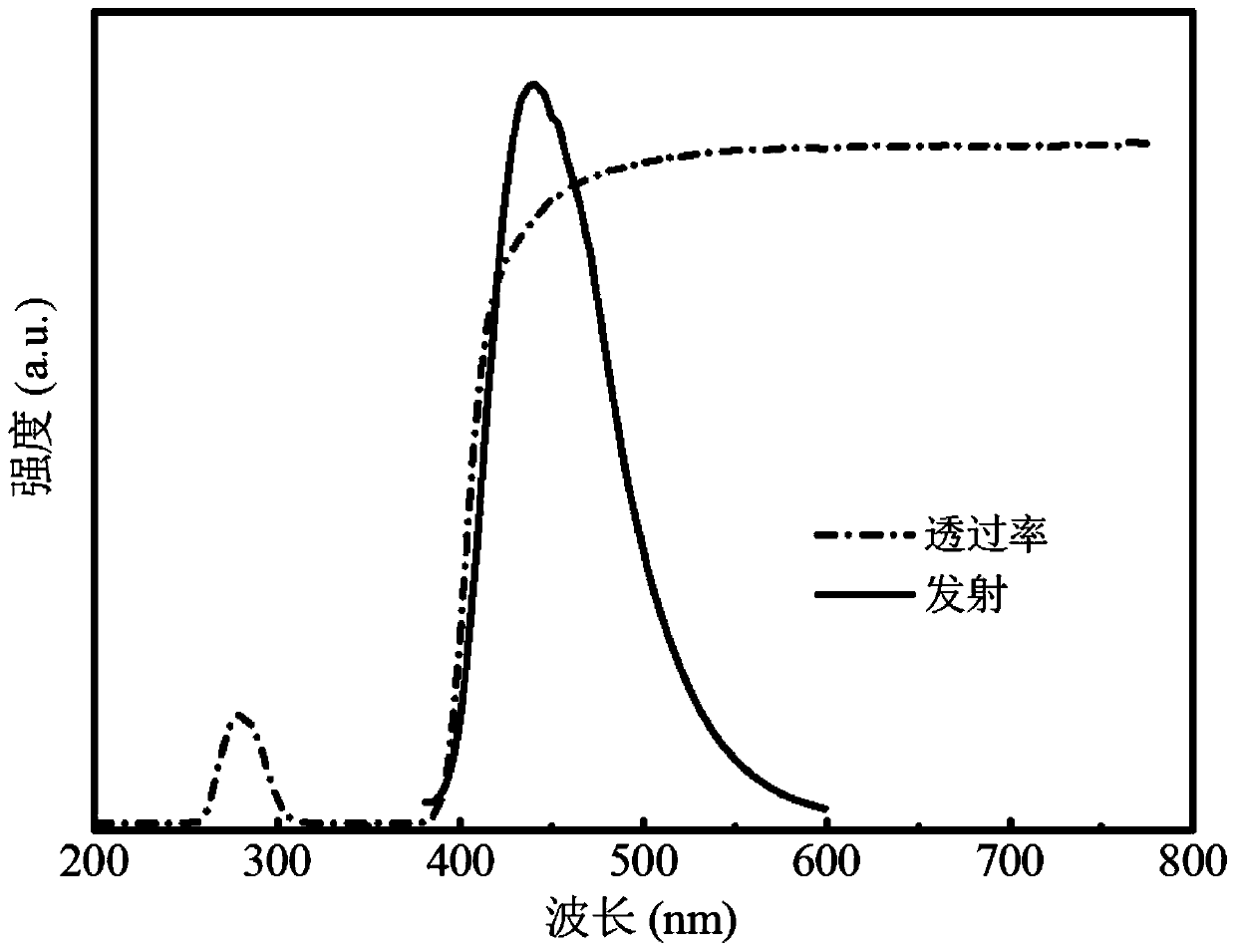
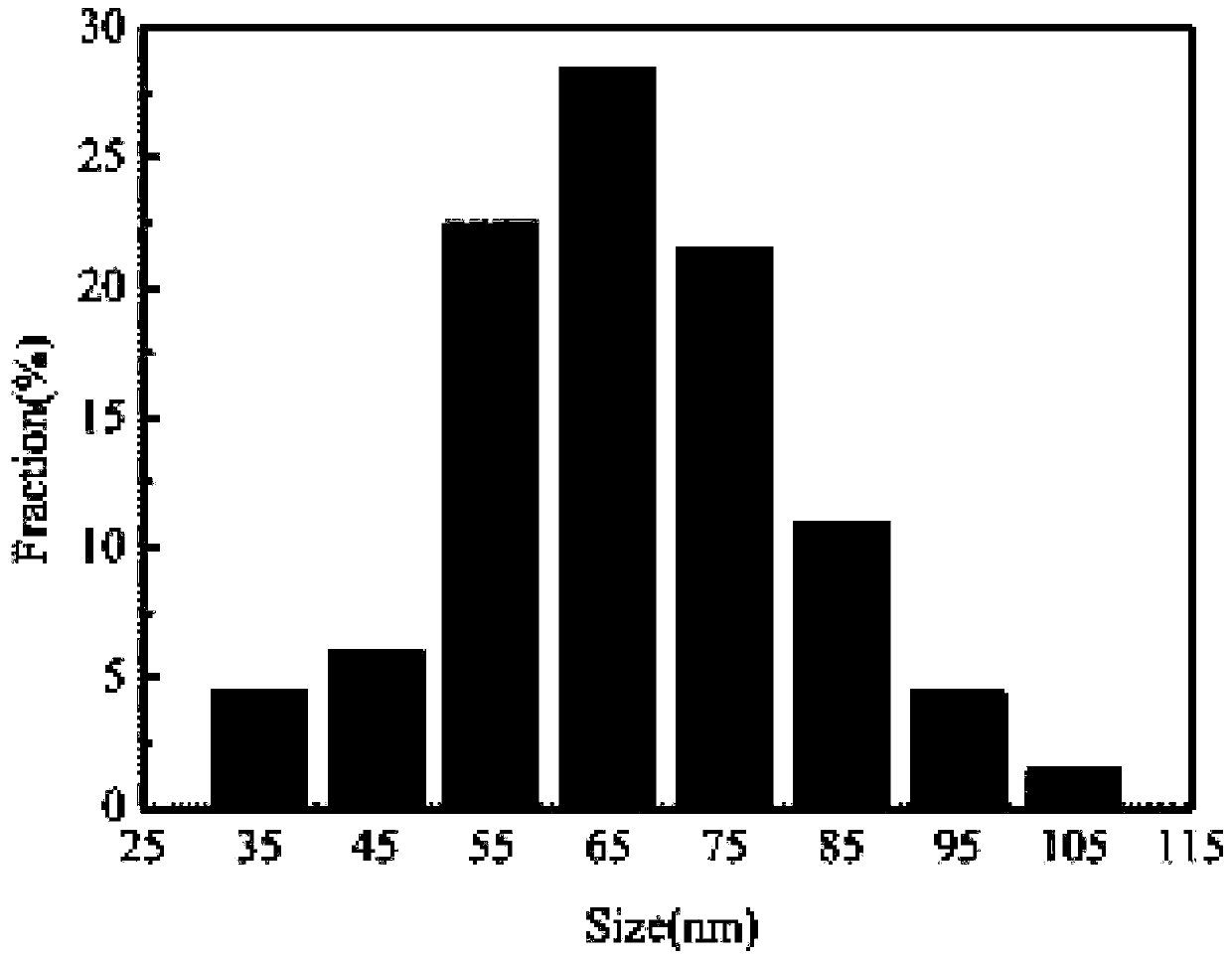
Carbon dot composite nanoparticles, carbon dot/fluoride composite material, preparation method and application
A technology of composite nanoparticles and composite materials, applied in the field of new materials, can solve the problems of easy migration of carbon points, low temperature resistance, complex synthesis methods, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
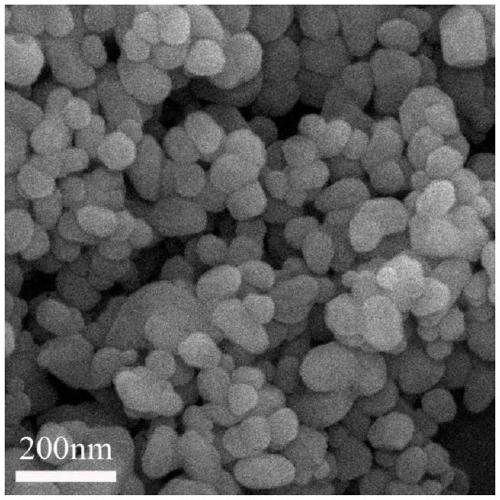
[0050] Example 1 Preparation of CDs@CaF 2 composite nanoparticles
[0051] 1. Preparation of fluorescent carbon dots
[0052]Weigh 1g of anhydrous citric acid and dissolve it in 30mL of deionized water, add 1.6mL of ethylenediamine (the mass ratio of anhydrous citric acid to ethylenediamine is 1:1.6), mix well and carry out hydrothermal reaction in an oven at 200°C for 5h , after natural cooling, the reaction solution was taken out, dialyzed at 1000D for 24 hours, the solution in the bag was distilled under reduced pressure and freeze-dried to obtain solid carbon dots (CDs), which were configured into an aqueous solution of carbon dots with a concentration of 0.5 mg / mL for future use.
