Method for recycling ceramic-grade iron phosphate for multi-metal dangerous waste
A hazardous waste and polymetallic technology, applied in the direction of non-metallic elements, chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, etc., can solve the problems of complex components, bacterial inactivation, and great harm, and achieve simple equipment and operation methods and high added value , low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] (1) Raw material analysis
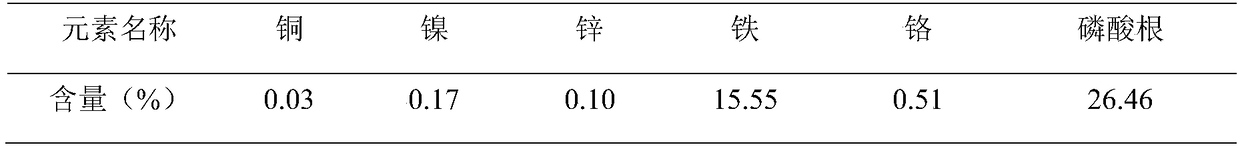
[0026] Take phosphating wastewater to treat sludge and Fe-containing 3+ Sludge is calculated as Fe by mass percentage 3+ : PO 4 3- =1.2~1.5 ingredients, mix uniformly, analyze its metal content with flame atomic absorption spectrophotometer, analyze phosphate radical content with visible spectrophotometry, analyze water content with weight loss method, the results are shown in Table 1, the present embodiment Fe 3+ : PO 4 3- = 1.24.
[0027] Table 1 Sludge composition list
[0028]
[0029] (2) Acid leaching experiment
[0030] Take 500g of the above-mentioned mixed sludge in a 2000mL beaker, add 1000mL of water, put mechanical stirring into the beaker, adjust the rotating speed to 300r / min to make the sludge slurry, and then slowly add 98% sulfuric acid to the slurry, and the sludge gradually Dissolve, add sulfuric acid until the sludge no longer reacts, continue to stir for 30 minutes, and keep the pH value at about 0.5 to complet...
Embodiment 2
[0045] (1) Raw material analysis
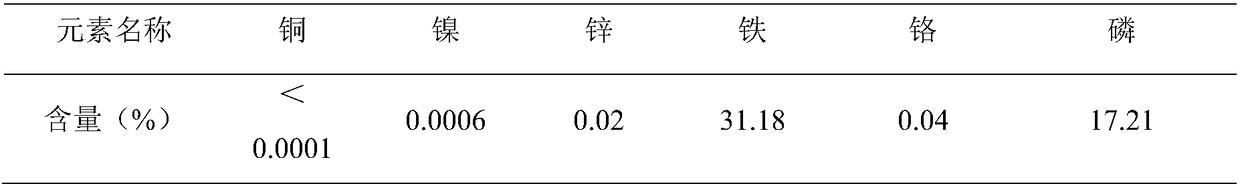
[0046] Take phosphating wastewater to treat sludge and Fe-containing 3+ Sludge is calculated as Fe by mass percentage 3+ :PO 4 3- =1.2~1.5 ingredients, mix uniformly, analyze its metal content with flame atomic absorption spectrophotometer, analyze phosphate radical content with visible spectrophotometry, analyze water content with weight loss method, the results are shown in Table 4, the present embodiment Fe 3+ :PO 4 3- = 1.45.
[0047] Table 4 Sludge composition list
[0048]
[0049] (2) Acid leaching experiment
[0050] Take 500g of the above-mentioned mixed sludge in a 2000mL beaker, add 1000mL of water, put mechanical stirring into the beaker, adjust the rotating speed to 300r / min to make the sludge slurry, and then slowly add 98% sulfuric acid to the slurry, and the sludge gradually Dissolve, add sulfuric acid until the sludge no longer reacts, continue to stir for 30 minutes, and keep the pH value at about 0.6 to completely ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com