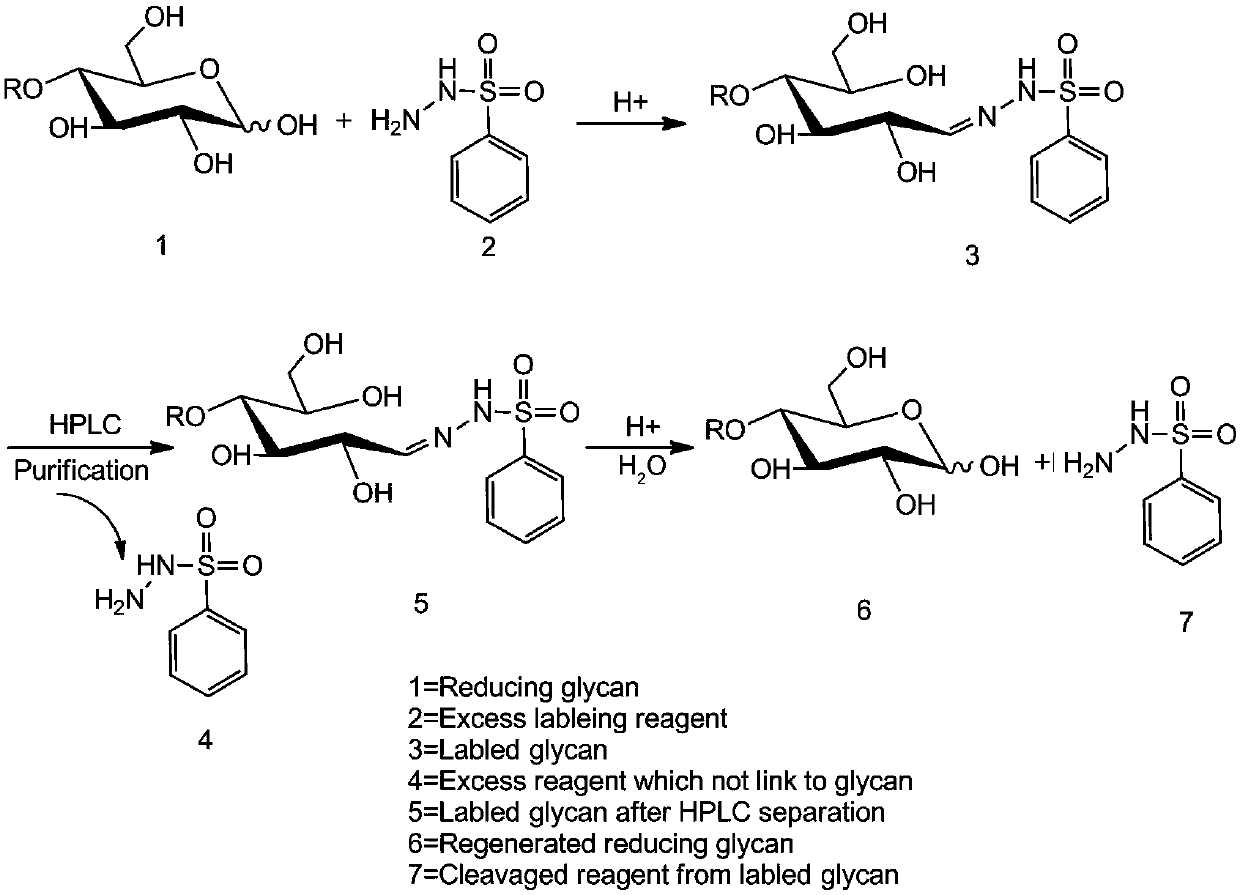
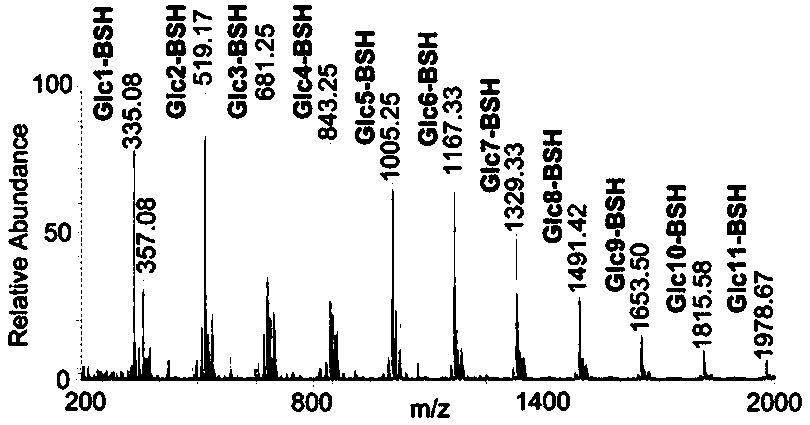
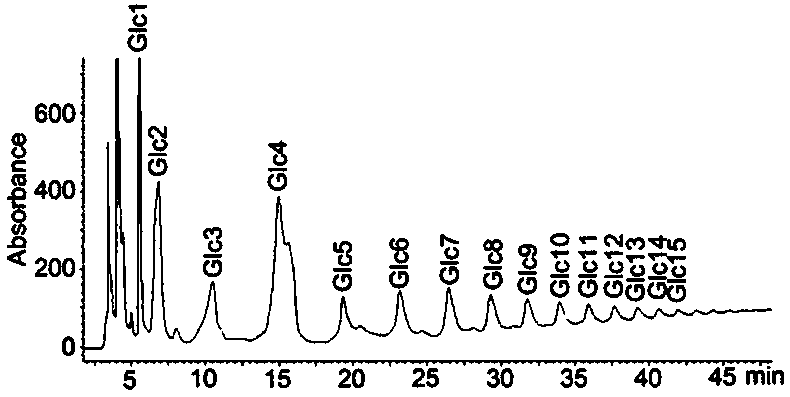
Method for regenerating reducing sugar from hydrazine chromophoric reagent derivative of reducing sugar
A chromogenic reagent and derivative technology, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of high yield of by-products, harsh reaction conditions, low yield of reducing sugar chains, etc., and achieves high recovery rate, mild reaction and simple operation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Example 1: Regeneration of free reduced maltooligosaccharide monomers from BSH derivatives of maltodextrin
[0064] Specific steps are as follows:
[0065] (1) Take 5 mg of standard maltodextrin, take BSH (10 mg) according to the molar ratio of not less than 1:10, and dissolve maltodextrin and BSH in 1 mL of weak acid aqueous solution of organic solvent (500 μL ethanol + 50 μL acetic acid + 450 μL Water=1mL, containing 50% ethanol and 5% acetic acid), shake well, react at 60°C for 45min, then concentrate and dry.
[0066] (2) The obtained sample was dissolved in water, then extracted with an organic solvent (dichloromethane), centrifuged, and the supernatant was taken, and repeated 3-5 times, and finally the obtained supernatant was concentrated and dried.
[0067] (3) Dissolve the obtained sample with acetonitrile, and then perform HILIC-HPLC separation. The liquid phase conditions are: when performing HILIC-HPLC separation, use a 4.6mm×250mm TSK-GEL Amide-80 column, ...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Example 2: Regeneration of free reduced maltooligosaccharide monomers from TSH derivatives of maltodextrin
[0071] Specific steps are as follows:
