Phytopathogen antagonistic bacterium and its application in plant disease control
A plant disease and disease technology, which is applied to a plant pathogenic bacteria antagonism and its application in the prevention and control of plant diseases, can solve the problems of destroying soil microecology, adverse effects on farmland environment, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Embodiment 1, screening and identification of phytopathogen antagonistic bacteria
[0020] 1. Screening of antagonistic bacteria of plant pathogens
[0021] The bacterial strain of the present invention is isolated from the inside of healthy cassava leaves (the cassava variety is Huanan No. 8). The specific method is: take 1g of leaves, cut them into small pieces of 5mm × 5mm, put them into 70% alcohol, and leave them for 60s. Finally, rinse once with sterile water, then put it into 3.25% sodium hypochlorite, and rinse repeatedly with sterile water after 5 minutes. Put it into a sterilized mortar with 9 mL of sterile water, add a little sterilized quartz sand to grind evenly, and let it stand for 15 minutes. Take 1mL and dilute to 10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 Concentration gradient, take 0.1mL from each concentration gradient suspension, and spread it on NA medium with a sterile applicator (recipe: peptone 5g, yeast extract 1g, beef extract 3g, agar powder 15g, glucose 10g, ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2, Paenibacillus sp. (Paenibacillus sp.) CEB33 CGMCC No.12719 antibacterial spectrum determination
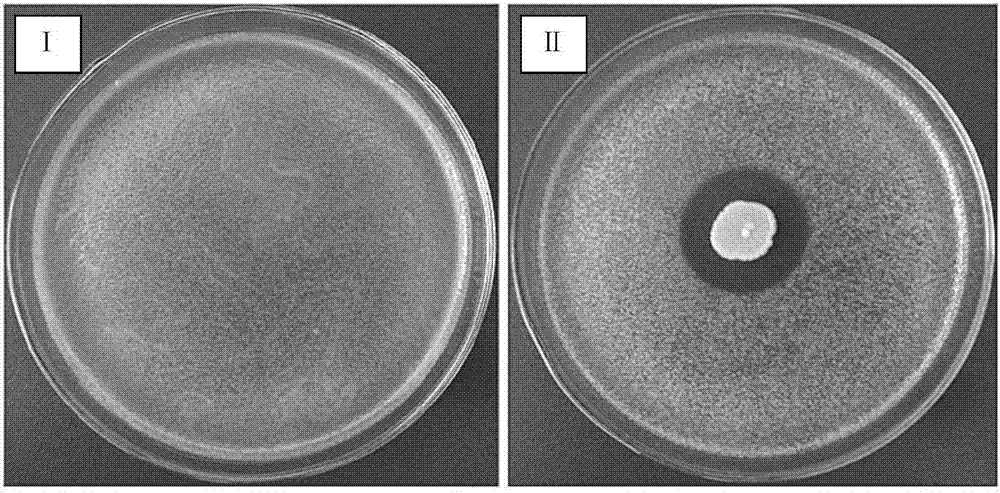
[0036] According to the method in Example 1, CEB33 was co-cultured with cassava bacterial wilt (Xanthomonasaxonopodis pv.manihotis, purchased from China Agricultural Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center, preservation number ACCC03517) ( figure 1 ). The results of the antagonistic effect of the strain on cassava bacterial wilt were as follows: figure 1 As shown, the results showed that the screened strains had a strong antagonistic effect on cassava bacterial wilt. figure 1 Middle II is the confrontation culture test between CEB33 and cassava bacterial wilt, and I is the growth of control cassava bacterial wilt. This bacterial strain has good inhibitory effect to cassava bacterial wilt, and the diameter of the inhibition zone is 1.7cm (such as figure 1 shown).
