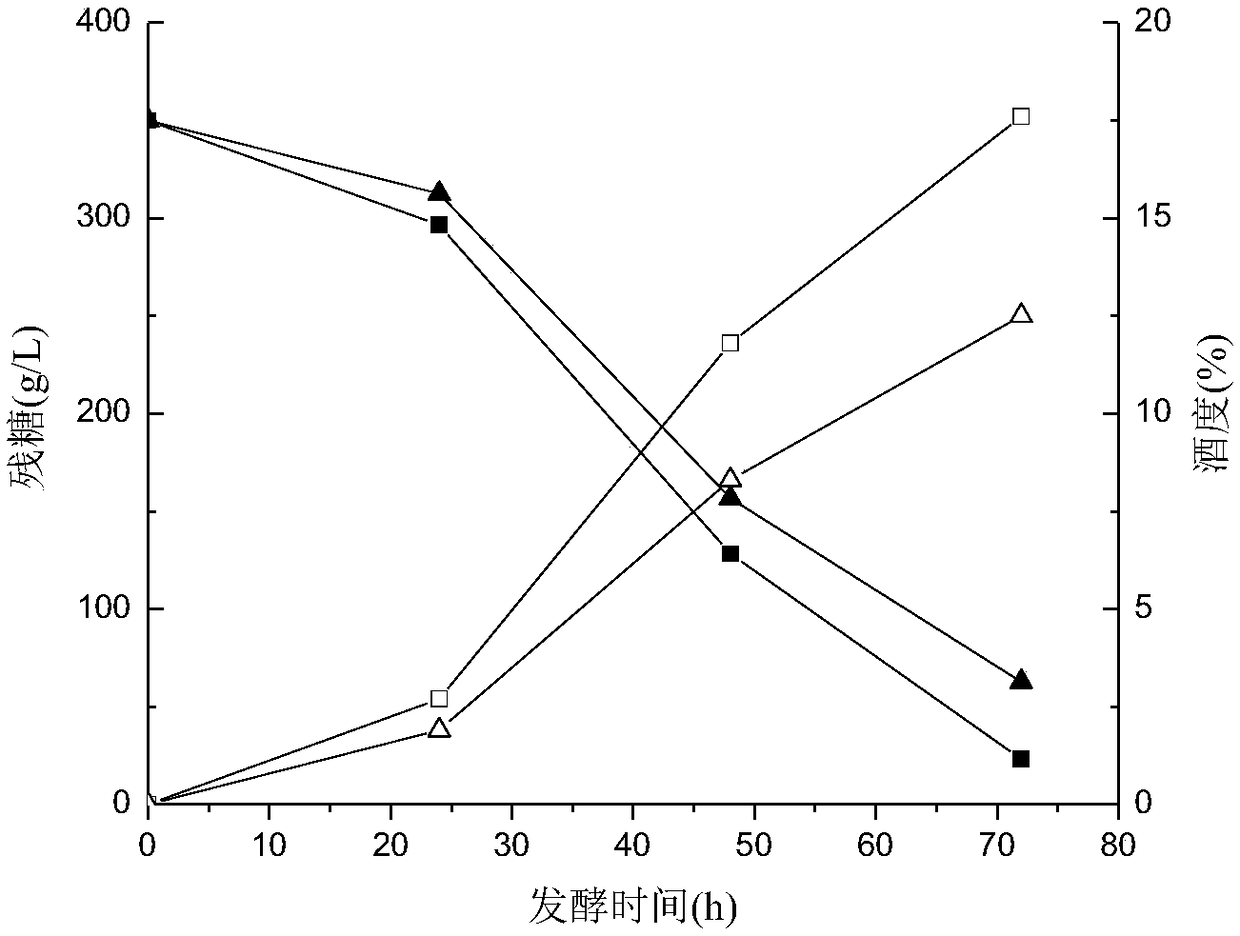
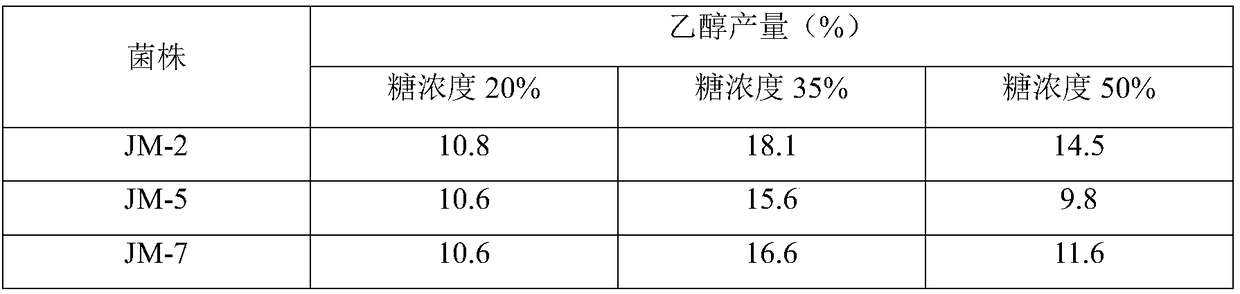
Sugar-tolerant ethanol-resistant brewing yeast and application thereof
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and ethanol resistance, applied in the field of winemaking, can solve the problems of yeast fermentation inhibition, inhibition, yeast intolerance, etc., and achieve the effects of improving ethanol production capacity, high application value, and improving raw material utilization rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Example 1 strain screening
[0022] 1. Primary screening of strains
[0023] Materials: Sichuan Jiannanchun (Group) Co., Ltd. distiller's yeast.
[0024] ①Wort preparation: Take a certain amount of barley malt, crush it, add water 4 times the amount of malt, keep warm and saccharify in a water bath at 55-60°C, and stir continuously. After 3-4 hours, until the reaction between the saccharification liquid and the iodine liquid until blue. After boiling, filter, dilute the filtrate to 6°Bé, add a certain amount of lactic acid, and sterilize at 115°C for 20 minutes for later use.
[0025] ② Take 10g of distiller's yeast in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask filled with 100mL of sterile water and glass beads, place it on a bed, shake it at room temperature for 30min, and let it stand still. Take 10mL of the supernatant into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 90mL of wort, and incubate at 200rpm / min at 28°C for 24h in a squeeze bed.
[0026] ③Take the bacterial solution cultivated...
Embodiment 2
[0040]Embodiment 2 Yeast strain identification
