A method for producing 4-o-desmethylbarba lichenic acid by using Aspergillus terreus strain and then synthesizing and synthesizing oakmoss
A technology for synthesizing oak moss with methyl balba, applied in the field of microbial fermentation technology and chemical synthesis, and new strains, can solve the problems of high cost, restricting the development of synthetic oak moss, complex preparation process, etc., to improve efficiency and simplify synthesis steps and technological process, the effect of cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
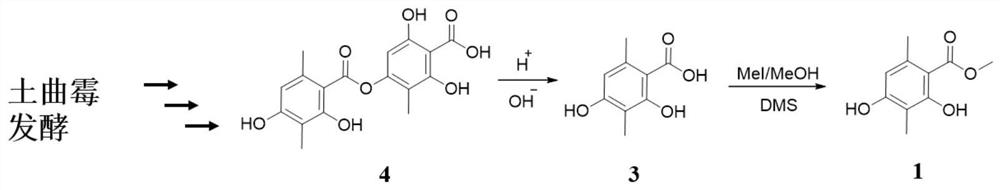
[0071] Screening of an Aspergillus terreus strain capable of producing 4-O-desmethylbarbalicic acid.
[0072] The needlefish (Alennes anastomella) frozen at -20°C from the waters of Yangma Island in Muping, Yantai was sterilized with 75% ethanol on the surface, and part of the internal organs of the fish were taken under aseptic conditions for grinding. Then use sterile water to make different gradient dilutions (V / V% 0, 10, 100, 1000), and apply the stock solution and dilutions of different concentrations to ampicillin (0.05g / L) and streptomycin (0.03 g / L) on the PDA plate of two kinds of antibiotics, culture at 28 ℃, observe whether there is the growth of fungal colony every other day in the process of cultivating, and pick single colony, carry out purification.
[0073] The different fungi obtained by separation and purification were cultured on PDA plates for 7 days. After the spores grew, the spore concentration was calculated by the hemocytometer plate counting method, a...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Example 1 The application of Aspergillus terreus MEFC06, which produces 4-O-desmethylbarbalicic acid obtained through screening, in the fermentative production of 4-O-desmethylbarbalicic acid.
[0081] Include the following steps:
[0082] Step 1, preparation of Aspergillus terreus seed liquid, inoculating the seed liquid into the fermentation medium for fermentation and cultivation;
[0083] Step 2, separating and purifying the fermentation broth to obtain 4-O-desmethylbarbalicic acid.
[0084] The preparation of the seed solution described in step 1 is specifically: inoculate Aspergillus terreus MEFC06 on the PDA plate medium, cultivate at 28°C for 4-9 days, grow spores, inoculate the spores on the plate into the seed medium, inoculate Quantity is 10 6 -10 8 Each / 35mL, 28°C, 220rpm shaker culture for 2 days, to obtain seed liquid.
[0085] In step 1, the inoculation amount of the seed solution inoculated into the fermentation medium is 3:35 according to the volume...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3 The method for preparing synthetic oakmoss by chemical synthesis using 4-O-demethylbarbalicic acid as raw material
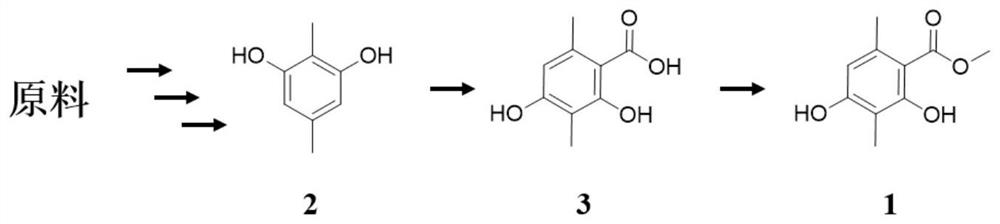
[0090] Step (1) Obtain 2,4-dihydroxy-3,6-dimethylbenzoic acid by acid hydrolysis or alkali hydrolysis of 4-O-desmethylbarbaric acid;
[0091] Step (2) 2,4-dihydroxy-3,6-dimethylbenzoic acid is methylated to obtain methyl 2,4-dihydroxy-3,6-dimethylbenzoate.
[0092] This embodiment is specifically:
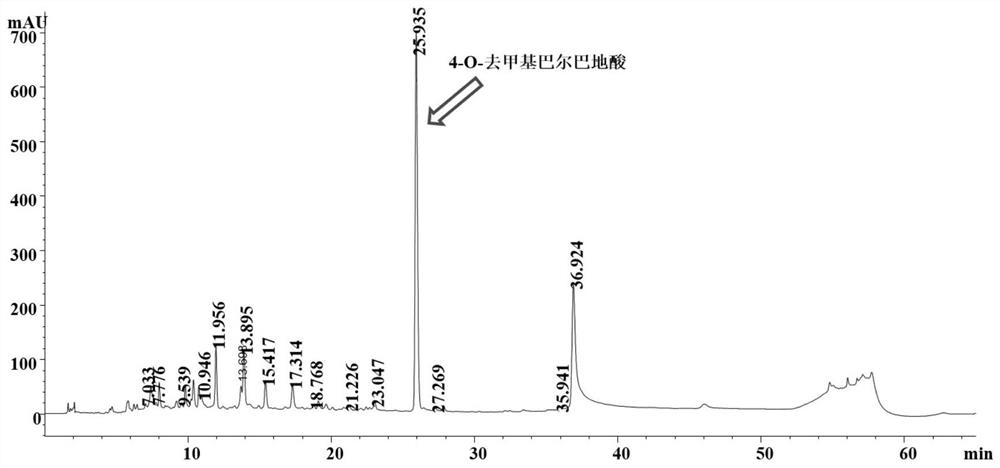
[0093]Add 2.2g (6.3mmol) solid crystals of 4-O-demethylbarbalicic acid in the there-necked flask, then add 10ml of catalytic amount (dissolving the solid crystals completely) of concentrated sulfuric acid with a mass fraction of 98%, in a water bath at 26°C Under stirring reaction, and adopt the HPLC analysis method reaction monitoring of 2,4-dihydroxyl-3,6-dimethylbenzoic acid and 2,4-dihydroxyl-3,6-dimethylbenzoate, the result shows The reaction was complete after 10 minutes, and no by-products were produced until 40 minutes after the late reacti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com