[0053] 2. CDs@CaF 2 Preparation of Composite Nanoparticles
[0054] Select 11g of anhydrous calcium chloride and 4g of ammonium fluoride as raw materials, add water respectively according to the molar ratio of the two to 1:1.1 to prepare 20mL of solutions A and B for use, and part of the sol...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2 Preparation of CDs@CaF 2 composite nanoparticles
[0061] 1. Preparation of fluorescent carbon dots
[0062] Weigh 1g of anhydrous citric acid and dissolve it in 30mL of deionized water, add 1.6mL of ethylenediamine (the mass ratio of anhydrous citric acid to ethylenediamine is 1:1.6), mix well and carry out hydrothermal reaction in an oven at 200°C for 10h , after natural cooling, the reaction solution was taken out, dialyzed at 1000D for 24 hours, the solution in the bag was distilled under reduced pressure and freeze-dried to obtain solid carbon dots (CDs), which were configured into an aqueous solution of carbon dots with a concentration of 0.5 mg / mL for future use.
[0063] 2. CDs@CaF 2 Preparation of Composite Nanoparticles
[0064] Select 11g of anhydrous calcium chloride and 5.5g of ammonium fluoride as raw materials, and add water respectively according to the molar ratio of the two to 1:1.5 to prepare 20mL of solutions A and B for use, wherein par...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3 Preparation of CDs@CaF 2 composite nanoparticles
[0066] 1. Preparation of Carbon Dots
[0067] Weigh 1g of anhydrous citric acid and dissolve it in 30mL of deionized water, add 1.6mL of ethylenediamine (the mass ratio of anhydrous citric acid to ethylenediamine is 1:1.6), mix well and carry out hydrothermal reaction in an oven at 200°C for 7h , after natural cooling, the reaction solution was taken out, dialyzed at 1000D for 24 hours, the solution in the bag was distilled under reduced pressure and freeze-dried to obtain solid carbon dots (CDs), which were configured into an aqueous solution of carbon dots with a concentration of 0.5 mg / mL for future use.
[0068] 2. CDs@CaF 2 Preparation of Composite Nanoparticles
[0069] Select 11g of anhydrous calcium chloride and 7.5g of ammonium fluoride as raw materials, and add water at a molar ratio of 1:2 to prepare 20mL each of solutions A and B for use. Part of the solvent in solution A is 10mL of 0.5mg / mL car...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com