[0041] Utilize the automatic microbial identification instrument of American Biolog Company, Biolog Company's original carbon source utilization method, use the metabolism of microorganisms to different carbon sources, cooperate with tetrazole chromogenic substances (such as TTC, TV), and immobilize the reaction substrate in 96 wells On the plate (well A1 is the negative control), inoculate the bacterial suspension and incubate for a certain period of time, and detect the color change (absorbance) caused by the reaction between the oxidoreductase produced during the metabolic process of microbial cells using different carbon sources and the chromogenic substance. And the difference in turbidity (turbidity) due to microbial growth, compared with the standard strain database, the final identification result can be obtained, as shown in Table 3.
[0042] The test steps are as follows:
[0043] ① Cultivate the yeast to be identifie...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3 Morphological characteristics and biological characteristic identification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain of the present invention
[0058] 1. Observation of colony and bacterial morphology
[0059] Streak inoculated the activated bacteria on the wort plate medium, cultivated at 28°C, and observed the colony morphology; dipped a little bacteria with an inoculation loop, and observed the morphology of the bacteria under a field emission environment scanning electron microscope (see figure 1 ).
[0060] The observation results are as follows: the bacterium is oval in shape, budding and reproducing; the colony is milky white, smooth, moist and opaque.
[0061] 2. Sugar fermentation experiment
[0062] 12.5% of the sugar-free bean sprouts juice base solution was divided into test tubes containing Duchenne tubes, sterilized at 0.1 MPa for 15 minutes, and the tested sugars (glucose, sucrose, galactose, maltose) were prepared into 10% The solution was boi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com