Multi-microbe solid fermentation ethanol and acetic acid production key microbe quantitative analysis method
A technology of solid-state fermentation and quantitative analysis, applied in the field of brewing, to achieve the effect of good specificity, high sensitivity and good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Example 1 Extraction of Microorganism Genome DNA from Fermented Grains
[0054] Weigh 7.5g of fermented grains sample in a 50ml centrifuge tube, add 20ml of nucleic acid extraction buffer (2% CTAB (w / v), 100mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 20mM EDTA (pH8.0), 1.4M NaCl), 20g of sterile quartz sand, shake for 1min with a nucleic acid extractor, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 10min; add an equal volume of P:C:I (phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol = 25:24:1) to the supernatant, and centrifuge at 11000rpm for 20min; Add 2 times the volume of silica gel membrane-binding solution (4M guanidine hydrochloride, 0.5M potassium acetate), filter through the adsorption column, and discard the filtrate; dry the adsorption column for 1 hour under natural conditions, add 300 μL sterile water to dissolve the DNA, filter, and fill the filtrate in 1.5 mL without Store in centrifuge tubes at -20°C for later use.
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 standard curve construction
[0056] 1. Synthesis of specific primers for Saccharomyces cerevisiae HIS3, Saccharomyces pombe ADH1 and Lactobacillus 16SrRNA
[0057] Saccharomyces cerevisiae specific primer sequence (5'-3'):
[0058] SEQ ID NO.1
[0059] S. cere-F: GGGCTGGAAGATCGGTGACTAC
[0060] SEQ ID NO.2
[0061] S. cere-R: AGCGTGAGGACAGTTGGATTCG
[0062] Schizosaccharomyces pombe-specific primer sequence (5'-3'):
[0063] SEQ ID NO.3
[0064] S. pombe-F: CGAGACGAGACGAGACGAGATG
[0065] SEQ ID NO.4
[0066] S. pombe-R: CGACAAACGGCACACCAAACG
[0067] Lactic acid bacteria specific primer sequence (5'-3'):
[0068] SEQ ID NO.5
[0069] Lac.16s-F: AGAACACCAGTGGCGAAGG
[0070] SEQ ID NO.6
[0071] Lac.16s-R: CAGGCGGAGTGCTTAATGC
[0072] 2. Obtain specific amplification target fragment
[0073] Using the pure DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe and the total DNA of fermented grains as templates, S.cere-F / S.cere-R, S.pombe-F...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Example 3 Fluorescence quantitative PCR of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe and lactic acid bacteria in the microbial community of fermented grains
[0087] Quantification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, S. pombe and lactic acid bacteria in the fermented grain sample: use the total DNA of the fermented grains obtained in Example 1, and use the specific primers for Saccharomyces cerevisiae, S. pombe and lactic acid bacteria in Example 2. Fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis of wine fermented grains was carried out according to the fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction system and fluorescent quantitative PCR program in Example 2.
