Extraction method of candida fungal biofilm extracellular matrix
A technology of biofilm and Candida, which is applied in the biological field and can solve the problems of EPS not being able to identify components, missing components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Embodiment 1: A kind of extraction method of candida fungus biofilm extracellular matrix
[0060] Step 1. First, soak each section of about 6cm grooved medical grade polyvinyl chloride (PVC) catheter piece in 75% ethanol overnight to keep it sterile, and then take it out and soak it in sterile water for use. After activating SC5314, adjust the bacterial concentration to 1×10 6 CFU / mL, place the catheter piece in the shaker (37°C 220rpm / min) and incubate for 4 hours to make the white nipple adhere to the catheter piece. After adhesion, the catheter pieces were taken out, and five catheter pieces were placed in a centrifuge tube containing 40 mL of 1640 medium in a centrifuge tube at a constant temperature of 37°C for 24 hours to form a biofilm. After 24 hours, use sterilized tweezers to gently take out the catheter piece, put it in a test tube filled with 6 mL of sterile water, and vortex for 1 min.
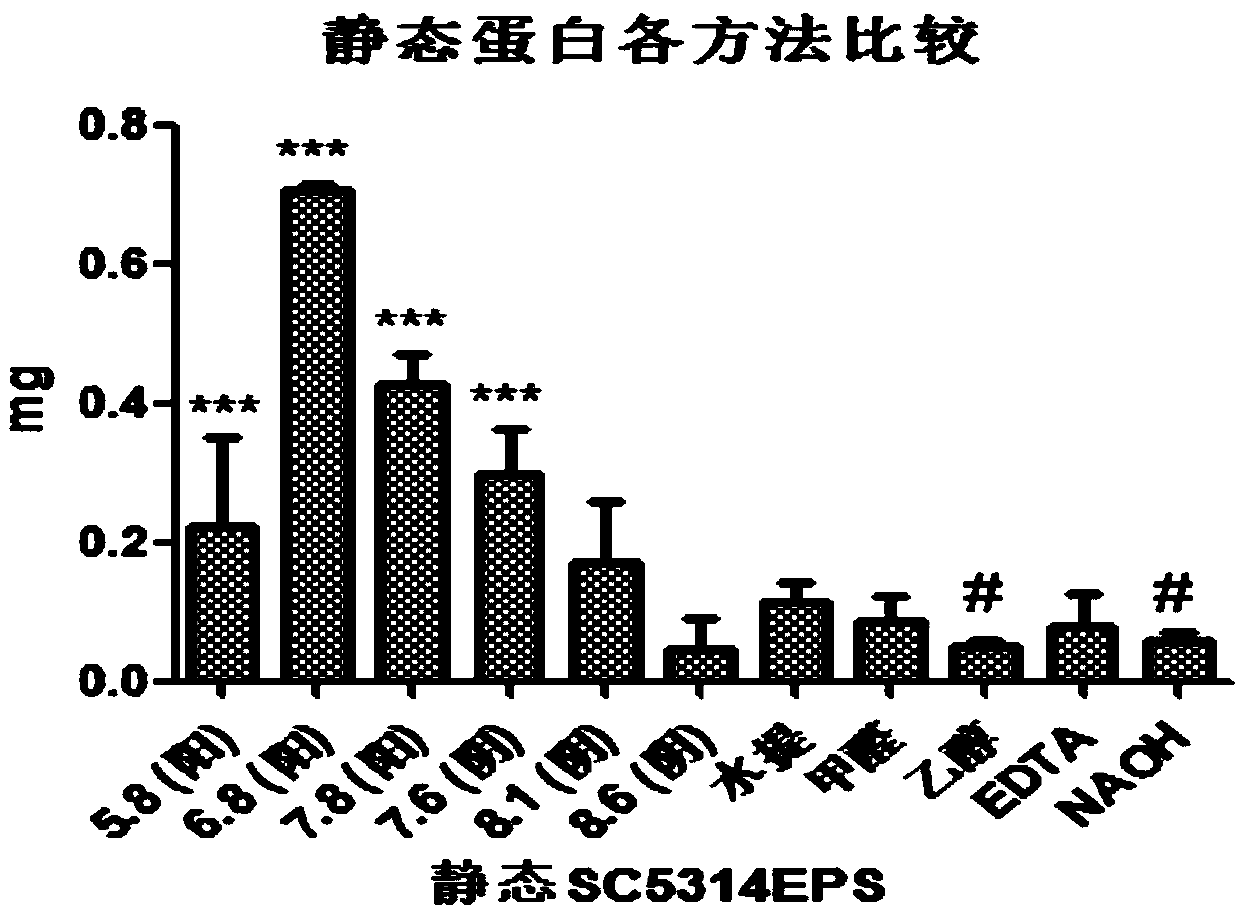
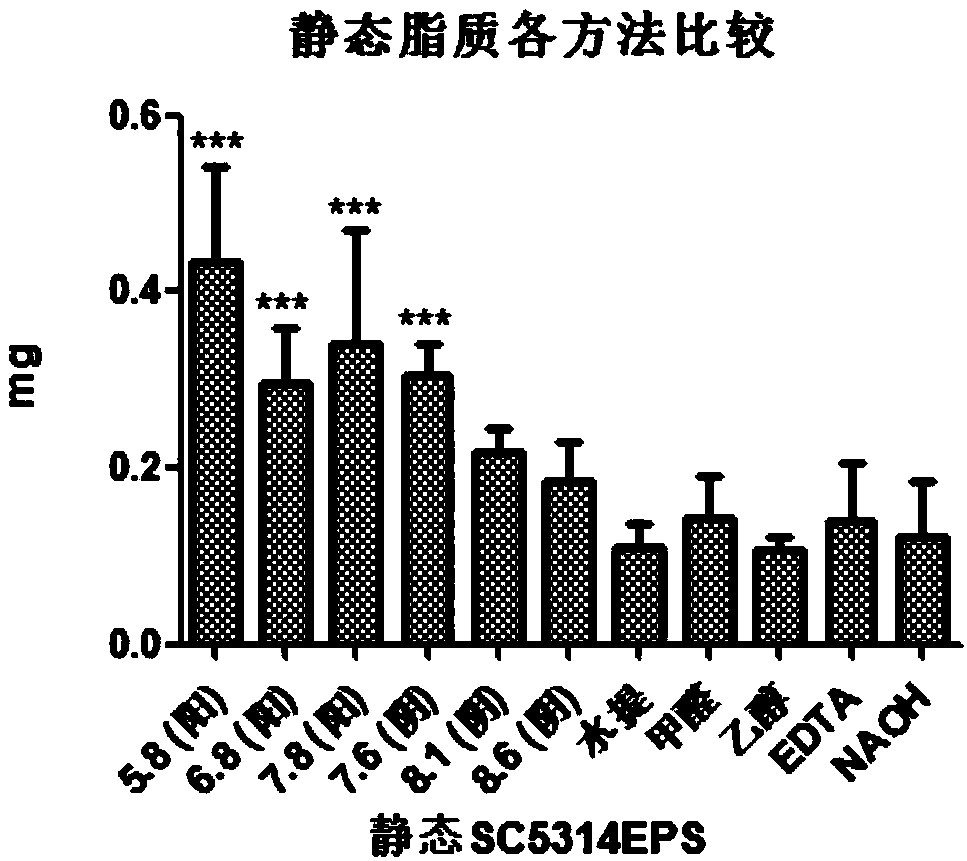
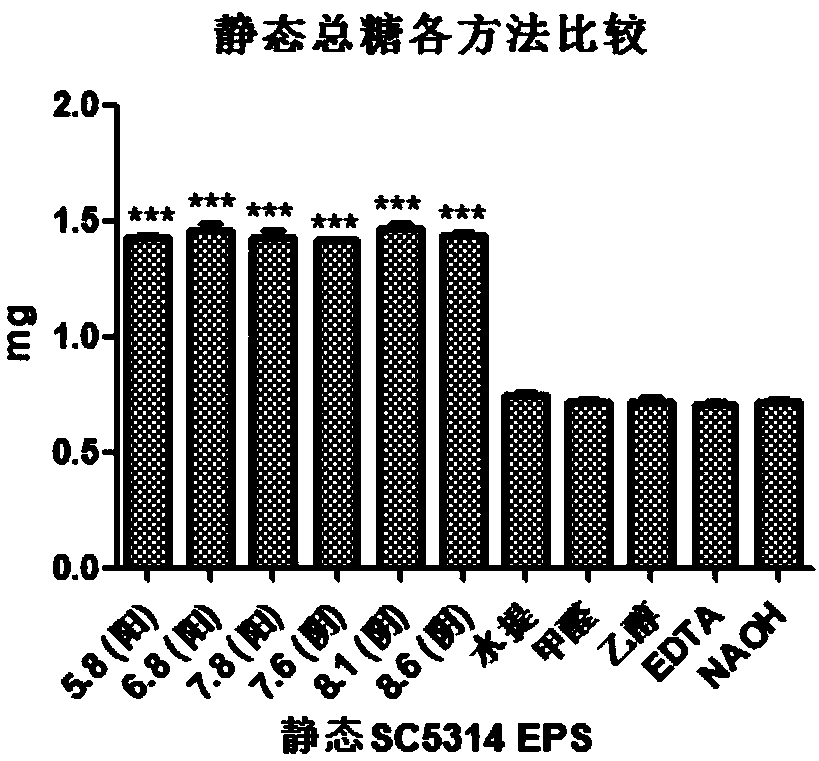
[0061] Step 2. Extraction of static SC5314 EPS by ion exchange resi...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Embodiment 2: A kind of extraction method of candida fungi biofilm extracellular matrix
[0073] Non-Candida albicans EPS extraction under static conditions.
[0074] Candida tropicalis (ATCC750), Candida glabrata (ATCC15126), Candida krusei (ATCC1182) were formed in static models. In the static model, the resuspended fungal cells were diluted to 4-6 × 10 in RPMI-1640 medium 6 CFU / mL used. PVC strips and diluted strains were co-incubated at 37 °C for 4 h as previously described to facilitate initial cell adhesion. Afterwards, the PVC catheter piece was taken out with sterile tweezers, washed gently with PBS to remove non-adherent cells, put into a 50 mL centrifuge tube, and incubated at 37°C for 20 h.
[0075] Detect the EPS production of water extraction method and cation exchange resin (pH5.8, pH6.8, pH7.8). Add 6 mL of NaH to the catheter piece after film formation 2 PO 4 -Na 2 HPO 4 Ionic buffer solution (PH5.8, PH6.8, PH7.8), vortex for 1min, mild and ...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Embodiment 3: A kind of extraction method of candida fungus biofilm extracellular matrix
[0081] A method for extracting the extracellular matrix of a Candida fungus biofilm, comprising the following steps:
[0082] The first step: first soak the catheter piece with ethanol to make it sterile, then take out the catheter piece and soak it in sterile water, then activate the bacteria of the genus Candida, and adjust the concentration of the bacteria solution to 1×10 6 CFU / mL;
[0083] The second step: place the catheter piece in the bacterial solution, and then incubate on a shaking table to make the bacteria adhere to the catheter piece, then take out the catheter piece and place it in a centrifuge containing 1640 medium Incubate the tube at a constant temperature of 37°C for 20-28 hours to form a biofilm;
[0084] Step 3: Take out the catheter piece obtained in the second step, and then put it in disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer or Tris-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com