Identification and application of IAA in secondary metabolite of streptomyces roseoflavus strain NKZ-259
A technology of NKZ-259, Streptomyces flavus, applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of non-compliance with mass production, time-consuming consumables, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Embodiment 1 Streptomyces roseoflavum NKZ-259 produces the gene prediction of IAA
[0046] Inoculate about 1 cm2 of bacteria block from Streptomyces roseoflavum NKZ-259 strain cultured on MS solid medium for 7 days and inoculate in liquid medium YEME, culture at 28°C and 200 rpm for 2 days, and use GENMED Streptomyces bacteria genomic DNA to purify The kit extracts the genomic DNA of the strain.
[0047] The key gene iaaM (Genbank accession No.: NP-625735) of the model bacteria Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) IAA biosynthesis was found from Genbank, and primers were designed according to the iaaM gene:
[0048] iaaM-3F (5'-3'): GCCGATCACCATGTTCGGGC (SEQ ID NO: 1)
[0049] iaaM-3R (5'-3'): CTAGTCCTCGGGGAGTTCCA (SEQ ID NO: 2)
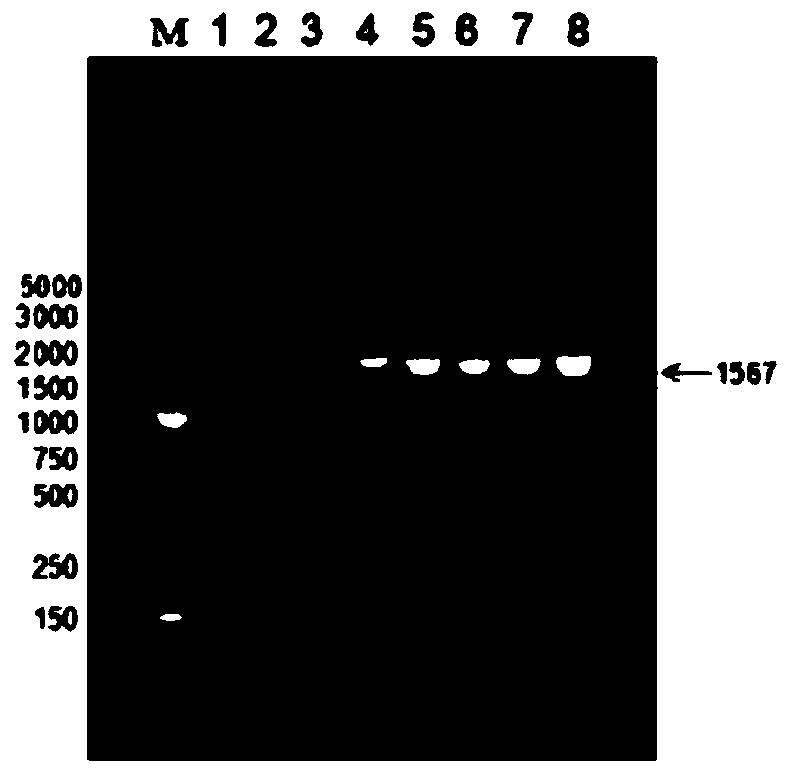
[0050] Using Streptomyces roseoflavum NKZ-259 (preservation number is CGMCC No.13416) DNA as a template to amplify the full length of the iaaM gene, the amplified gene sequence is shown in sequence 3, such as figure 1 shown. The amplified gene was ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Detection of IAA in embodiment 2 Streptomyces roseus flavum NKZ-259
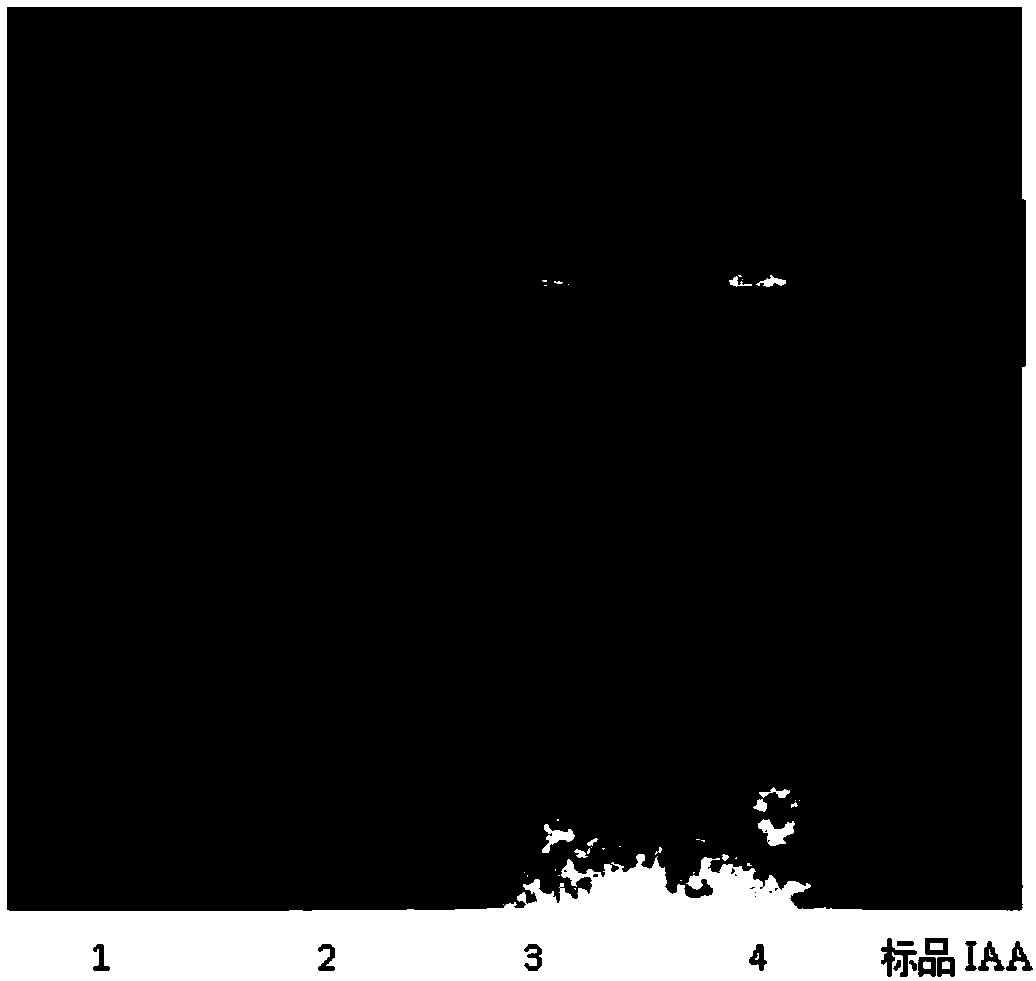
[0052] (1) TLC method to detect the presence of IAA in the secondary metabolites of Streptomyces roseoflavus NKZ-259
[0053] TSB fermentation medium: tryptone 15g, soybean peptone 5g, sodium chloride 5g, L-tryptophan 5.0g, water 1L, adjust pH to 7.2±0.2