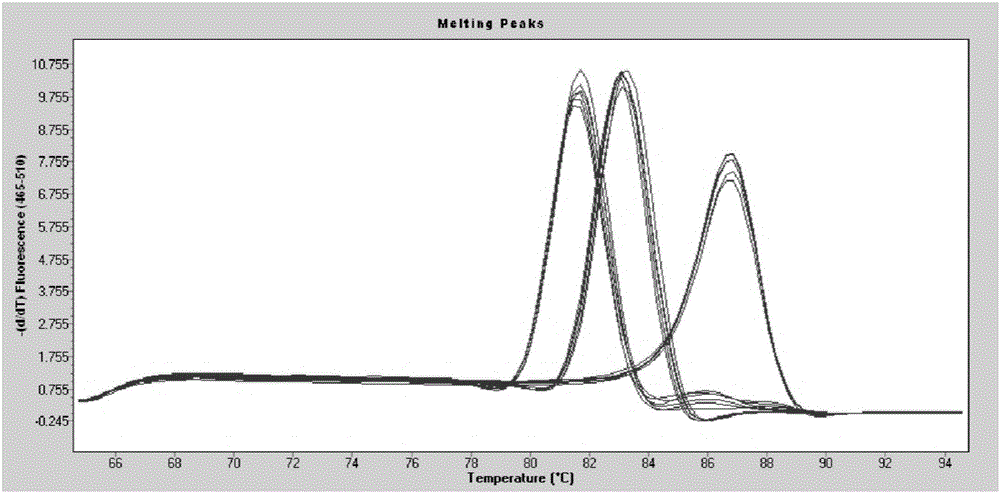
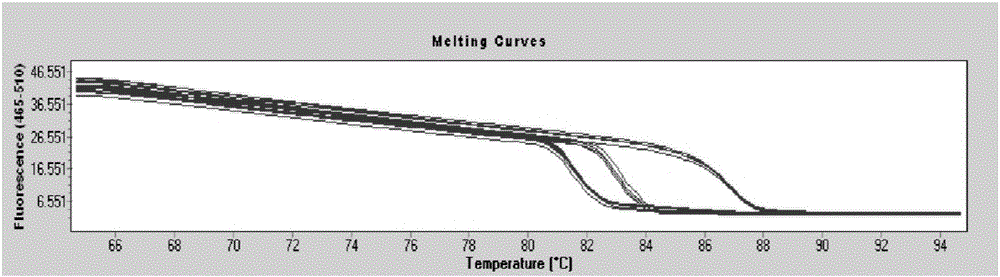
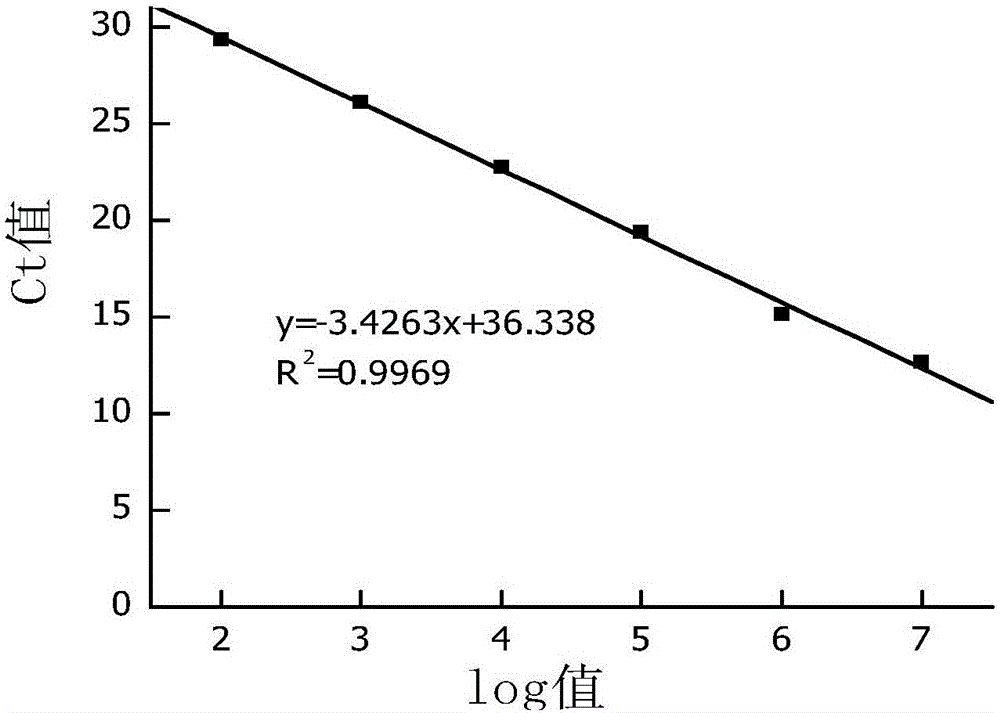
[0088] According to the fluorescent quantitative PCR of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae standard substance, the linear equation y=-3.4263x+36.338 (R 2 =0.9969) (such as image 3 shown) to calculate the copy number of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the fermented grains sample, and the fluorescence quantitative PCR amplification curve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com