Electrochemical oxidation treatment device and method of low-salt wastewater through micro-fluid reactor
A technology of microfluidic reactor and oxidation treatment, applied in chemical instruments and methods, sterilization/microdynamic water/sewage treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of increasing investment cost, secondary pollution, etc., and achieve improvement Efficiency, prolonging life, and reducing the effect of plate spacing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1, a certain degreasing agent production enterprise waste water treatment:
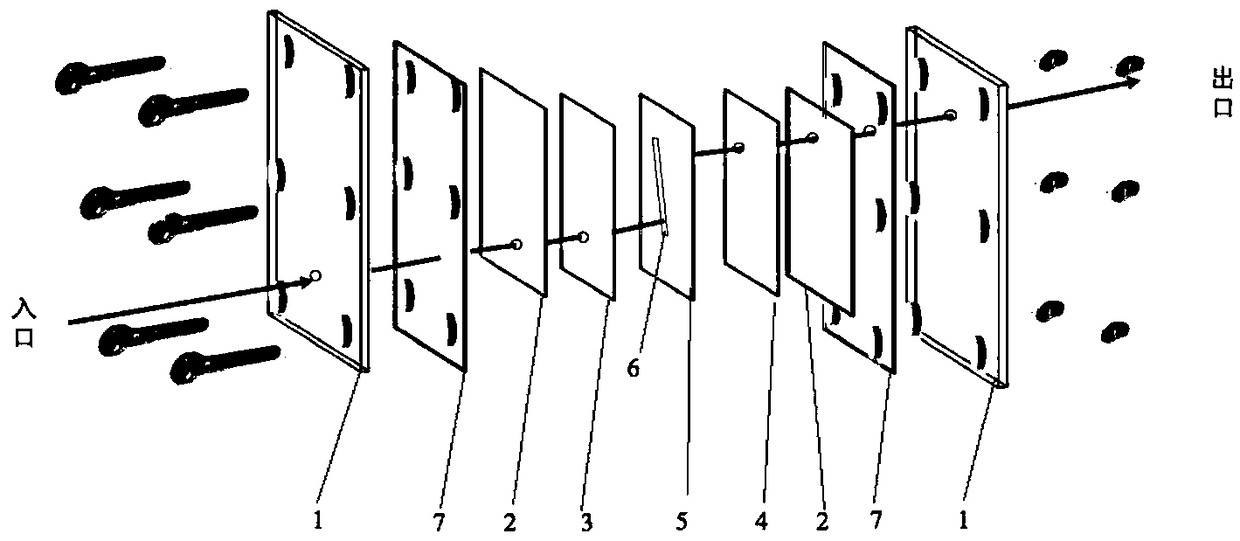
[0047] The effluent from the secondary sedimentation tank of the degreasing agent manufacturer was treated with microfluidic electrochemical oxidation. The initial total organic carbon content of the wastewater was 210±15mg / L, and the conductivity was 1.42ms / cm. In step 1, direct electrochemical oxidation was selected as the electrolytic process. The boron diamond electrode is used as the anode, the nickel is used as the cathode, and the area of the reaction hole 6 is 3.75cm 2 , that is, the plate reaction area is 3.75cm 2 , the thickness of the isolation film layer 5 is 50 μm, that is, the distance between the plates is 50 μm, the current intensity is 20mA, 60mA, 100mA and 200mA, and the corresponding current density is 5.3~53mA / cm 2 , the organic matter removal effect is as figure 2 As shown, the power consumption required for the reaction varies with the injection flow rate a...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2, a certain chemical enterprise wastewater treatment:
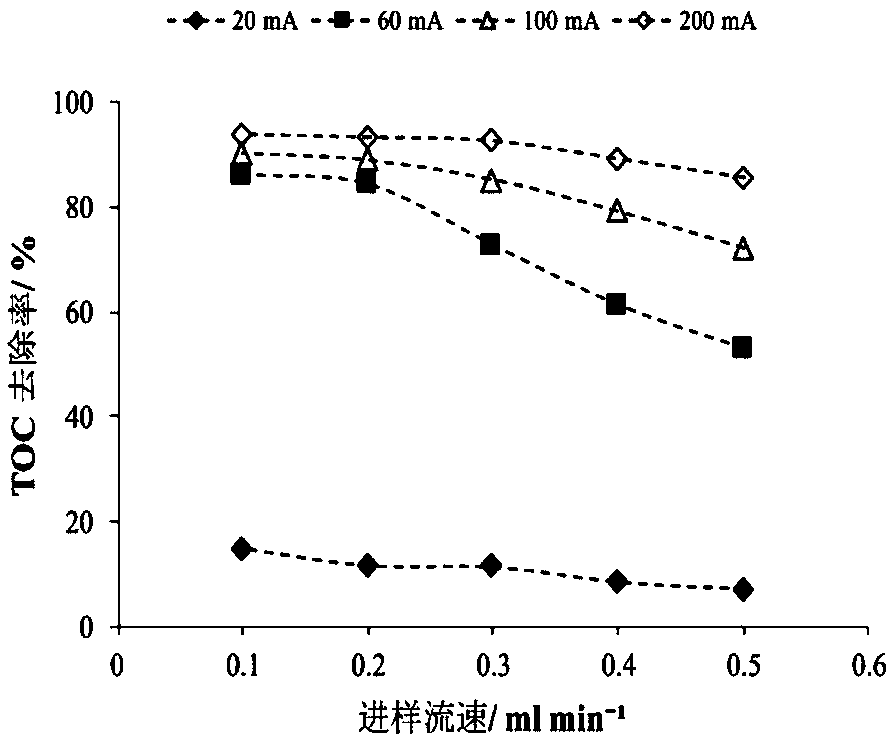
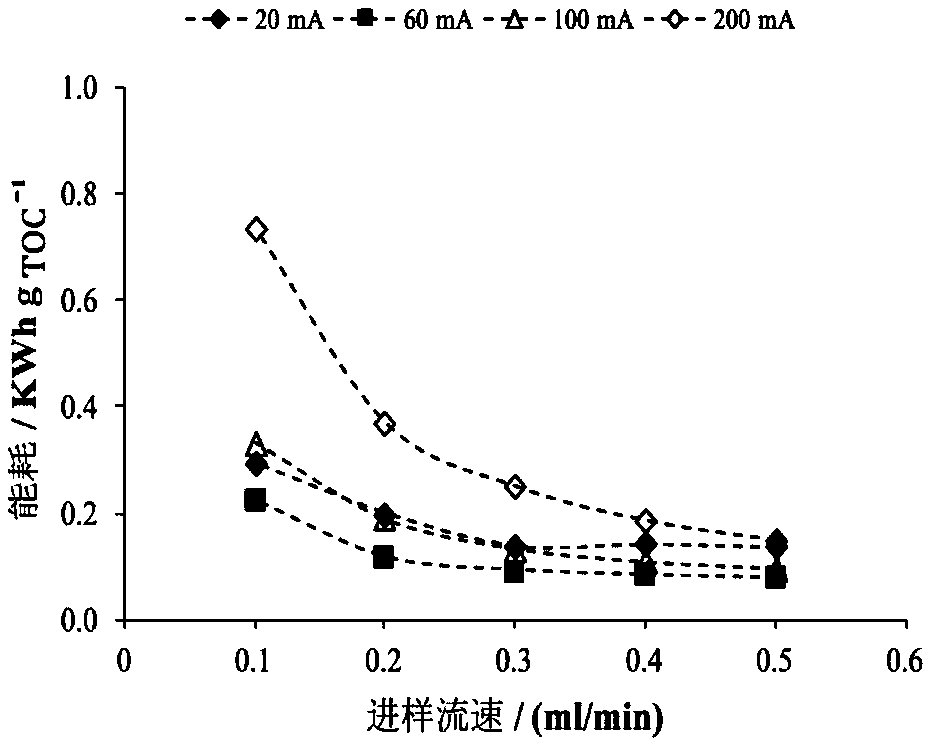
