Chelating fiber, its preparation method and its detection application of cu(ii) in preserved eggs
A technology for chelating fibers and preserved eggs is applied in the field of chemistry, achieving good application prospects, realizing mass production and automatic control, and being convenient and simple to operate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] A kind of preparation method of novel chelating fiber, carries out following steps successively:
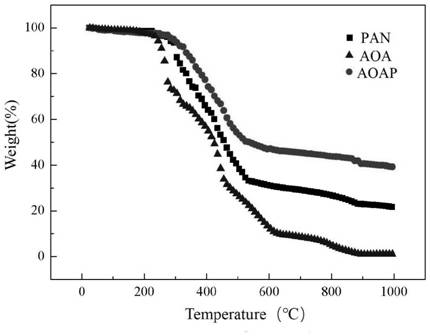
[0044] Accurately weigh 15 mg of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fibers and soak them in 25 mL of deionized water for 12 h to fully swell the fibers. After that, the ligand 5-aminoorotic acid (AOA) was added, the reaction molar ratio (PAN:AOA) was 1:4, deionized water was used as the solvent, and the mixture was stirred at a speed of 150rpm / min under nitrogen atmosphere for 1.5h , to exhaust the air, and then rapidly heated to 90 ° C, and stirred at the same speed for 10 h until the end of the reaction. After the reaction stopped, the reaction fiber was washed with distilled water until it was colorless, and placed in a vacuum oven at 50°C to dry to constant weight to obtain a new type of chelating fiber (AOAP)
[0045] After measuring the nitrogen content of the chelating fiber obtained by elemental analysis, by the following formula (1), (2) calculates the functional group conv...
Embodiment 2
[0063] The glass transition temperature of PAN fiber is 80-100°C. Therefore, when the reaction temperature is higher than the glass transition temperature of acrylic fiber, the reaction can proceed smoothly. The boiling point of the reaction solvent water is 100°C, and the melting point of the ligand AOA is 632.8°C. Too high reaction temperature will not only evaporate the reaction solvent, but also cause the structure of PAN fiber to be destroyed.
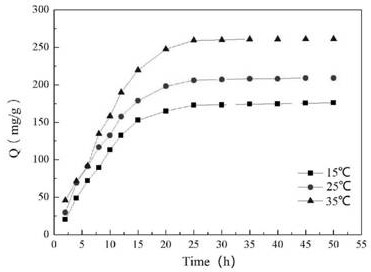
[0064] Therefore present embodiment changes reaction temperature 90 ℃ in embodiment 1 step (2) to 60 ℃, 70 ℃ and 80 ℃, other conditions are identical with embodiment 1, after measuring the content of N element in the chelating fiber with EA, pass through above-mentioned The formula calculates the conversion rate of the functional group of the chelating fiber, and the influence of the reaction temperature on the conversion rate of the functional group of the chelating fiber is obtained as follows: Figure 5 shown.
[0065] accor...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Change the reaction molar ratio (matrix: ligand) 1:4 of step (2) in embodiment 1 to 1: 2, 1:3 and 1:5, other conditions are identical with embodiment 1, obtain reaction molar ratio to chelate The influence of the conversion rate of synthetic fibers such as Figure 6 shown.
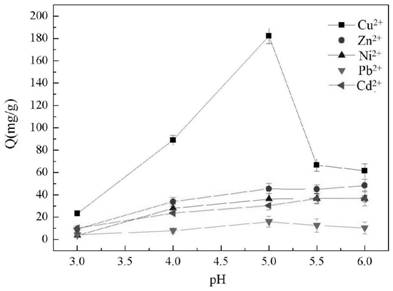
[0068] according to Figure 6 It is known that the functional group conversion rate of AOAP increases with the increase of ligand dosage; when the reaction molar ratio is 4, the functional group conversion rate of AOAP is the highest. This may be due to the fact that -NH in the ligand 2 The concentration is small, and the contact with the parent is small, resulting in an incomplete reaction. When the molar ratio of the reaction increases, it means that the dosage of the ligand increases, which makes -NH 2 As the concentration of β increases, the amount diffused into the interior of PAN fibers increases, and the contact between the matrix and the ligand increases.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com