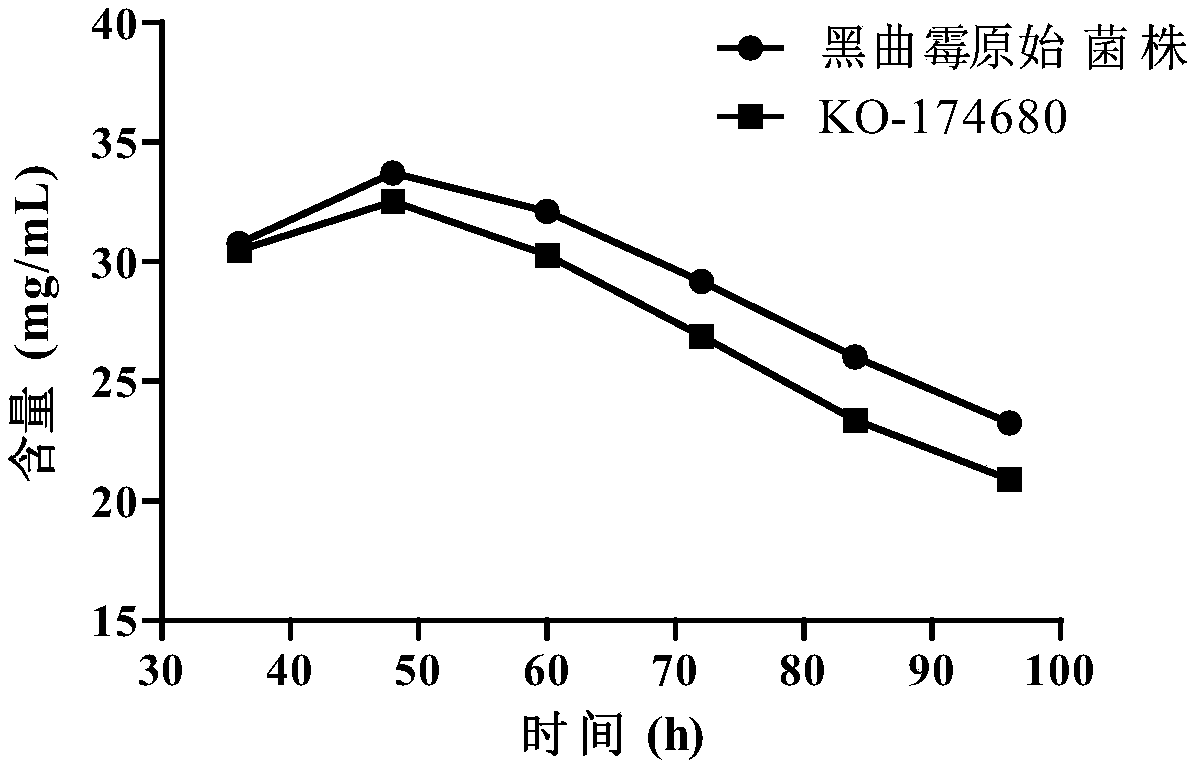
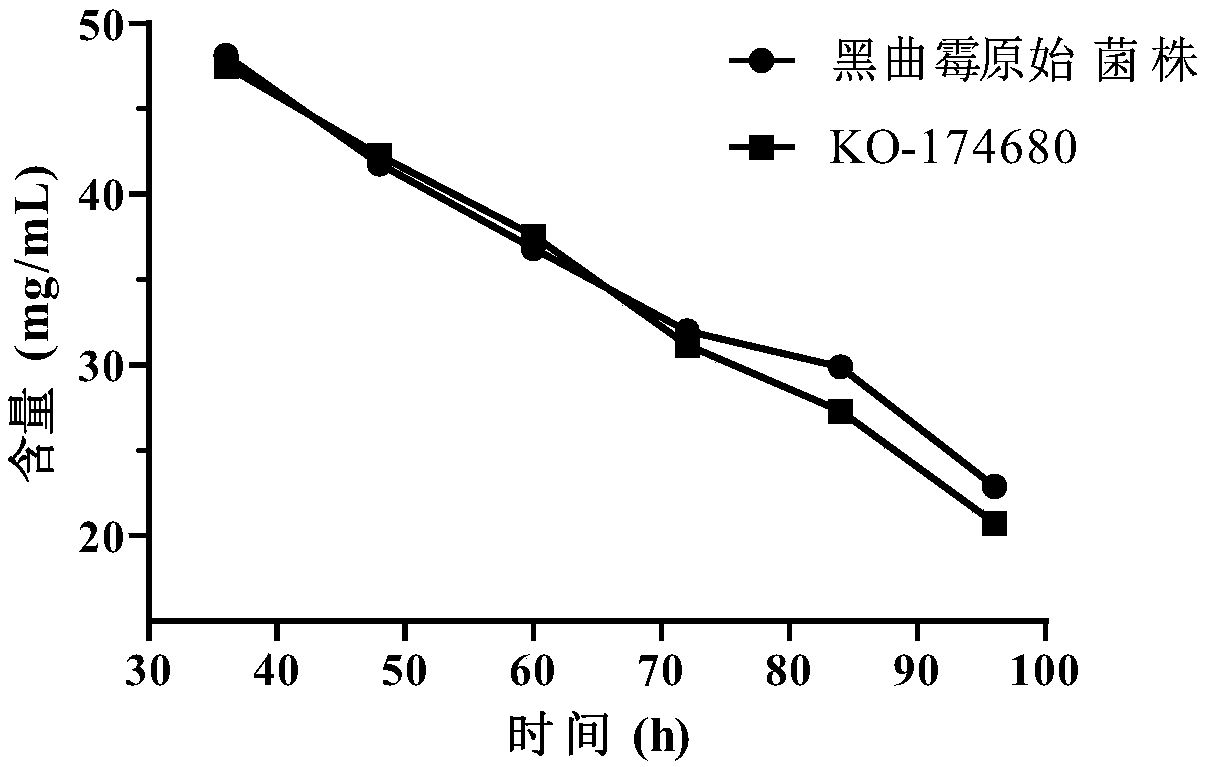
Method for increasing sugar utilization rate and yield of citric acid in citric acid fermentation and application
A technology of citric acid and utilization rate, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering, can solve the problem of low citric acid yield of sugar utilization rate, and achieve significant economic benefits and increased yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Cloning of the glucosyltransferase gene in Aspergillus niger Co860
[0035] (1) Extraction of the total RNA of Aspergillus niger Co860
[0036] a. Filter the cultured bacteria with sterile gauze, rinse with sterile water 2 to 3 times, and collect the bacteria;
[0037] b. The collected fresh bacteria are quickly put into a mortar filled with an appropriate amount of liquid nitrogen, and continuously ground in a clockwise direction until the bacteria become a uniform powder;
[0038] c. Quickly add the above bacterial powder into a 50mL centrifuge tube containing an appropriate amount of Trizol, and vortex for 20 minutes;
[0039] d. Dispense the homogenate into 1.5mL EP tubes, 1mL in each tube, and let stand for 10min;
