Safe treatment method for recycling valuable metals and arsenic from arsenic-containing smoke
A technology for valuable metals and arsenic soot, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of low comprehensive recovery rate of valuable elements, limited market for arsenic products, untreated sodium arsenate, etc. The effect of high comprehensive utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
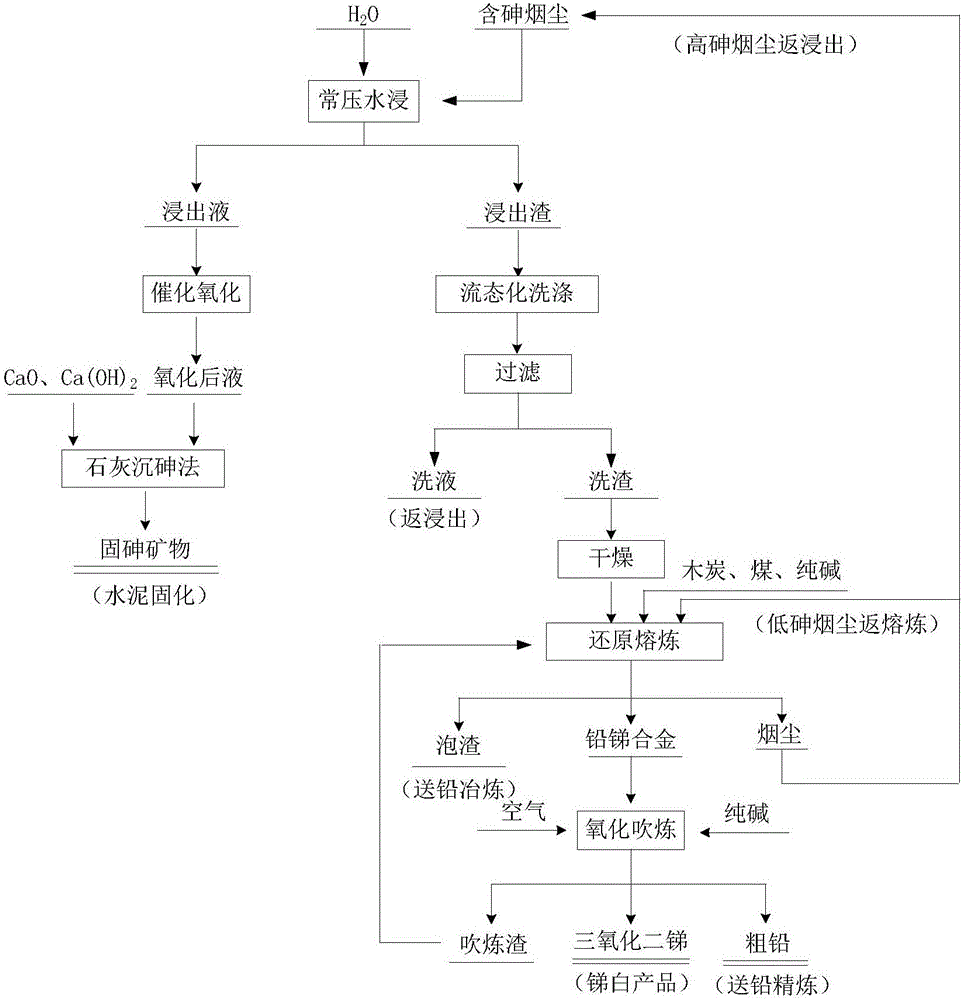
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Taking arsenic-containing soot from a lead-zinc smelter in China as an example, the main components of the raw materials are Pb 1.57%, As 48.56%, Sn 0.51%, Sb 21.24%, Zn 0.73%, Te 0.35%, Se 0.25%.
[0043] Proceed as follows:
[0044] (1) Weigh a certain amount of high arsenic and antimony fumes in the reaction kettle, and carry out the leaching experiment according to the liquid-solid volume-to-mass ratio of 5:1, the stirring speed of 100r / min, the leaching temperature of 70°C, and the leaching time of 4h. After leaching, the slurry was removed and separated by filtration. The arsenic leaching rate was 41.53%, and the element concentrations in the leachate were Pb 709.60ppm, Se 31.02ppm, Sb 1.26g / L, Te123.28ppm, As 20.17g / L.
[0045] (2) The leaching liquid adopts the method of catalytic oxidation to convert As 3+ Oxidized to As 5+ , the control conditions are that the oxygen flow rate is 5L / min, the As / Mn molar ratio is controlled at 10:1, and the temperature of the...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Taking arsenic-containing soot from a lead-zinc smelter in China as an example, the main components of the raw materials are Pb 6.88%, As 36.51%, Sn 1.11%, Sb 29.77%, Zn 0.54%, Te 0.24%, Se 0.05%.
[0051] Proceed as follows:
[0052] (1) Weigh a certain amount of high-arsenic and antimony fumes in the reactor, and carry out the leaching experiment according to the liquid-solid volume-to-mass ratio of 20:1, stirring speed of 300r / min, leaching temperature of 40°C, and leaching time of 2h. After leaching, the slurry was removed and separated by filtration. The arsenic leaching rate was 41.29%, and the concentrations of elements in the leach solution were Pb 515.20ppm, Se 31.56ppm, Sb 0.88g / L, Te122.26ppm, As 15.07g / L.
[0053] (2) The leaching liquid adopts the method of catalytic oxidation to convert As 3+ Oxidized to As 5+ , the control conditions are as follows: the oxygen flow rate is 10L / min, the As / Mn molar ratio is controlled at 40:1, and the temperature of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Taking arsenic-containing soot from a lead-zinc smelter in China as an example, the main components of the raw materials are Pb 5.46%, As 30.29%, Sn 0.98%, Sb 29.58%, Zn 0.68%, Te 0.26%, Se 0.07%.
[0059] Proceed as follows:
[0060] (1) Weigh a certain amount of high-arsenic and antimony fumes into the reaction kettle, and carry out the leaching experiment according to the liquid-solid volume-to-mass ratio of 15:1, the stirring speed of 50r / min, the leaching temperature of 90°C, and the leaching time of 3h. After leaching, the slurry was removed and separated by filtration. The arsenic leaching rate was 44.52%, and the element concentrations in the leach solution were Pb 956.35ppm, Se 18.91ppm, Sb 0.93g / L, Te144.92ppm, As 13.48g / L.
[0061] (2) The leaching liquid adopts the method of catalytic oxidation to convert As 3+ Oxidized to As 5+ , the control conditions are as follows: the oxygen flow rate is 1L / min, the As / Mn molar ratio is controlled at 20:1, and the tem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com