[0050] The chemical company is mainly engaged in the development and production of surfactants, pharmaceutical excipients, and synthetic lubricating oil. The initial total organic carbon content of wastewater is 4500±150mg / L, and the conductivity is 5.42ms / cm. The electrolysis process adopts direct electrochemical oxidation and electro-fen The anode material is a boron-doped diamond electrode, the cathode material is a graphite electrode, and the reaction area of the plate is 3.75cm 2 , the distance between the plates is 50μm, and about 0.5mmol / L of Fe is added to the wastewater 2+ , the current intensity is 20mA, 60mA, 100mA and 200mA respectively, corresponding to the current density of 5.3 ~ 53mA / cm 2 , the organic matter removal effect and the power consumption required for the reaction are shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5 .
[0051] Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that by adjusting the cu...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3, Wastewater Treatment of a Food Processing Enterprise
[0053] After testing the waste water of the food processing enterprise, the initial total organic carbon content was 120±5mg / l, the main component was maleic acid, and the conductivity was about 3.8ms / cm. The indirect electrochemical oxidation process was selected according to the effective components in the waste water. Anode material DSA, cathode nickel, plate spacing 75μm, reaction area 3.75cm 2 . Current intensity 10mA~100mA (current density 2.7mA / cm 2 -27mA / cm 2 ), the injection flow rates were 0.5mL / min, 0.3mL / min, and 0.1mL / min, respectively. Under the conditions of injection flow rate of 0.3mL / min, current intensity of 100mA, injection flow rate of 0.1mL / min, and current intensity of 50 and 100mA, the removal efficiency of organic matter can reach more than 80%, and the energy consumption per unit mass of organic carbon is 0.24±0.06kW h / gTOC, such as Figure 6 and Figure 7 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com