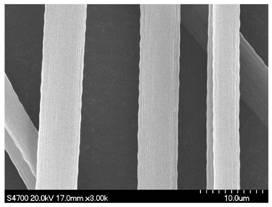
Low-diameter high-strength polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fibers and preparation method thereof
A polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber, polyacrylonitrile spinning technology, applied in the direction of fiber raw material processing, fiber chemical characteristics, synthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paper, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Preparation of polyacrylonitrile spinning solution
[0028]Acrylonitrile, itaconic acid, and methyl acrylate were blended and put into the polymerization reactor at a molar ratio of 93:1:6, and then a dimethyl sulfoxide solvent with a mass ratio of 5.45:1 to the monomer was added, and the initiator was added Azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN), the amount of initiator is 0.2% (molar concentration) of the monomer, stirred and polymerized at a temperature of 55°C and a speed of 40rpm, and the molar ratio of adding and itaconic acid is 0.3:1 when reacting for 10 hours 1,2-ethanediol, after 22 hours of polymerization reaction, a spinning stock solution of an acrylonitrile copolymer with a molecular weight of 120,000 was obtained, and the viscosity of the spinning stock solution at 25°C was measured at 200 poise by a rotational viscometer;
[0029] Spinning solution was obtained after de-monolysis and de-aeration, and the content of acrylonitrile copolymer in the obtained poly...
Embodiment 2
[0045] (1) Preparation of polyacrylonitrile spinning solution
[0046] Acrylonitrile, itaconic acid, and methyl acrylate were blended and put into the polymerization reactor at a molar ratio of 95:1:4, and then dimethyl sulfoxide solvent with a mass ratio of 6.41:1 to the monomer was added, and the initiator was added Azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN), the amount of the initiator is 0.2% (molar concentration) of the monomer, stirred and polymerized at a temperature of 57°C and a speed of 35rpm, and adding itaconic acid in a molar ratio of 0.25:1 after reacting for 10 hours 1,3-propanediol, after 22 hours of polymerization reaction, the spinning stock solution of acrylonitrile copolymer with a molecular weight of 105,000 was obtained, and the viscosity of the spinning stock solution at 25°C was measured as 170 poise by a rotational viscometer;
[0047] Spinning solution was obtained after de-monolarization and defoaming, and the content of acrylonitrile copolymer in the spinning so...
Embodiment 3
[0052] (1) Preparation of polyacrylonitrile spinning solution
[0053] Acrylonitrile, itaconic acid, and methyl acrylate were blended and put into the polymerization reactor at a molar ratio of 94:1:5, and then dimethyl sulfoxide solvent with a mass ratio of 6.81:1 to the monomer was added, and the initiator was added Azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN), the amount of the initiator is 0.18% (molar concentration) of the monomer, stirred and polymerized at a temperature of 53°C and a speed of 30rpm, and adding itaconic acid in a molar ratio of 0.2:1 after reacting for 10 hours 1,3-propanediol, after 22 hours of polymerization reaction, the spinning stock solution of acrylonitrile copolymer with a molecular weight of 133,000 was obtained, and the viscosity of the spinning stock solution at 25°C was measured by a rotational viscometer to be 230 poises;
[0054] Spinning solution is obtained after de-monolarization and degassing, and the content of acrylonitrile copolymer in the spinning...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bulk density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bulk density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com