[0040]e. Add 200 μL of chloroform to each tube, close the cap tightly, shake vigorously for 30 seconds, and let stand for 10 minutes;
[0041] f. Centrifuge at 12000r / min for 10min at 4°C, and transfer the supernatant to a new EP tube;
...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Embodiment 2: the extraction of Aspergillus niger Co860 genomic DNA:
[0066] (1) Inoculate Aspergillus niger spores into the wort medium, culture at 35°C and 220r / min for 48h;
[0067] (2) Use six layers of gauze to filter and collect the thalli, wash 3 times with sterile ultrapure water, and dry the water;
[0068] (3) rapid liquid nitrogen freezing, liquid nitrogen grinding to powder;
[0069] (4) Distribute the bacterial cell powder into 1.5mL EP tubes, add 900μL of lysate (5g / L SDS, 14g / LNaCl, 7.5g / L EDTA, 5% β-mercaptoethanol, 25% of 50mM Tris-HCl (pH7.5)) mix, 12000r / min centrifugal 15min;
[0070] (5) Transfer the supernatant to another new EP tube, add 20 μL of proteinase K (20 mg / mL), and bathe in water at 56°C for 2-6 hours;
[0071] (6) Add 30 μL of RNase (20 mg / mL) to the EP tube and place at 37°C for 1-2 hours;
[0072] (7) Add an equal volume of phenolform, shake and mix well, and centrifuge at 12000r / min for 5min;
[0073] (8) Repeat step (7) 1-2 ti...
