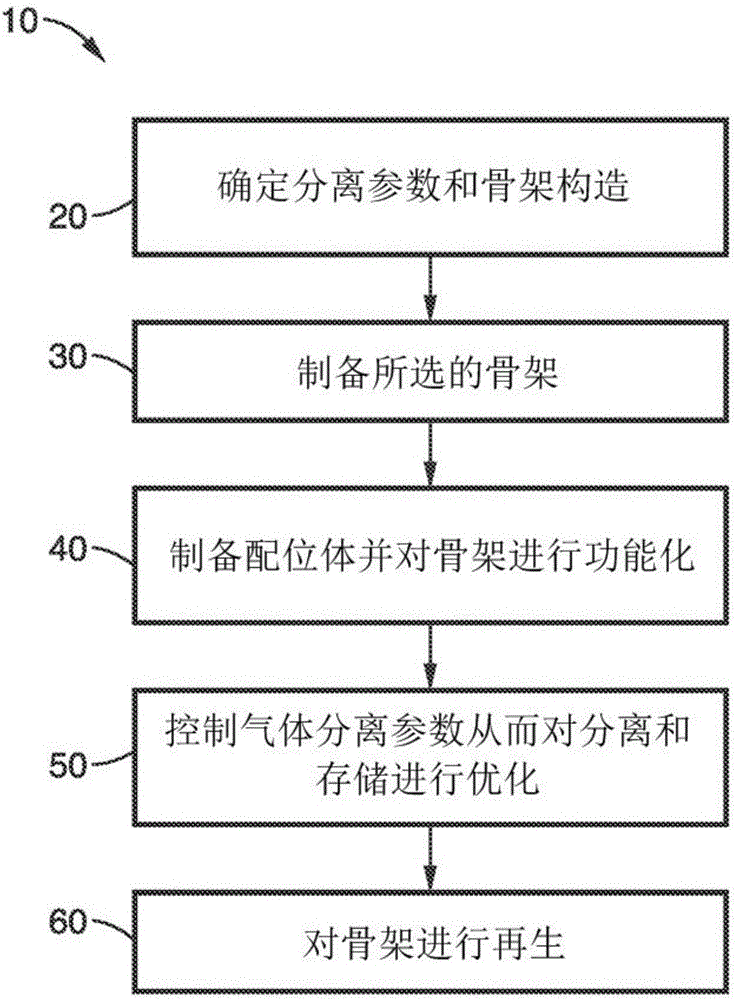
Cooperative chemical adsorption of acid gases in functionalized metal-organic frameworks
An acid gas, organic framework technology, applied in the field of metal-organic frameworks with metal atoms, which can solve problems such as reduced adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0107] To illustrate the present technique, several metal-organic frameworks (mmen-M 2 (dobpdc): mmen=N, N'-dimethylethylenediamine; M=Mg, Mn, Fe, Co, Zn; dobpdc 4- = 4,4'-Dioxybiphenyl-3,3'-dicarboxylate).
[0108] All reagents and solvents were purchased and were of reagent grade purity or higher; N,N'-dimethylethylenediamine (mmen) was dissolved in n-hexane to form a stock solution with a concentration of 10% v / v for amines functional reaction. mmen solution in N 2 stored in a 200 mL Schlenk bottle under conditioned conditions and by adding freshly ground CaH 2 Keep sewage free of moisture. Compound H 4 (dobpdc) was synthesized using conventional methods.
[0109] for Mg 2 (dobpdc) synthesis, the H 4 dobpdc (27.4mg, 0.10mmol) was added to a 20ml glass scintillation vial, followed by Mg(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O (64.0 mg, 0.25 mmol) and 10 ml of mixed solvent (55:45 MeOH:DMF). The scintillation vials were then sealed with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) lined caps and plac...
example 2
[0113] To further illustrate the principle of operation of the method, spectroscopic and diffraction measurements were used to determine the sorbent (such as mmen-Mg 2 (dobpdc)) Adsorption of CO 2 The mechanism behind the formation of steep steps. In particular, in the isomeric compound mmen-Mn 2 Powder X-ray diffraction studies performed on (dobpdc) provide insight into the CO 2 How to key in specific structural information in the channel of the material. After exposing the sample to 5 bar CO 2 Diffraction data collected at 100K before or after showed only a 1.112(8)% shrinkage in unit cell volume, but exhibited large changes in the relative intensities of selected diffraction peaks.
[0114] By using the simulated annealing method, a complete structural model for data setting is formed, such as Rietveld refinement of the data after implementation by TOPAS-Academic software. When exposed to CO 2 Previously, the mmen molecule was bonded to the Mn through an amine group ...
