PCR identifying method for nitrite bacteria
A technology of nitrosating bacteria and identification methods, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial determination/inspection, etc. It can solve the problems of low specificity of PCR amplification results, prolonging the identification cycle of bacteria species, and failing to achieve rapid detection, etc. problems, to achieve the results of high reliability, shortened overall time, and short detection time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
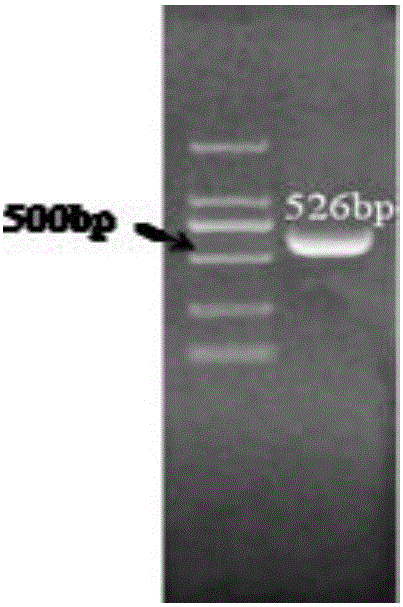
[0024] Embodiment 1 A kind of PCR identification method of nitrosative bacteria
[0025] Sample source: Petrochemical atmospheric and vacuum plant sewage, after phenol and desulfurization treatment, enters the biochemical treatment pool, and the waste water from this treatment pool is selected as sample 1.
[0026] Sample testing:
[0027] (1) Design and synthesis of primers: Using the exclusive characteristic gene ammonia monooxygenase gene (amoA) of nitrosative bacteria as a template, according to the principles of primer design, a pair of specific primers were designed and synthesized using primer 5.0 software. The specific sequences of the primers are as follows :
[0028] Upstream primer (F): 5'-GGGGTTTCTACTCCTGGT-3', the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in Seq ID No:1;
[0029] Downstream primer (R): 5'-CCCCTCGGGAAAGCCTTCTTC-3', the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in Seq ID No:2;
[0030] (2) Extraction of bacterial strain genomic DNA: Genomic DNA in the wa...
Embodiment 2
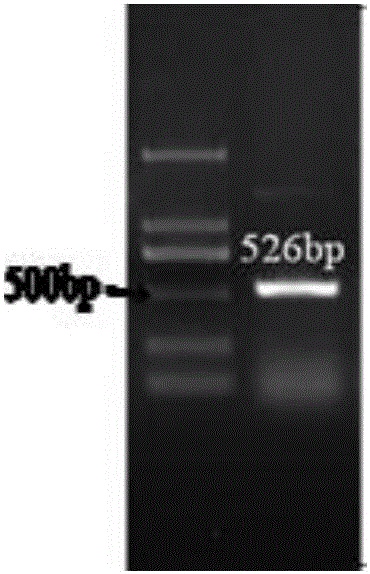
[0036] Embodiment 2 A kind of PCR identification method of nitrosative bacteria
[0037] Source of sample: Wastewater from thiourea chemical plant, after treatment to remove residual thiourea, it enters the biochemical treatment pool, and the wastewater from this treatment pool is selected as sample 2.
[0038] Sample testing:
[0039] (1) Design and synthesis of primers: Using the exclusive characteristic gene ammonia monooxygenase gene (amoA) of nitrosative bacteria as a template, according to the principles of primer design, a pair of specific primers were designed and synthesized using primer 5.0 software. The specific sequences of the primers are as follows :
[0040] Upstream primer (F): 5'-GGGGTTTCTACTCCTGGT-3', the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in Seq ID No:1;
[0041] Downstream primer (R): 5'-CCCCTCGGGAAAGCCTTCTTC-3', the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in Seq ID No:2;
[0042](2) Extraction of bacterial strain genomic DNA: Genomic DNA in sample 2 wa...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Embodiment 3 A kind of PCR identification method of nitrosative bacteria
[0049] Sample source: Wastewater from the agrochemical ether ester plant, after removing sulfides and macromolecular organic hydrocarbons, enters the biochemical treatment pool, and the wastewater from this treatment pool is selected as sample 3.
[0050] Sample testing:
[0051] (1) Design and synthesis of primers: Using the exclusive characteristic gene ammonia monooxygenase gene (amoA) of nitrosative bacteria as a template, according to the principles of primer design, a pair of specific primers were designed and synthesized using primer 5.0 software. The specific sequences of the primers are as follows :
[0052] Upstream primer (F): 5'-GGGGTTTCTACTCCTGGT-3', the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in Seq ID No:1;
[0053] Downstream primer (R): 5'-CCCCTCGGGAAAGCCTTCTTC-3', the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in Seq ID No:2;
[0054] (2) Extraction of bacterial strain genomic DNA: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com