Application of magnetic nanoparticles in nucleic acid extraction and preparation method thereof
A magnetic nanoparticle and nanoparticle technology, applied in the field of nanomaterials, can solve problems such as low adsorption efficiency, and achieve the effects of reducing preparation cost, simplifying preparation process, and high adsorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
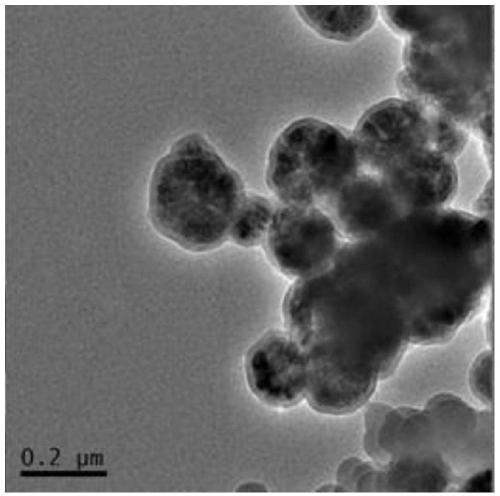
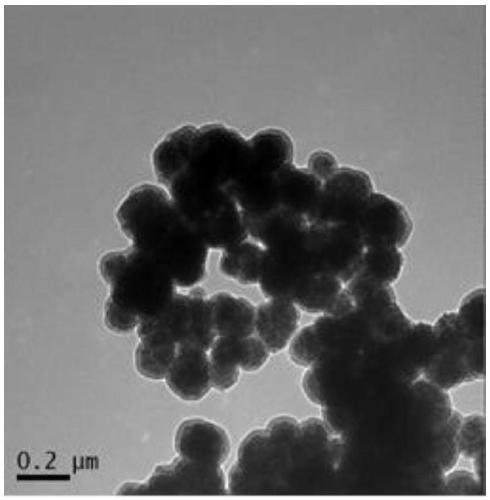
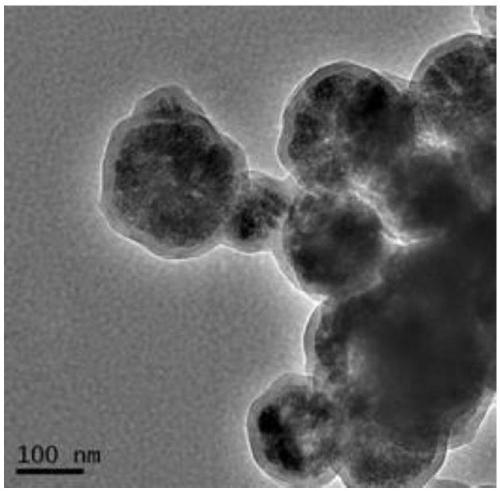
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] This embodiment provides a magnetic nanoparticle (PDA@Fe 3 o 4 ) preparation method, comprising the following steps:
[0059] (1) with FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O as raw material, magnetic Fe synthesized by hydrothermal method 3 o 4 Nanoparticles
[0060] FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O (1.35 g) was dissolved in ethylene glycol (40 mL) and a clear solution was formed by sonication. Then, sodium acetate (3.6 g) and polyethylene glycol 10000 (1.0 g) were added to the solution, and the mixture was vigorously stirred until a homogeneous dark yellow solution was obtained. The solution was put into a polytetrafluoroethylene high pressure reactor and heated at 200° C. for 48 hours. The product was washed several times with ethanol and water, and dried under a nitrogen atmosphere at 60 °C for 10 h to obtain carboxyl-modified magnetic Fe 3 o 4 Nanoparticles, spare;
[0061] (2) Dopamine hydrochloride (200 mg) was mixed with 0.12 g of Tris-HCl buffer (10 mM, pH 8.5) and 100 ml of water to prepare ...
Embodiment 2
[0076] This embodiment provides a nucleic acid extraction kit, including nucleic acid binding solution and magnetic nanoparticles:
[0077] The nucleic acid binding solution includes 20% (w / v) polyethylene glycol, 4mol / L sodium chloride, and the pH of the nucleic acid binding solution is 2;
[0078] The magnetic nanoparticles are the magnetic nanoparticles prepared in Example 1 (PDA@Fe 3 o 4 ).
Embodiment 3
[0080] This embodiment provides a nucleic acid extraction method, using the nucleic acid extraction kit provided in Example 2, the extraction method includes the following steps:
[0081] (1) Cleavage of DNA in human whole blood samples
[0082] ①Put 300μl EDTA-K2 (EDTA dipotassium) anticoagulated blood into a 1.5ml centrifuge tube with a micropipette. Afterwards, 300 μl of sterile deionized water was added to the tube to disrupt the erythrocyte membrane. After repeated mixing several times, the mixture was centrifuged at 12000rpm / min for 3 minutes, and the supernatant was discarded to obtain a precipitate;
[0083] ② Add buffer CL (300 μl) to the precipitate, and mix the mixture several times. The mixture was centrifuged at 12000 rpm / min for 1 minute, and the supernatant was discarded;
[0084] ③ Prepare proteinase K-buffer FG mixture (1:100) (g / V) and add it to the precipitate. Immediately invert the solution slightly several times until the precipitate is completely dis...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Saturation magnetization value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com