Preparation method for low-viscosity poly-alpha-olefin synthetic oil
An olefin synthetic oil, low viscosity technology, applied in the treatment of hydrocarbon oil, hydrocarbon oil treatment products, production of liquid hydrocarbon mixtures, etc., can solve the problems of easily causing corrosion, large energy consumption, etc., reducing operating costs, realizing recovery, and operation. easy effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
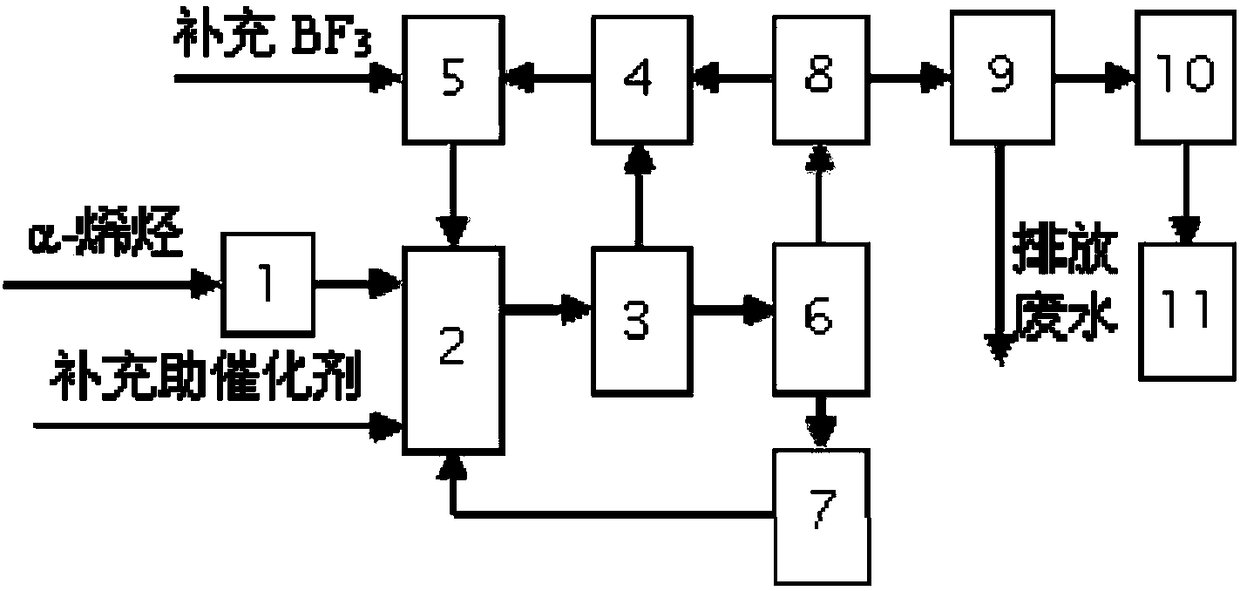
[0053] see figure 1 Shown, the preparation method of low-viscosity polyalpha-olefin synthetic oil of the present invention specifically comprises the following steps:
[0054] (1) Dehydrating and refining the α-olefin raw material through a molecular sieve fixed bed (ie molecular sieve dehydration tower 1), so that the water content of the raw material is ≤ 10ppm;
[0055] (2) Put the α-olefin raw material and the recovered monomer and dimer (obtained by the following step (5)) into the reactor 2, and add the reclaimed complex catalyst (obtained by the following step (4)) And supplementary co-catalyst (water content ≤ 10ppm), filled with BF 3 To carry out the reaction, co-catalyst with BF 3 Combined to obtain a complex catalyst.
[0056] (3) Polymerization product flash treatment: the reaction product is flashed through flasher 3 to obtain the first oil phase and gas phase, the catalyst activity is terminated, and BF is recovered 3 ,Recycling.
[0057] Vacuum Flash BF 3 ...
