Method for extracting macro fungus genome DNA
A genome and fungal technology, applied in the field of extracting large fungal genome DNA, can solve the problems of low DNA yield, unpurified treatment, cumbersome steps, etc., and achieve the effect of high purity, high yield and clear interface
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
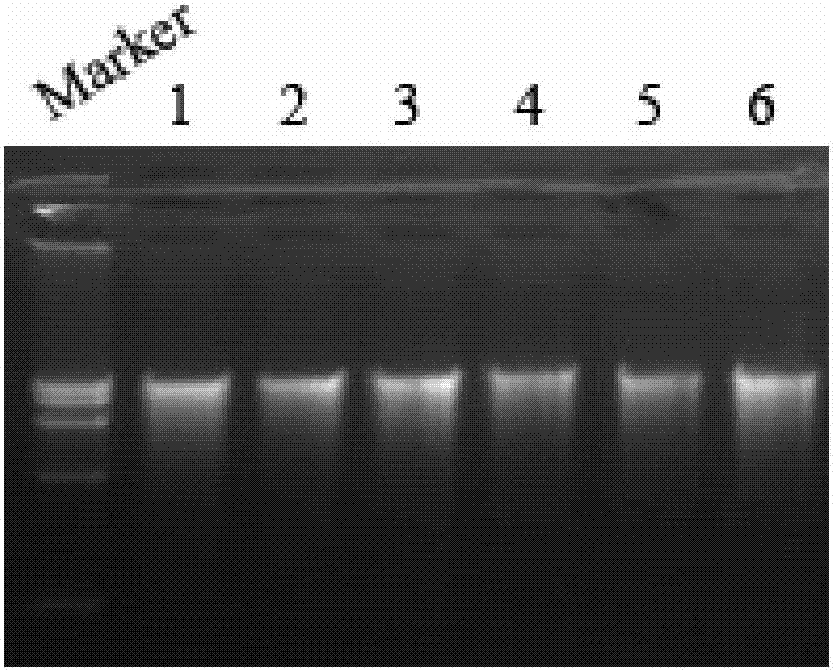
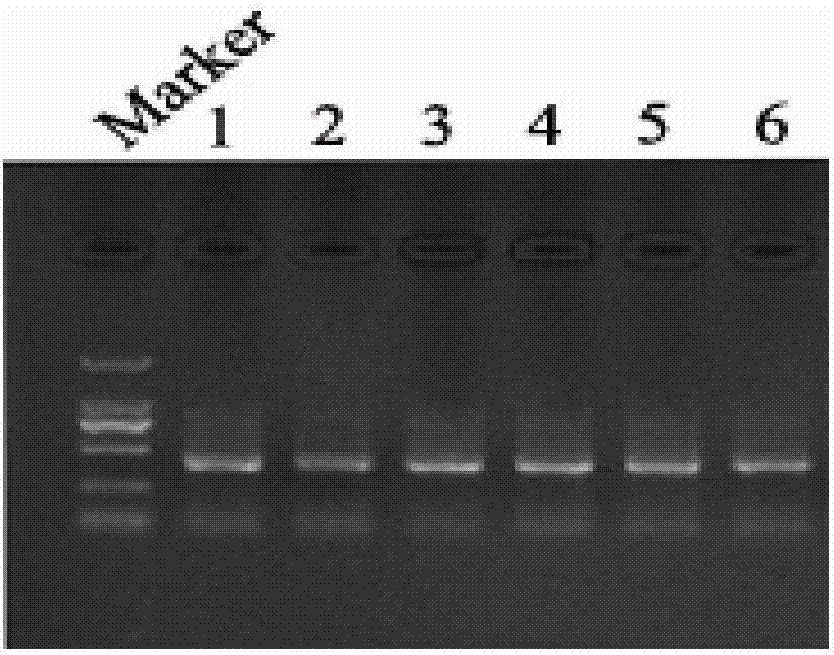
[0045] Utilize the inventive method to extract the genomic DNA of 6 different macrofungi samples (fruiting bodies and hyphae of straw mushroom, shiitake mushroom and Hericium erinaceus) respectively, and the extraction steps are as follows:
[0046] 1. Take 100 mg of fungal fruiting bodies or 20 mg of fungal hyphae, grind them into powder in liquid nitrogen, add 600 μl of preheated reagent I, mix well, warm bath at 65°C for 30 minutes, and centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 10 minutes.
