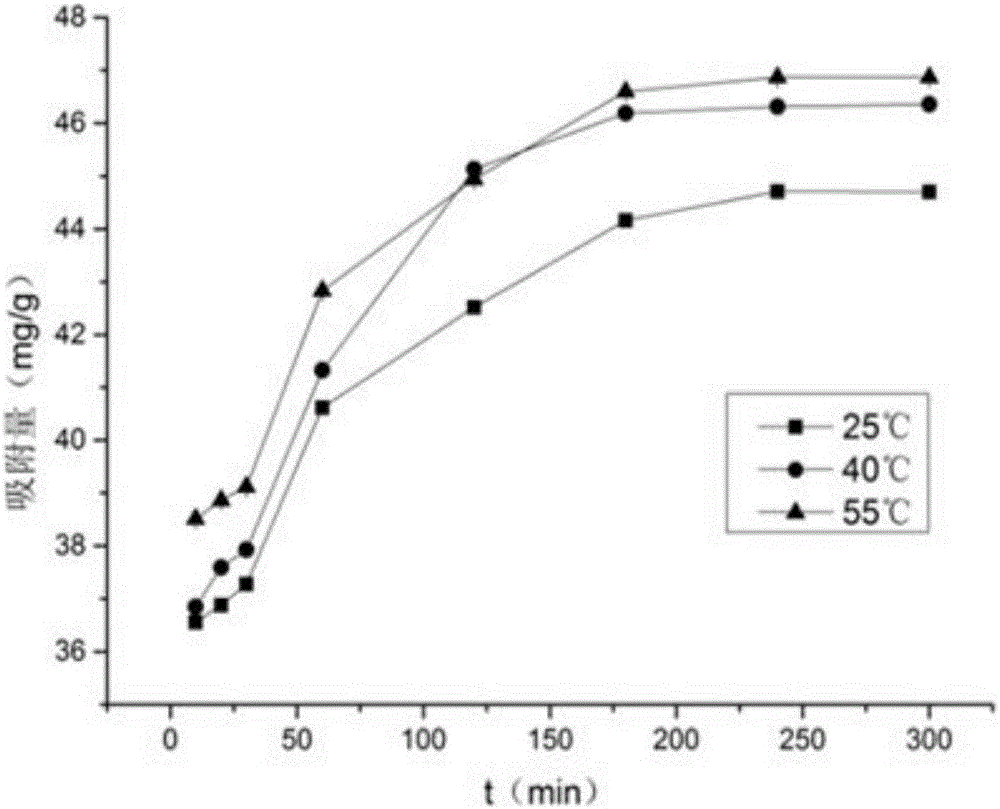
[0036] 3. Add the selective mercury removal material in 2 into the mercury-containing wastew...
Embodiment 2
[0038] 1. The straw with a length of 3-5 cm is subjected to steam explosion treatment at 1.5 MPa and 210° C., and then cracked in vacuum and nitrogen at 700° C. to obtain an adsorption carrier for future use.
[0039] 2. Immerse the adsorption carrier in 1 into the mixed solution of reducing sulfur-containing groups (ammonium thiocyanate 3.0mol / L, mercaptoacetic acid 0.8mol / L, ammonium thiosulfate 2.0mol / L), at 50°C Under stirring for 1h, filtered and dried at room temperature. The dried impregnated material is mixed according to the ratio of carbon-sulfur mass ratio (C / S) 1:2, heated to 450°C under the condition of vacuum and nitrogen, and maintained for 2h, and the temperature is programmed to 800°C, and kept under vacuum and nitrogen 2h. Cool to room temperature and grind to obtain a sulfur load of 5.1wt% and a specific surface area of 435m 2 / g of selective mercury removal material.
[0040] 3. Add the selective mercury removal material in 2 into the mercury-containin...
Embodiment 3
[0042] 1. The straw with a length of 3-5 cm is subjected to steam explosion treatment at 1.5 MPa and 210° C., and then cracked in vacuum and nitrogen at 700° C. to obtain an adsorption carrier for future use.
[0043]2. Immerse the adsorption carrier in 1 into the mixed solution of reducing sulfur-containing groups (ammonium thiocyanate 0.5mol / L, thioglycolic acid 0.8mol / L, ammonium thiosulfate 1.0mol / L), Under stirring for 1h, filtered and dried at room temperature. The dried impregnated material is mixed according to the ratio of carbon-sulfur mass ratio (C / S) 1:1, heated to 450°C under vacuum and nitrogen gas, and maintained for 2 hours, and the temperature is programmed to 700°C, and vacuum and nitrogen gas are maintained. 2h. Cool to room temperature and grind to obtain a sulfur load of 4.68wt% and a specific surface area of 412m 2 / g of selective mercury removal material.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com