[0072] (1) Take 5 mg of standard maltodextrin, take TSH (10 mg) according to the molar ratio of not less than 1:10, dissolve maltodextrin and TSH in 1 mL of weak acid aqueous solution of organic solvent (500 μL ethanol + 50 μL acetic acid + 450 μL Water=1mL, containing 50% ethanol and 5% acetic acid), shake well, react at 60°C for 45min, then concentrate and dry.
[0073] (2) The obtained sample was dissolved in water, then extracted with an organic solvent (dichloromethane), centrifuged, and the supernatant was taken, and repeated 3-5 times, and finally the obtained supernatant was concentrated and dried.
[0074] (3) Dissolve the obtained sample with acetonitrile, and then perform HILIC-HPLC separation. The liquid phase conditions are: when performing HILIC-HPLC separation, use a 4.6mm×250mm TSK-GEL Amide-80 column, the ...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Example 3: Regeneration of free reduced maltooligosaccharide monomers from BZH derivatives of maltodextrin
[0078] Specific steps are as follows:
[0079] (1) Take 5 mg of standard maltodextrin, take BZH (10 mg) according to the molar ratio of not less than 1:10, dissolve maltodextrin and BZH in 1 mL of weak acid aqueous solution of organic solvent (500 μL ethanol + 50 μL acetic acid + 450 μL Water=1mL, containing 50% ethanol and 5% acetic acid), shake well, react at 60°C for 45min, then concentrate and dry.
[0080] (2) Dissolve the obtained sample in water, then pass through C18 and PGC solid-phase extraction column to purify the sample, first pass through the C18 column, the specific operation is: 3mL acetonitrile activation, 12mL water balance, sample loading, then 0%, 5%, 10%, 15% acetonitrile washes 3mL every 5% gradient to remove impurities, 3mL 20% acetonitrile elutes the sugar chain, and then passes through the PGC column. The specific operation is: 3mL aceto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com