Preparation method of ferric pyrophosphate and application of ferric pyrophosphate in sodium-ion batteries
A technology of sodium ferric pyrophosphate and phosphoric acid, applied in the directions of phosphate, phosphorus oxyacid, secondary battery, etc., can solve the problem of high rate performance, poor cycle life and poor conductivity, poor repeatability, difficult to achieve large-scale production, phase purity It can achieve the effect of uniform morphology, excellent cycle stability and high surface electrochemical activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
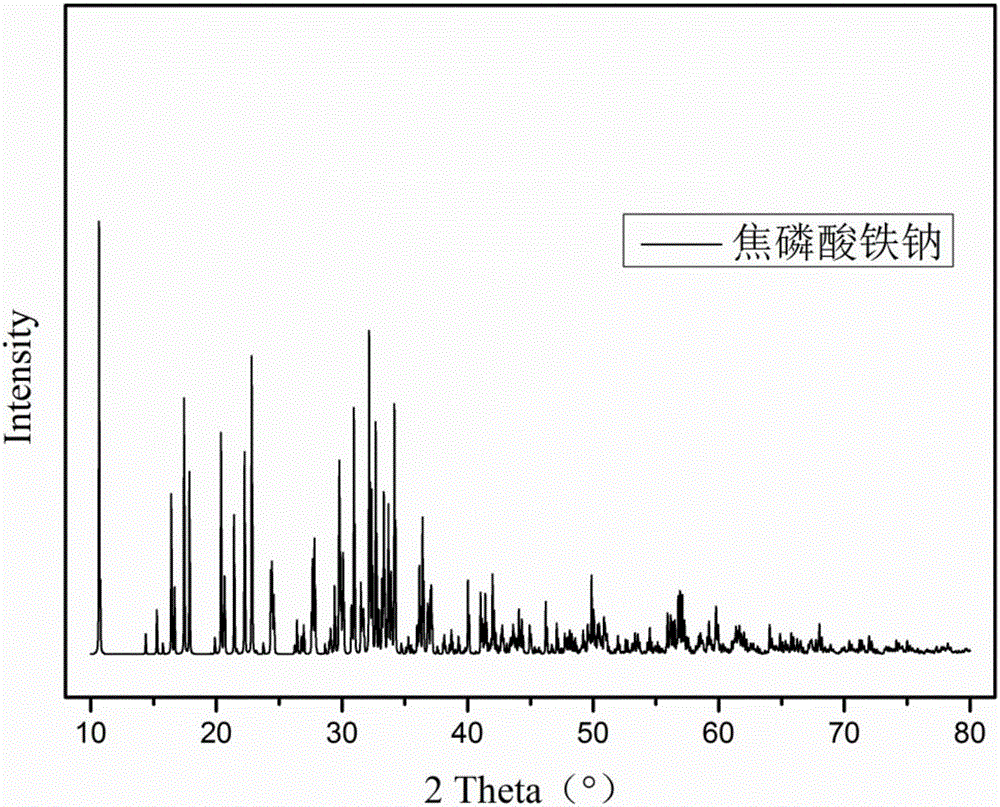
[0038] 1) In this example, 0.03 mol of the target product, sodium ferric pyrophosphate, is designed, and 0.03 mol of ferrous oxide is added to 6.92 g of phosphoric acid (85% in mass concentration), stirred for 3 days at 200° C., and the obtained white powder is obtained by using acetone After washing three times, filter and dry to obtain FeH 2 P 2 o 7,From Figure 4 It can be seen that the obtained product is pure phase FeH 2 P 2 o 7 .
[0039] 2) Combine 0.0315mol sodium oxalate with the FeH obtained in the above steps 2 P 2 o 7 Mixed uniformly by high-energy ball milling to obtain the precursor of sodium ferric pyrophosphate;
[0040] 3) The precursor is placed in a hydrogen-argon mixed gas atmosphere, heated at 5°C / min to 580°C for sintering for 9 hours, and naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain the sodium iron pyrophosphate material.
