Method for selectively hydrogenating carbon-4 and carbon-5
A C4C5 selectivity and selectivity technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, hydrogenation hydrocarbons, carbon compound catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of low olefin content and unsuitable use of terpene resin blockers, etc., to achieve The effect of sufficient reaction, increased contact area, and improved conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0020] Preparation of nickel catalyst: firstly, heating the nickel containing 53.0-85.0% by weight and 9.0-20% by weight of silicon to melt, then rapidly solidifying the melt at a cooling rate greater than 1000°C / S, and adding the solidified product under stirring to the Extract the alkali solution with a temperature of 100°C to fully react the silicon in the alloy with the alkali, then decant the liquid, wash the sample with distilled water until the pH value is less than 10, and then add it to an acid solution at 100°C to oxidize the surface of the catalyst Passivation, the sample after pickling is washed with distilled water until the pH is 6.5 to obtain the nickel catalyst, the concentration of the alkali solution is 20% by weight, and the weight ratio of the alloy to the alkali is 1:5; the acid The concentration of the liquid is 20% by weight, and the weight ratio of the alloy to the acid is 1:5, wherein the acid is HNO3.
[0021] Preparation of nickel-molybdenum catalyst...
Embodiment 1
[0023] The material to be hydrogenated is fed into the reactor from the bottom up. The reactor is loaded with a selective hydrogenation catalyst nickel catalyst. The material to be hydrogenated includes C4-C6 dienes and alkynes, and the C4 content is 30 %, the content of carbon five is 85%, and hydrogen is added to the reactor at the same time. The difference is 0.02-0.025MPa. When the pressure difference is large, the contact between hydrogen and the material is insufficient, and the hydrogenation of dienes and alkynes is incomplete; A large amount of reaction with alkynes will cause the loss of olefins, the height of the hydrogenation catalyst will change, and the pressure difference will be adjusted accordingly. The contact time between the material to be hydrogenated and the selective hydrogenation catalyst is 15 minutes. After cooling, the reaction product enters the gas-liquid separation tank for separation treatment , Activated carbon is added to the gas-liquid separati...