[0047] 2. Transfer the supernatant to a sterilized 1.5ml centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of reagent II, mix well for 2 minutes, and centrifuge at 12,000rpm for 10 minutes.
[0048] 3. Draw the supernatant into a sterilized 1.5ml centrifuge tube, add isopropanol equal to the volume of the supernatant, mix well, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10min, discard the supernatant, keep the precipitate, add 60μl of reagent III, use the specification model 200μl sterilized pipette tip to thoroughly mix the pr...
Embodiment 2
[0067] In this example, the content of each component in reagent I is: Tris-HCl 250mM, NaCl 250mM, EDTA 25mM, SDS cell lysate 0.45wt.%, vinylpolypyrrolidone 0.5wt.%, pH=7.8; each component in reagent II The content is: phenol, chloroform and isoamyl alcohol volume ratio (V / V=25:24:1); reagent III is: 1×TE buffer; the content of each component of reagent IV is: guanidine isothiocyanate 8M, Tris -HCl 40mM, EDTA 45mM, Triton X-100 25mM; the content of each component of reagent V is: guanidine isothiocyanate 8M, Tris-HCl 40mM; the content of each component of reagent VI is: Tris-HCl 40mM, NaCl 250mM, ethanol 73vol%.
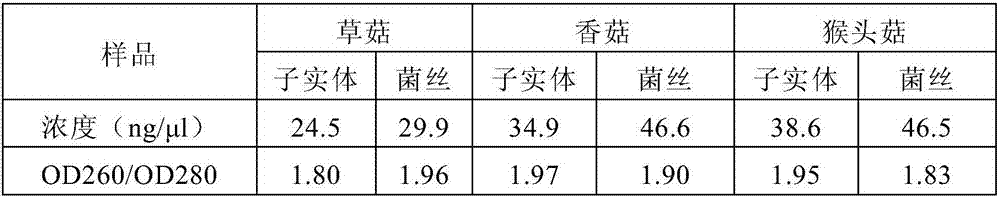
[0068] Other operating steps are the same as in Example 1, and the DNA concentration and purity results of the extracted water body samples are shown in Table 2.
[0069] Table 2
[0070]
[0071] It can be seen from Table 2 that the concentration of the obtained DNA is about 20-50 ng / μl, the ratio of OD260 / OD280 is between 1.8-2.0, and the purity and yield are ...
Embodiment 3
[0074] In this example, the content of each component in reagent I is: Tris-HCl 300mM, NaCl 300mM, EDTA 30mM, SDS cell lysate 0.5wt.%, vinylpolypyrrolidone 0.6wt.%, pH=8.0; each component in reagent II The content is: phenol, chloroform and isoamyl alcohol volume ratio (V / V=25:24:1); reagent III is: sterilized distilled water; the content of each component of reagent IV is: guanidine isothiocyanate 9M, Tris-HCl 50mM, EDTA 50mM, Triton X-100 30mM; the content of each component of reagent V is: guanidine isothiocyanate 9M, Tris-HCl 50mM; the content of each component of reagent VI is: Tris-HCl 50mM, NaCl 300mM, ethanol 75vol% .
[0075] Other operating steps are the same as in Example 1, and the results of DNA concentration and purity of the extracted water samples are shown in Table 3.
[0076] table 3
[0077]
[0078] It can be seen from Table 3 that the concentration of the obtained DNA is about 20-50 ng / μl, the ratio of OD260 / OD280 is between 1.8-2.0, and the purity an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com