[0054] (1) Streptomyces roseoflavum NKZ-259 was spread and inoculated onto MS medium with a sterile toothpick, and cultured at 28° C. in the dark for 7 days;
[0055] (2) Use a scalpel to inoculate a 1cm2 bacterial block into the fermentation medium, and ferment with shaking for 6 days (28°C, 200rpm);
[0056] (3) After filtering the obtained fermentation broth with filter paper, adjust the pH to 2 with 5N HCL, extract twice with ethyl acetate: fermentation broth = 1:1, combine the ethyl acetate phases, and steam at 40°C in a rotary evaporator. Dry and dissolve with a small amount of methanol.
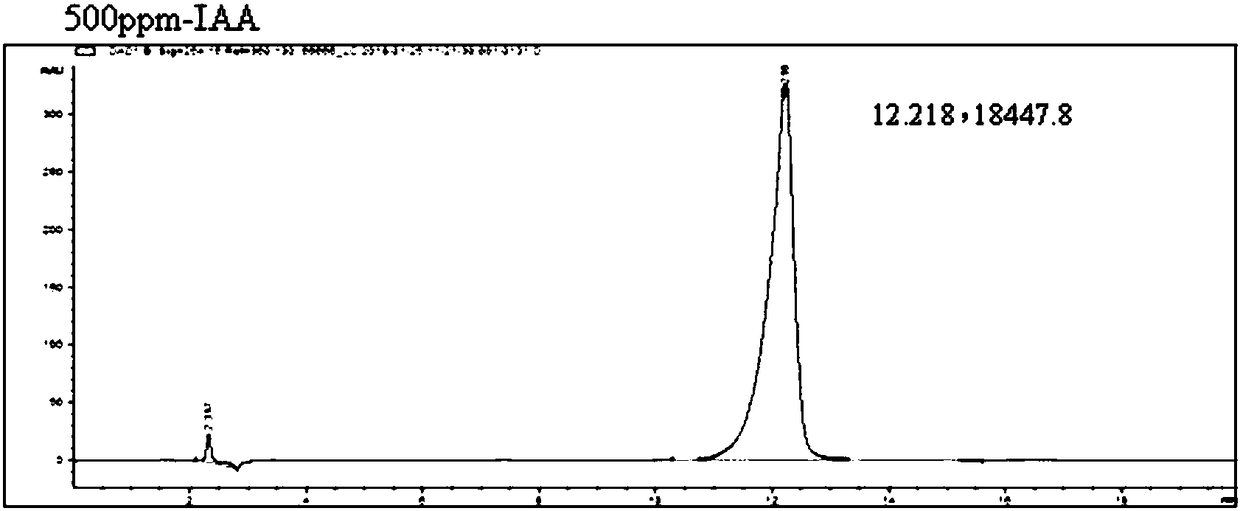
[0057] (4) The sample dissolved in methanol is sepa...
Embodiment 3
[0064] IAA bioactivity detection in embodiment 3 Streptomyces roseus flavum NKZ-259
[0065] Pepper Growth Promoting Test
[0066] (1) The test was planted in plug trays. The matrix was configured with nutrient soil and vermiculite at a ratio of 3:1, placed in the plug trays, and the nutrient soil was poured thoroughly. Then 2-3 pepper seeds were sprinkled in each hole, and then a small amount of Cover the seeds with nutrient soil, spray an appropriate amount of water, and cover with plastic wrap.
[0067] (2) Remove the plastic wrap when the pepper seedlings emerge from the soil and grow 2 cotyledons. The test was divided into three groups. The test group was irrigated with 50-fold and 100-fold diluted NKZ-259 fermentation broth, and the control group was irrigated with clear water. Each treatment had 20 seedlings, and three repetitions were set. Cultivate in a greenhouse at 25°C and a relative humidity of 60%.
[0068] (3) When the pepper seedlings grew 2 true leaves, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com