Application of als mutant protein and its gene in plant breeding based on gene editing technology
A gene editing and mutation technology, applied in the fields of application, plant peptides, plant products, etc., can solve the problems of inability to create variant types, heavy workload, unsatisfactory results, etc., and achieve the effect of improving breeding efficiency and speeding up the breeding process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Embodiment 1: Process of obtaining rice mutants resistant to imidazolinone herbicides (imazethapyr)
[0068] 1. Cloning and target site design of Nanjing 9108 ALS gene
[0069] Referring to the CTAB method of Murray et al., the genomic DNA of Nanjing 9108 was extracted (Murray M G, et al., Nucleic Acids Research, 1980, 8(19):4321-4326). Genomic DNA was amplified by PCR with primers ALS5-F: TCGCCCAAACCCAGAAACCC, ALS5-R: CTCTTTATGGGTCATTCAGGTC, and the amplified products were sent to Yingwei Jieji (Shanghai) Trading Co., Ltd. for sequencing. The sequencing results were compared with the NCBI (https: / / blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / Blast.cgi) database for Blast analysis, and it was found that the sequence of the ALS coding region of Nanjing 9108 was the same as that of the reference genome rice Nipponbare.
[0070] According to the ALS gene sequence of Nanjing 9108, the CRISPR-GE website (http: / / skl.scau.edu.cn / targetdesign / ) was used to predict, and 5'-TCCTTGAATGCGCCCCCACT-3' wa...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Embodiment 2: ALS gene cloning of rice mutant resistant to imidazolinone herbicides
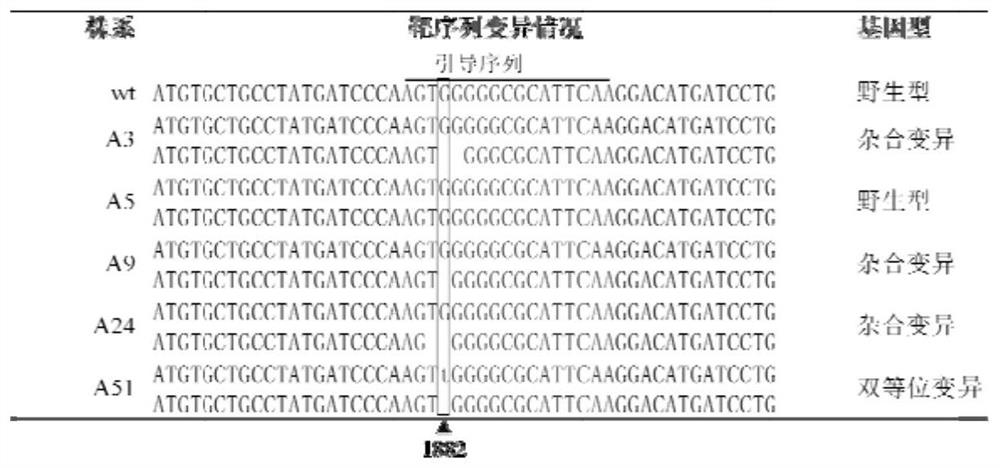
[0105] To the T of the A51 strain of the above-mentioned embodiment 1 1Generation 18 individual plants were numbered, their leaves were taken, and genomic DNA was extracted, and PCR amplification was performed with specific primers ALS-F5'-TCGCCCAAACCCAGAAACCC-3' and ALS-R 5'-CTCTTTATGGGTCATTCAGGTC-3' for the full length of the ALS gene . The amplified products were sent to Yingwei Jieji (Shanghai) Trading Co., Ltd. for sequencing. Comparing the sequencing results with the wild-type ALS gene of Nanjing 9108, it was found that the single plants numbered 1-9, 11, 14, 16 and 17 had a homozygous mutation from G to T at the 1882nd base; Single plants of 13 and 15 had biallelic variation, one of the alleles was the mutation from G to T at the 1882nd base, and the other allele was the deletion of the G base at the 1882nd position; no 1882nd base was obtained Homozygous single plants with b...
Embodiment 3
[0108] Example 3 T-DNA elimination of rice mutants resistant to imidazolinone herbicides
[0109] The binary T-DNA carrier for direct editing ALS gene constructed by the present invention, the T-DNA involved in the present invention mainly includes the hygromycin phosphotransferase HPT gene and the Cas9 nuclease gene, because the hygromycin phosphotransferase HPT gene and the The main function of the Cas9 gene is to complete the site-directed mutation of the target gene, and these two genes are foreign genes relative to the rice genome. On the one hand, hygromycin is an antibiotic and needs to be deleted. If the Cas9 gene is retained, it may lead to continued editing and other functions; on the other hand, the random insertion of T-DNA may also lead to unexpected gene mutations, so it needs to be cleared after it completes the gene editing task. Through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Nanjing japonica 9108, during the transgenic process, the T-DNA sequence will be ran...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com