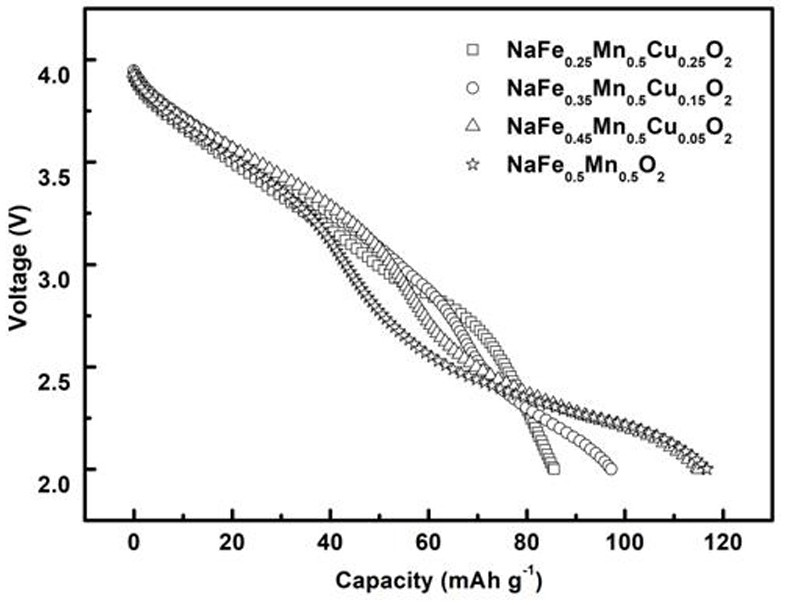
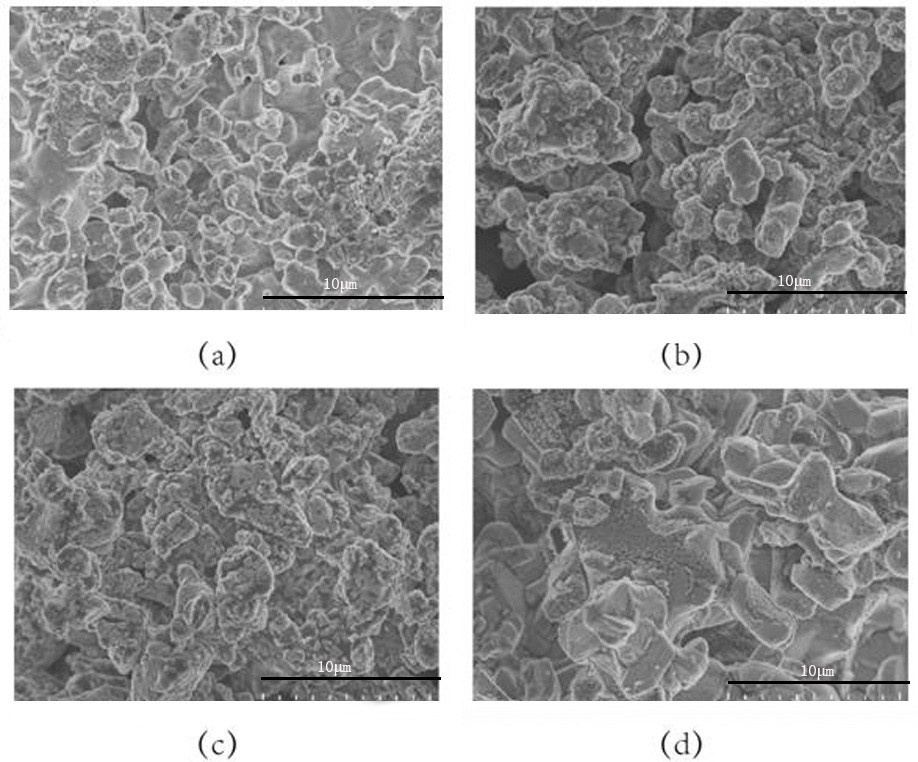
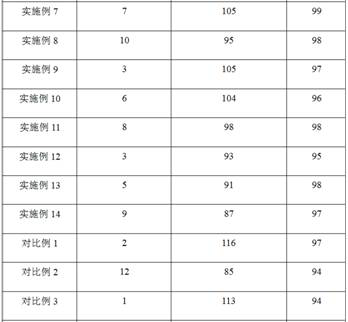
A class of large particle sodium ion battery positive electrode material and method for increasing material particle size
A technology for sodium ion batteries and cathode materials, which is applied in the fields of energy materials and electrochemical power sources, can solve the problems of harsh synthesis conditions, difficulty in realizing large-scale production, and complicated preparation processes, and achieves simple and easy-to-implement preparation processes and excellent electrochemical Stability, rich source of raw materials and a wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] (1) Preparation of 5% Cu-doped NaFe 0.45 mn 0.5 Cu 0.05 o 2 Cathode material.
[0030] Weigh Na according to the corresponding proportion 2 CO 3 , Fe 2 o 3 , Mn 2 o 3 , CuO ball milled for 24 h, pressed into a disc with a diameter of 10 mm under a pressure of 10 MPa, and calcined at 1000 °C for 12 h to obtain a sample powder.
[0031] (2) Preparation of 5% copper-doped NaFe 0.45 mn 0.5 Cu 0.05 o 2 Composite cathode
[0032] Mix the prepared positive electrode material with the conductive additive Super-P and the binder polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) at a mass ratio of 7:2:1, and add an appropriate amount of N-methylpyrrolidone, after pulping and smearing , drying and other processes to obtain the composite positive electrode.
[0033] (3) Assembling sodium-ion batteries
[0034] Assemble the sodium-ion battery with the composite positive electrode prepared above and the sodium negative electrode, and select carbonate electrolyte (1M NaClO 4 EC / PC (volum...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) Preparation of 15% Cu-doped NaFe 0.35 mn 0.5 Cu 0.15 o 2 Positive electrode material (concrete steps are the same as embodiment 1);
[0039] (2) Preparation of 15% copper-doped NaFe 0.35 mn 0.5 Cu 0.15 o 2 Composite positive electrode (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1);
[0040] (3) Assembling a sodium-ion battery (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1);
[0041] (4) Sodium ion battery test (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1).
Embodiment 3
[0043] (1) Preparation of 5% Cu-doped NaNi 0.45 co 0.5 Cu 0.05 o 2 Cathode material (raw material is Na 2 CO 3 , NiO, Co 2 o 3 , CuO, all the other steps are with embodiment 1);
[0044] (2) Preparation of 5% copper-doped NaNi 0.45 co 0.5 Cu 0.05 o 2 Composite positive electrode (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1);
[0045] (3) Assembling a sodium-ion battery (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1);
[0046] (4) Sodium ion battery test (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com