Embodiment 2
[0036] In order to verify that another catalyst has the same effect in the method provided by the invention, the reaction conditions in this example are the same as in Example 1, except that the nickel catalyst used in Example 1 is replaced by a nickel-molybdenum catalyst.
[0037] The nickel-molybdenum catalyst is mainly composed of transition metal elements nickel and molybdenum, and has the characteristics of low operating temperature and pressure, high hydrogenation activity, large specific surface area, uniform distribution of active components, and good stability.
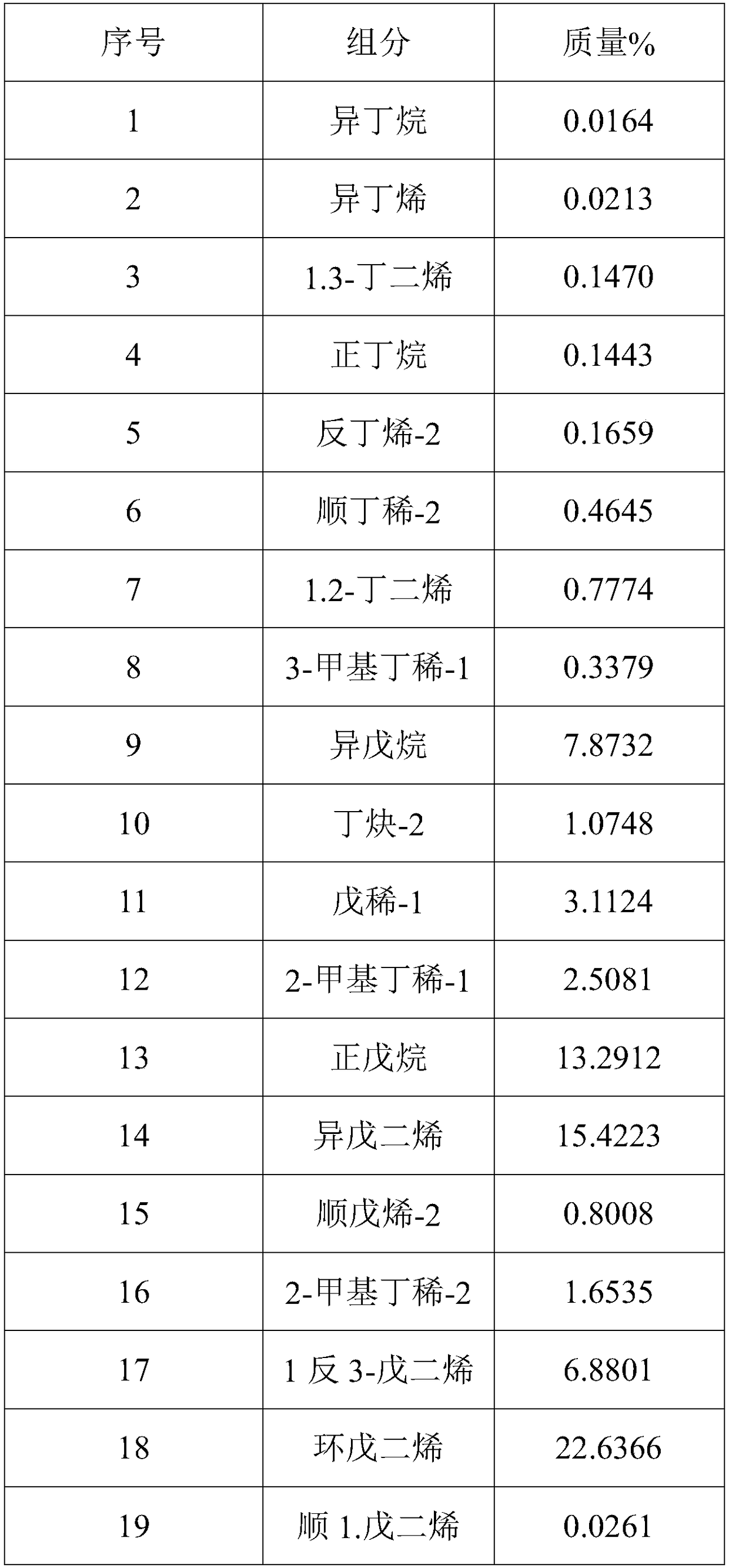
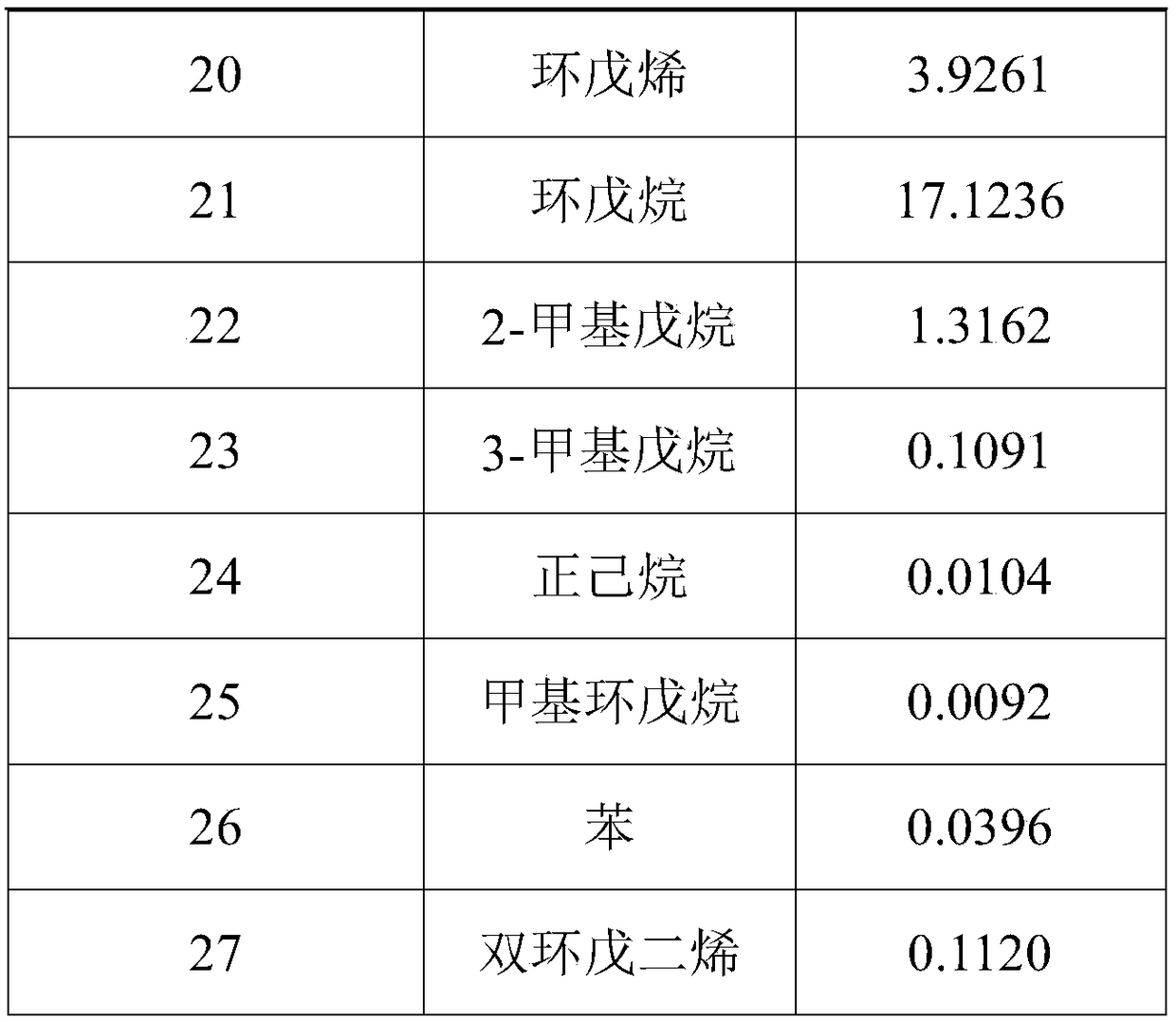
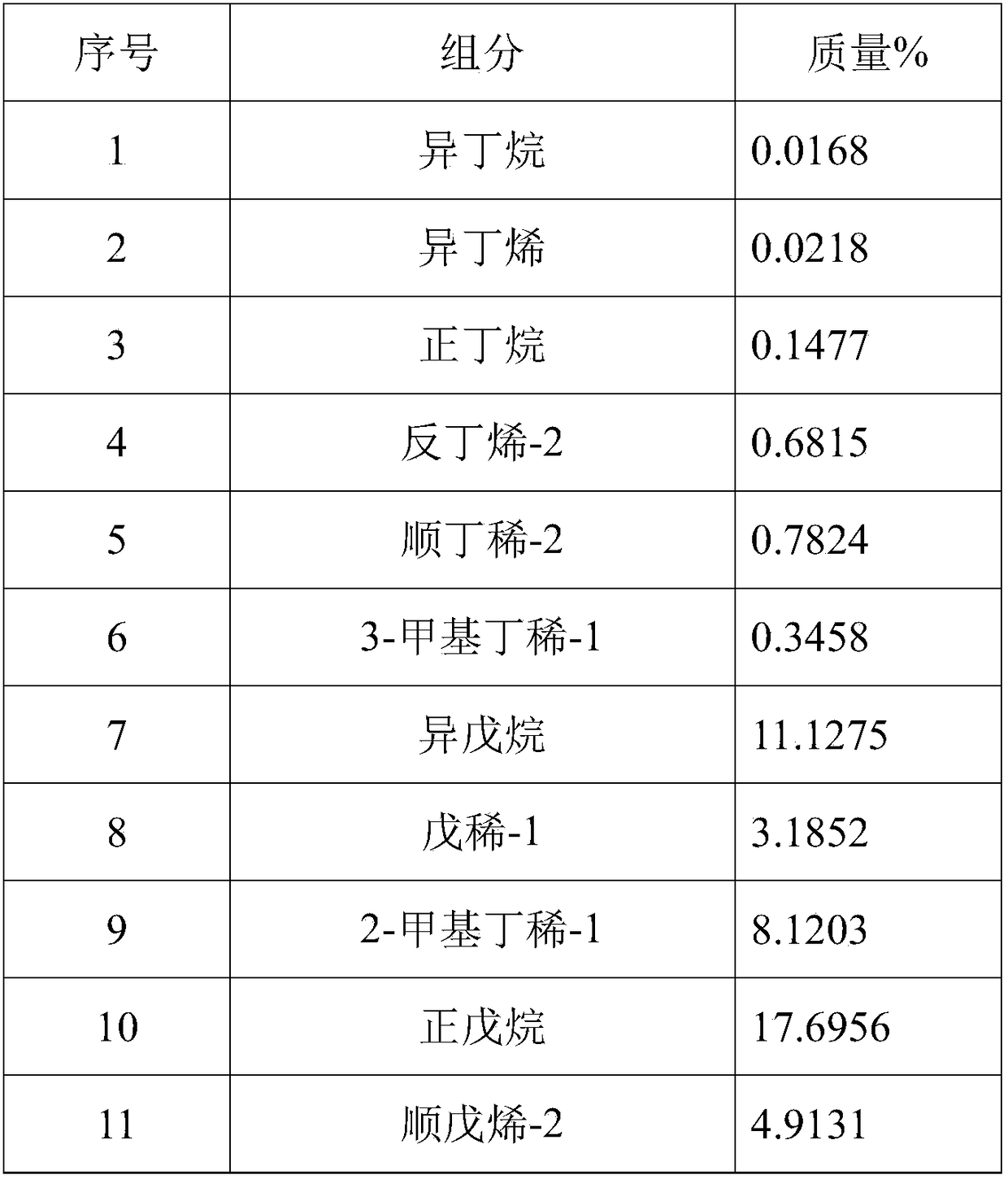
[0038] Present embodiment uses nickel-molybdenum catalyst to carry out the product after hydrogenation reaction as shown in the table below:
[0039]
[0040]
[0041] It can be seen from the reacted product that the obtained monoene content accounts for 49.9317% by mass of the total reactant, and the conversion rate is as high as 83.13%.
[0042] Example 2
[0043] In order to verify the influence of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com