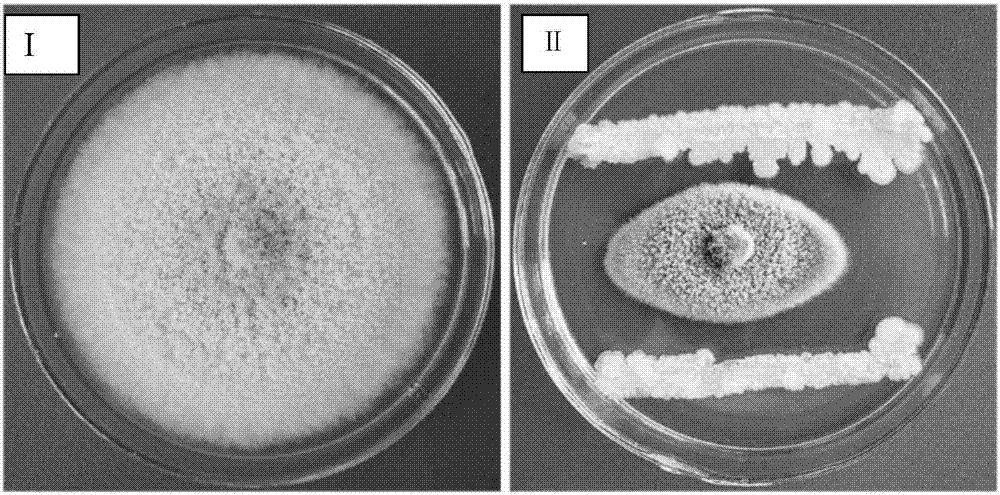
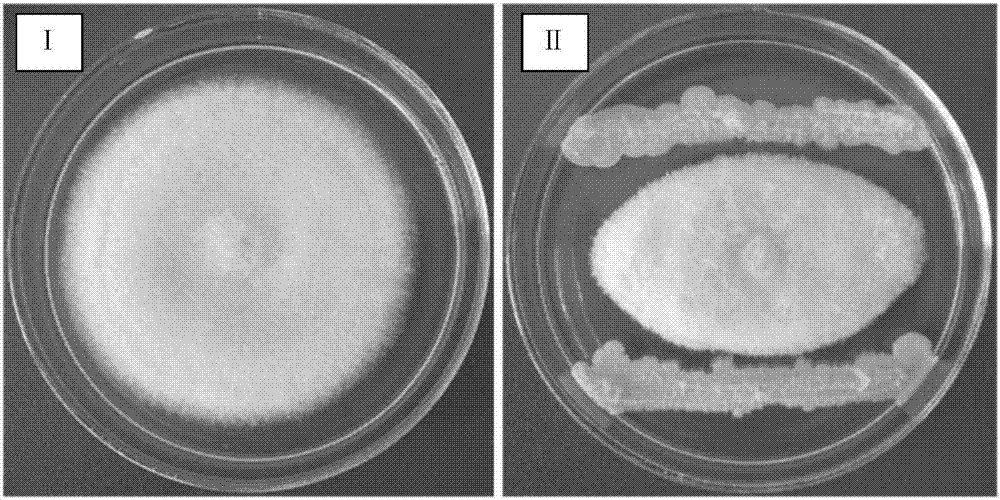
[0037] Use PDA medium plate (recipe: peeled potato 200g, glucose 20g, agar 20g, af...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3, Endogenous Determination of Paenibacillus sp. CEB33 CGMCC No.12719
[0039] 1. Acquisition of ampicillin-resistant bacteria from Paenibacillus sp. CEB33 CGMCC No.12719
[0040] Inoculate Paenibacillus sp. CEB33 into LB liquid medium containing 10 μg / mL ampicillin (Amp) (recipe: tryptone 10 g, sodium chloride 10 g, yeast extract 5 g, dilute to 1000 mL with distilled water, adjust pH to 7.0, sterilized at 121°C for 20 minutes), cultured by shaking for about 48 hours until the bacterial liquid became cloudy, inoculated a small amount of cultured bacterial liquid into LB liquid medium containing 15 μg / mL ampicillin (Amp), and cultured by shaking until the bacterium becomes cloudy. According to this method, the concentration of ampicillin was gradually increased for cultivation, and finally Paenibacillus that could grow stably on the LB medium containing ampicillin at a concentration of 300 μg / mL, and whose colony morphology and antagonism to pathogenic bacteria ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com