example 3
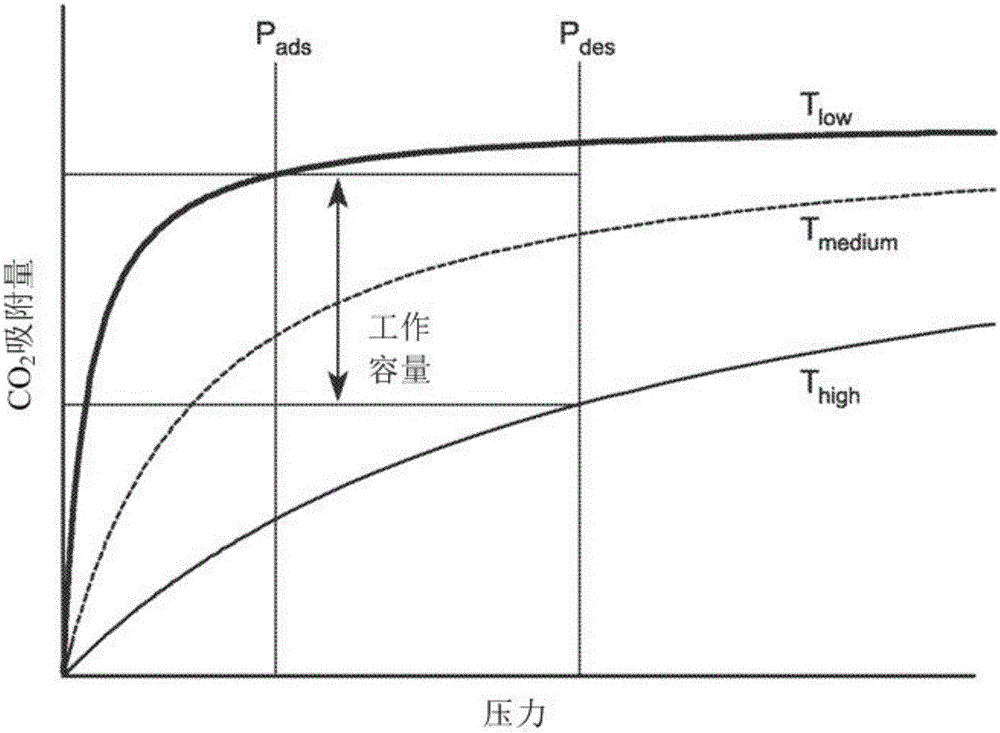
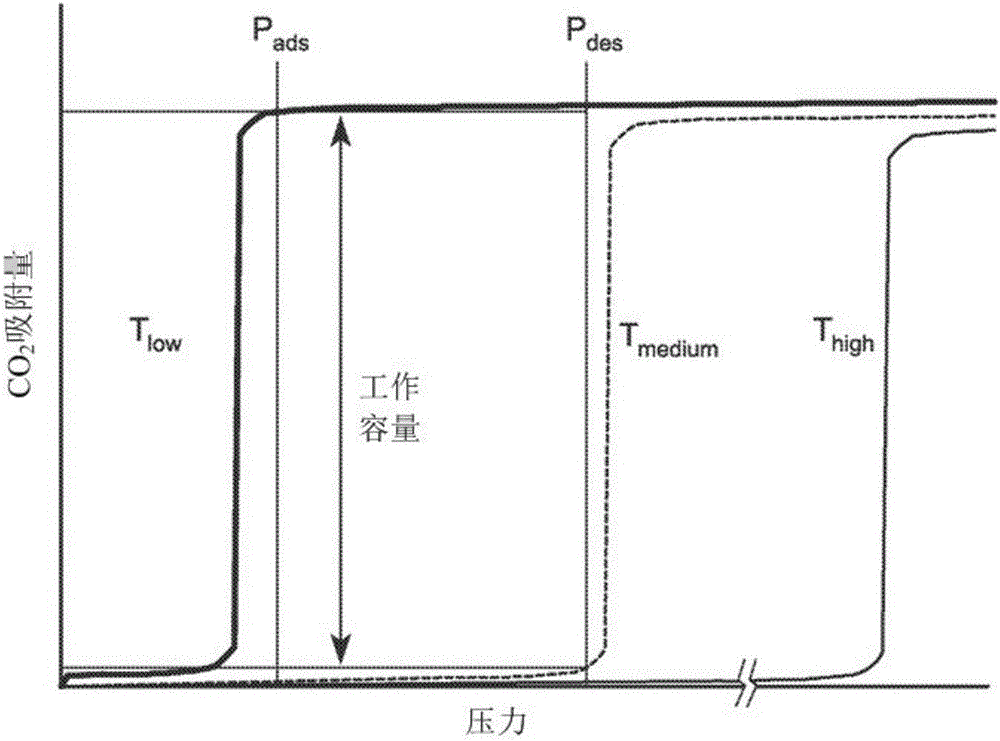
[0118] CO 2 The adsorption mechanism suggests that changes in the metal-amine bond strength may provide a means to tune the position of the isotherm step. Measured Mmen-M 2 CO of (dobpdc)(M=Mg, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Zn) compounds at 25, 40, 50 and 75°C 2 Adsorption isotherm series. With the exception of Ni compounds that show conventional Langmuir-type adsorption behavior, all other materials show steep isotherm steps that shift to higher pressures with increasing temperature. The Hill coefficients of M=Mg, Mn, Fe, Co, and Zn are 10.6, 5.6, 7.5, 11.5, and 6.0, respectively, through the analysis of the isotherm ladder at 25°C, reflecting the CO 2 Synergy of adsorption mechanism.
[0119] For a given temperature, the step position varies in the order of Mg<Mn<Fe<Zn<Co, which agrees with the published series for the stability of octahedral transition metal compounds. Ni compounds do not have steps even under very high pressure conditions, due to the special stability of the Ni-mme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com