Embodiment 1~6
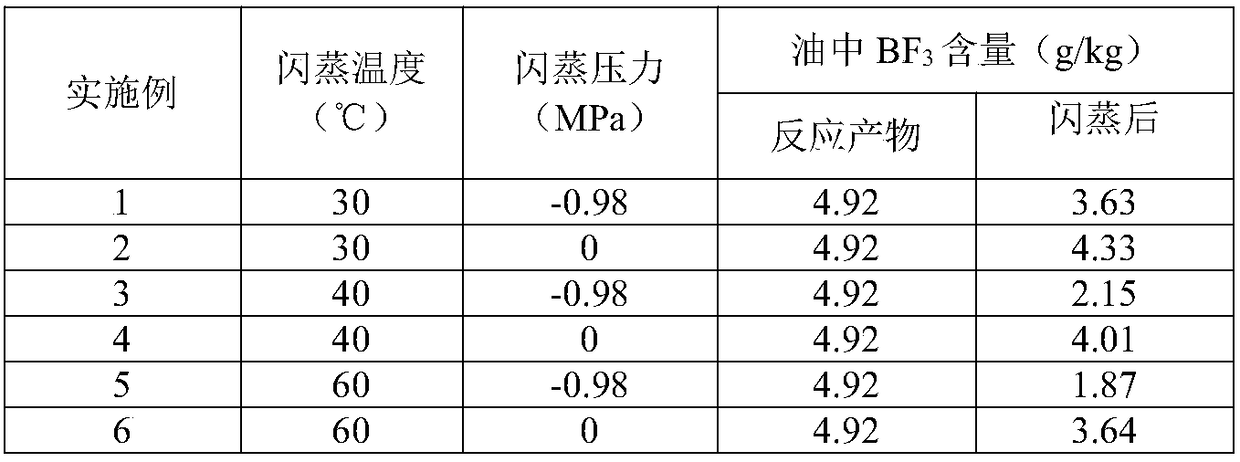
[0064] The low-viscosity PAO is synthesized from dehydrated and refined 1-decene (water content is 8ppm), and butanol (water content 9ppm) is used as a cocatalyst, and the amount ratio of butanol and 1-decene is 1:100 (substance volume), at 30°C, BF 3 Pressure is the reaction under the condition of 0.2MPa, and the reaction time is 1h, and the obtained reaction product is subjected to flashing treatment, adopts different flashing conditions to carry out flashing test (see Table 1, get embodiment 1-6) respectively, obtains the first oily phase And the gas phase, the gas phase, that is, the flash gas is pressurized and returned to the reactor, and the first oil phase enters the precipitator for precipitation treatment.
[0065] Table 1 Flash process on BF 3 The removal effect of
[0066]
Embodiment 7~11
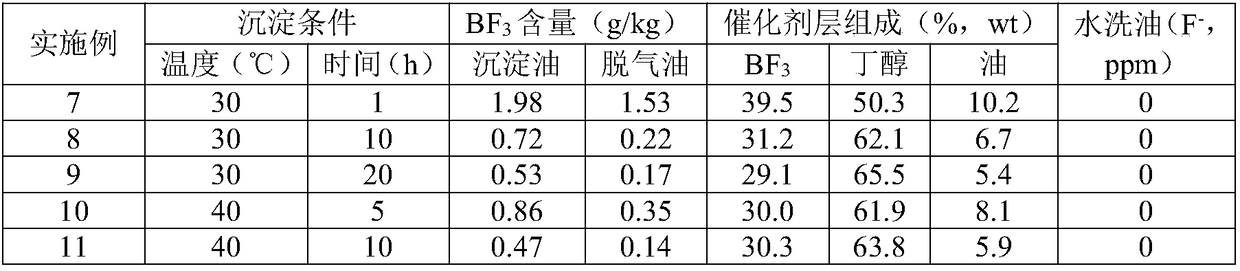
[0068] With the first oil phase of embodiment 3 as precipitation feedstock (i.e. precipitation oil), adopt respectively different precipitation conditions to carry out precipitation test (see table 2, obtain embodiment 7-11), obtain the second oil phase of upper strata and lower layer catalyst layer, the second oil phase is separated from gas and liquid, the resulting gas and flash gas are combined and compressed, and the remaining oil phase (i.e. degassed oil) is subjected to alkali washing and water washing treatment to obtain water-washed oil (i.e. clean intermediate product). The fluorine content of the oil was washed with water, and the composition of the lower catalyst layer was analyzed, which is listed in Table 2.
[0069] Table 2 Sedimentation separation on BF 3 The removal effect of
[0070]
[0071] Intermediate products continue to undergo vacuum distillation to separate monomers and dimers, and then undergo hydrogenation and saturation treatment to obtain poly...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com