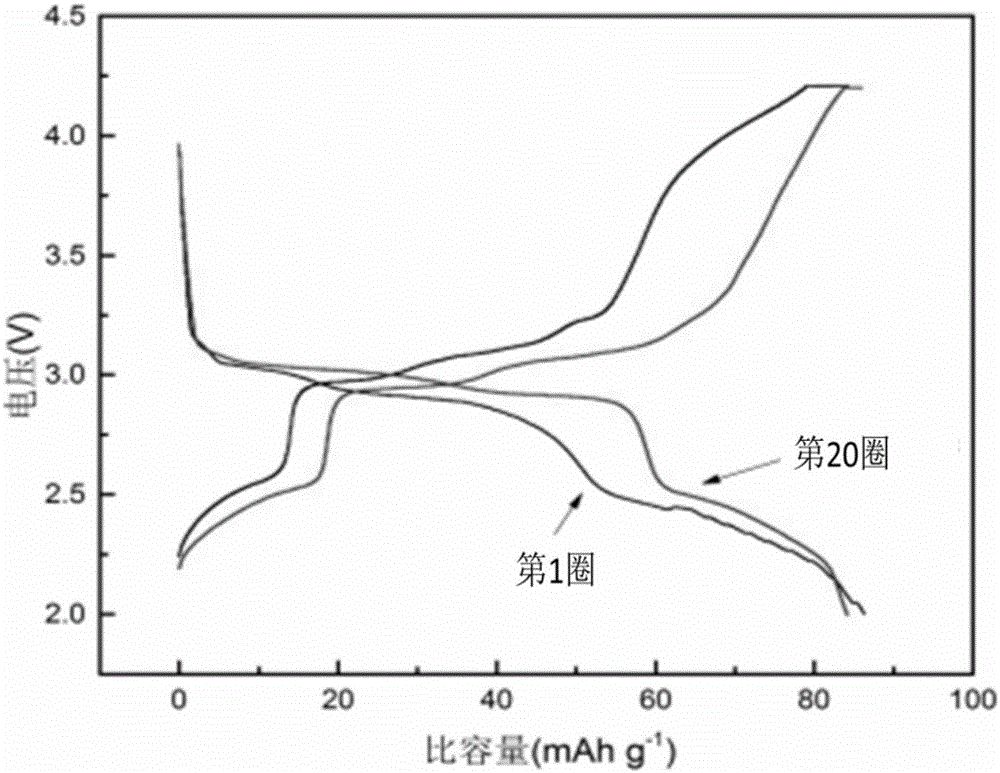
[0041] The sodium ion battery composite positive electrode material prepared in this example is assembled into a button ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0048] (1) This embodiment is designed to generate 0.03 mol of the target product, sodium ferric pyrophosphate, and 0.03 mol of ferrous oxide is added to 6.92 g of phosphoric acid (85% by mass), and stirred at 220°C for 3 days to obtain a white powder After washing three times with acetone, it was filtered and dried to obtain FeH 2 P 2 o 7 ;
[0049] 2) Combine 0.0315mol sodium oxalate with the FeH obtained in the above steps 2 P 2 o 7 Mixed uniformly by high-energy ball milling to obtain the precursor of sodium ferric pyrophosphate;
[0050] 3) The precursor is placed in a hydrogen-argon mixed gas atmosphere, heated at 5°C / min to 580°C for sintering for 9 hours, and naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain the sodium iron pyrophosphate material.
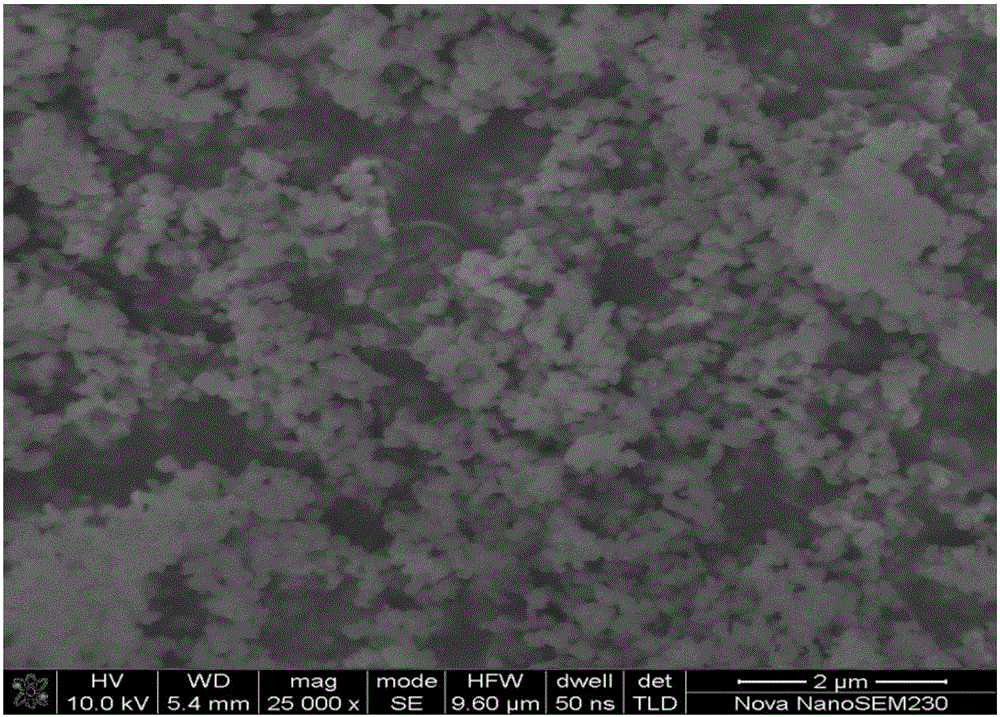
[0051] The battery assembly and testing methods of the materials obtained in this example are the same as those in Example 1, and the average particle size of the p...
Embodiment 3
[0053] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0054] 1) This embodiment is designed to generate 0.03 mol of the target product, sodium ferric pyrophosphate, and 0.03 mol of ferrous oxide is added to 6.92 g of phosphoric acid (85% concentration by mass), and stirred for 5 days at 200° C., and the obtained white powder is obtained by After washing with acetone three times, filter and dry to obtain FeH 2 P 2 o 7 ;
[0055] 2) Combine 0.0315mol sodium oxalate with the FeH obtained in the above steps 2 P 2 o 7 Mixed uniformly by high-energy ball milling to obtain the precursor of sodium ferric pyrophosphate;
[0056] 3) The precursor is placed in a hydrogen-argon mixed gas atmosphere, heated at 5°C / min to 580°C for sintering for 9 hours, and naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain the sodium iron pyrophosphate material.
[0057] The battery assembly and test method of the material obtained in this example are the same as in Example 1. The average particle siz...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com