High-temperature-resistant cellulase producing bacterium and application thereof
A cellulase bacteria, cellulase technology, applied in the application, enzyme, enzyme and other directions, can solve the problems of insufficient development and efficient utilization of cellulose, low utilization rate, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Embodiment 1: Isolation, screening and identification of strains
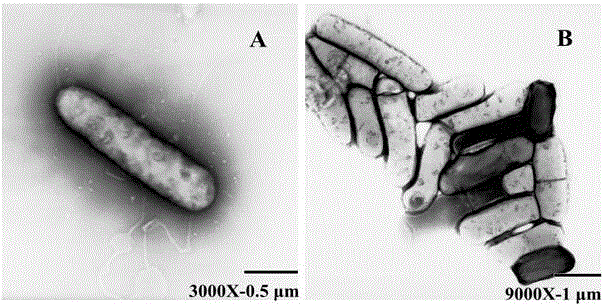
[0019] Strain AW1601 was isolated from a mixture of cow dung and straw in an earthworm farm in Tianjin. Take 5 g of the soil sample, filter it with sterile water to remove the residue, collect the filtrate, take the supernatant and dilute it according to the gradient of 1 / 10, 1 / 100, 1 / 1000, 1 / 10000 times, and apply the diluted solution on LB solid medium Above, culture at a constant temperature of 37°C. After bacteria appear, they are streaked and separated repeatedly. After obtaining pure strains, they are transferred to LB test tube medium for storage at 4°C.
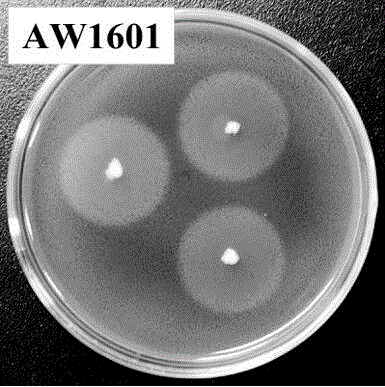
[0020] The purified strains were inoculated on carboxymethylcellulose sodium plate medium (CMC-Na 15 g, NaCl 5 g, KH 2 PO 4 1 g, MgSO 4 0.2 g, 1.0 g peptone, 1.0 g yeast powder, 18 g agar, 1000 mL deionized water, pH 7.2), 3 samples of each medium were placed, cultured at 37°C for 4 days, and 1 mg / mL Congo Stain with the red dye solution f...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Embodiment 2: the enzyme production condition of bacterial strain AW1601
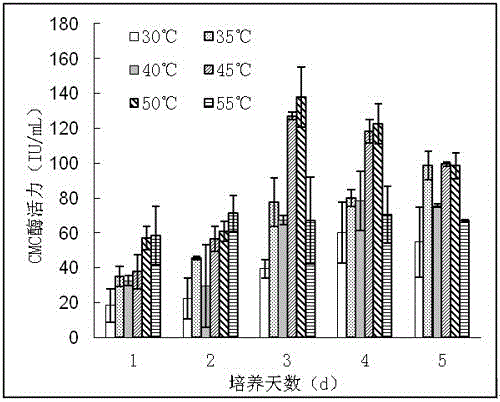
[0023] Make corn straw enzyme production medium: straw 10.0 g, NaCl 5.0 g, KH 2 PO 4 1.0 g, MgSO 4 0.2 g, 1.0 g peptone, 1.0 g yeast powder, 1000 mL deionized water, sterilized at 121°C for 20 min. Since the growth curves of the strain AW1601 at different pHs have been measured, it shows that the growth is the most vigorous when the pH is 7, so the pH of the corn straw enzyme production medium was adjusted to 7.
[0024] Use 3 mL of sterile water to make the bacteria suspension, take 0.5 mL and inoculate them in the enzyme production medium respectively, at 30°C, 35°C, 40°C, 45°C, 50°C, 55°C at 120 r / min Shaker shaking culture. The bacterial liquid was taken every 24 h, centrifuged at 5000 r / min for 15 min, and the supernatant was collected to determine the enzyme activity. The cellulase catalyzes the hydrolysis of the substrate to generate 1 μg of glucose per minute, which is defined as an ...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Embodiment 3: liquid state fermentation
[0028] The strain AW1601 was transferred from the slant medium to the LB medium, and cultured at 120 r / min at 37°C for 24 h to make a seed solution.
[0029] Put 5 g of straw into 100 mL of distilled water in a shaker flask, the inoculation amount of the strain was 3%, the fermentation temperature was set at 35°C, 40°C, 45°C, 50°C, 55°C and 60°C, at 120 r / min Cultured on a shaker for 7 days.
[0030] The substrate degradation rate was calculated by the differential gravimetric method, and the formula was:
[0031]
[0032] Among them, X is the degradation rate; M1 is the substrate weight (g) of the experimental group; M2 is the substrate weight (g) of the blank group; M is the initial addition amount of liquid fermentation straw.
[0033]The content of cellulose and hemicellulose was determined by Van Soest method, and the content of cellulose and hemicellulose in corn stover before treatment was 34.2% and 25.0%, respective...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com