Embodiment 3
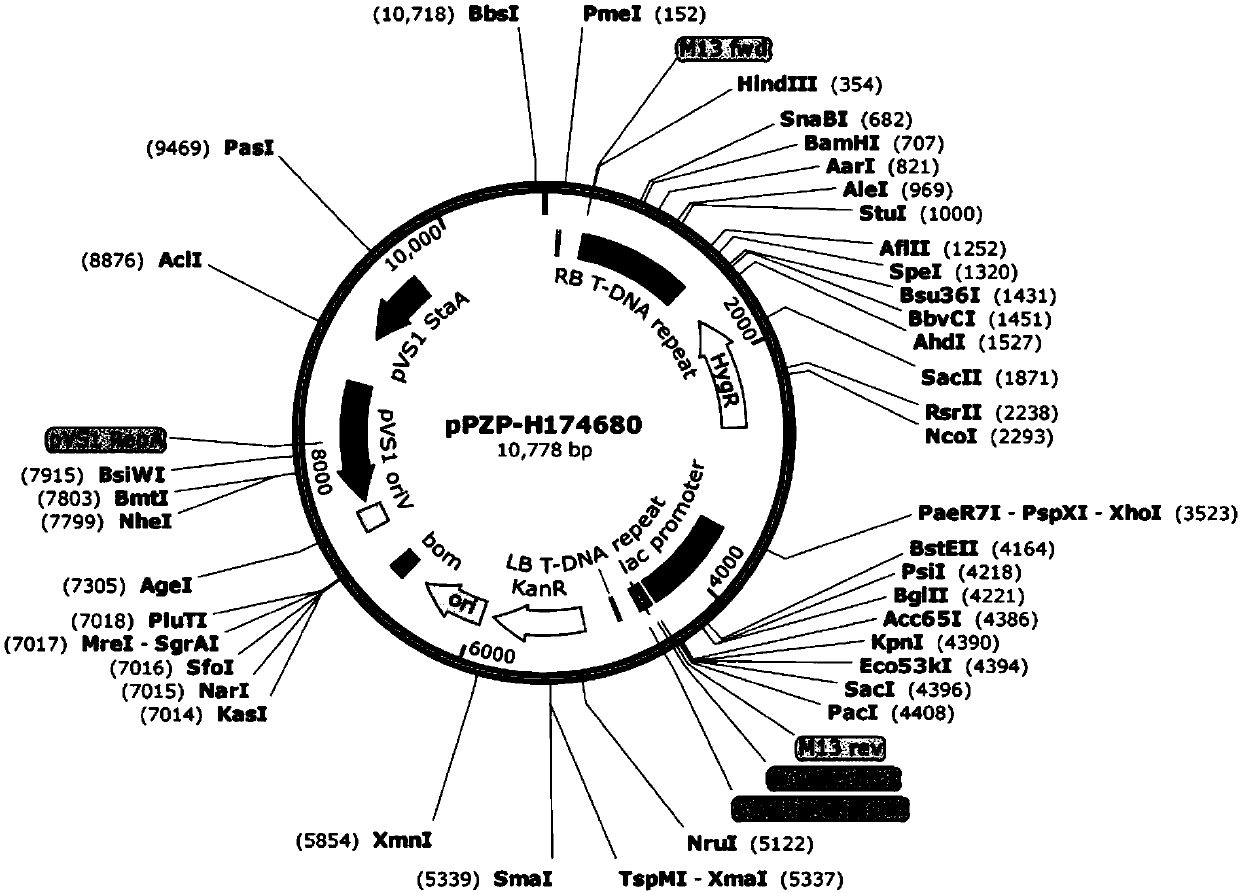
[0078] Embodiment 3: Construction of Aspergillus niger Co860 knockout vector
[0079] (1) Use primers 174680LF and 174680LR to PCR amplify the LB of the glucosyltransferase gene (candidate glucosyltransferase) (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.3) using Aspergillus niger Co860 genomic DNA as a template, the sequence contains HindIII and SpeI enzymes upstream and downstream Cutting site, connected to pMD19 and sequenced correctly, digested with these two restriction endonucleases, connected the sequence to pPZP-HYG2 cut with the same enzyme, and obtained pPZP-174680-LB;
[0080] (2) Use primers 174680RF and 174680RR to amplify the RB of the candidate glucosyltransferase gene (candidate glucosyltransferase) by PCR using the Aspergillus niger Co860 genome as a template (the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.4), and the upstream and downstream sequences contain XhoI and KpnI restriction enzymes site, connected to pMD19 and sequenced correctly, digested with these two restriction endonuclea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com