Lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery and electrolyte technology, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, non-aqueous electrolyte batteries, etc., can solve the problems of poor battery cycle performance and inability to firmly bond silicon negative electrodes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
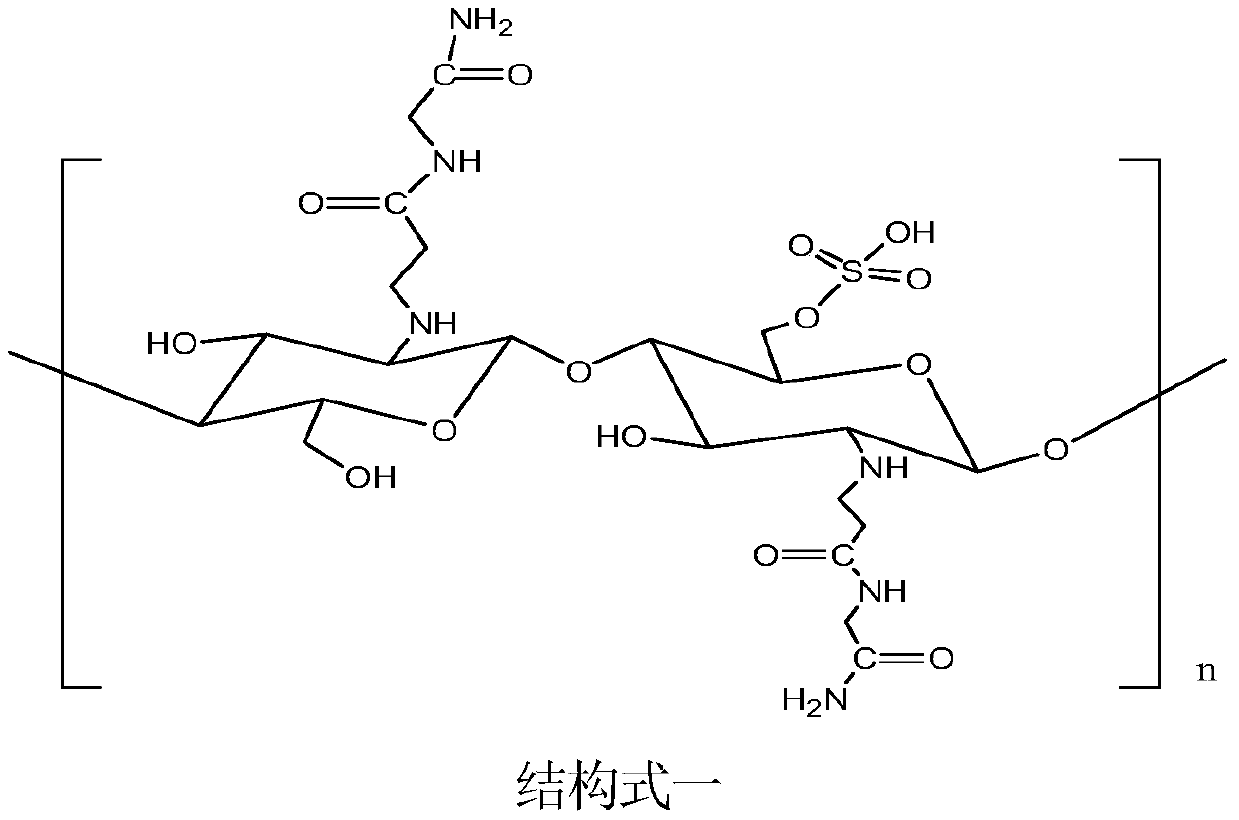
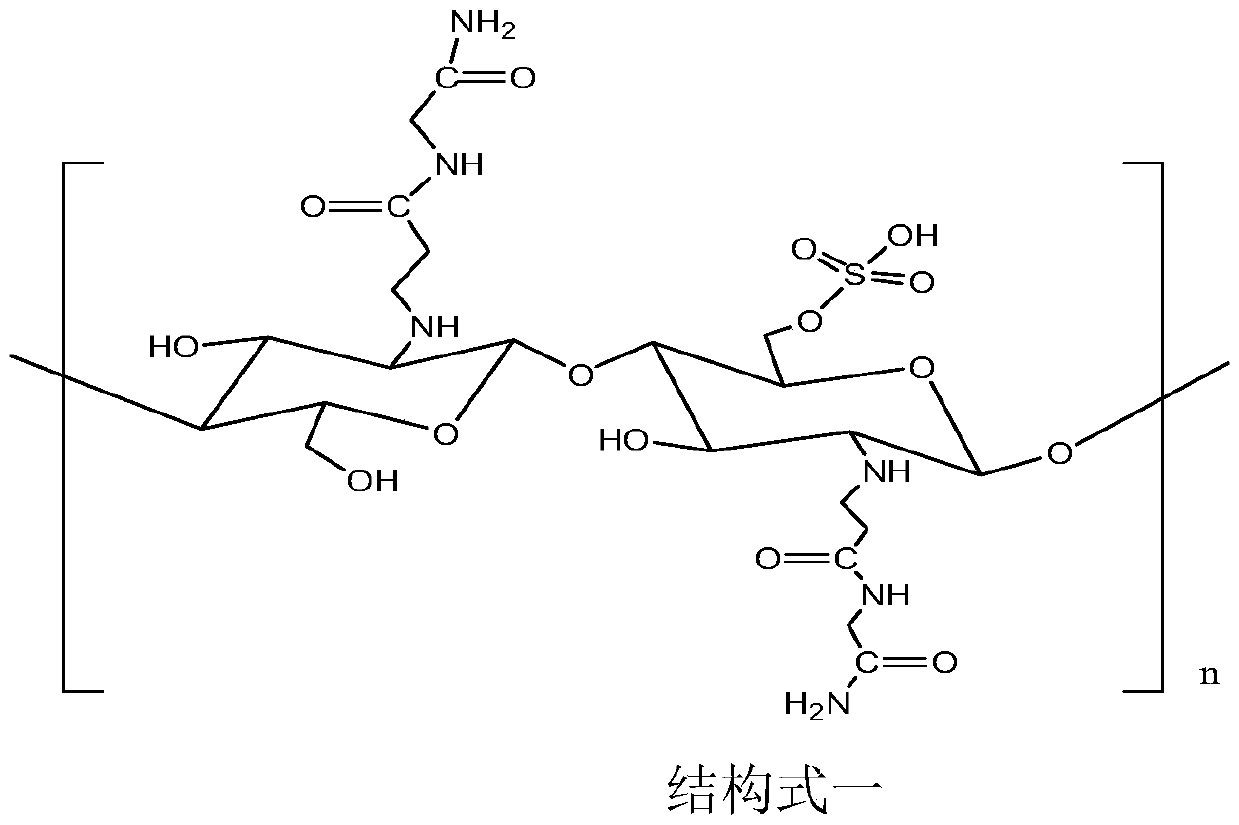
[0038] The preparation of structural formula one binding agent:
[0039] (1) Add the mixed solution of chitosan, dichloroacetic acid and formamide dropwise to the mixed solution of chlorosulfonic acid / dimethylformamide, stir for 2h, and filter to obtain the filtrate;
[0040] (2) The filtrate obtained in step (1) is added dropwise in ethanol, filtered after stirring for 2h, and the precipitate obtained by filtration is washed three times with ethanol to obtain chitosan sulfate;
[0041] (3) Add acryloyl chloride / ether solution dropwise to glycinamide hydrochloride, deionized water, potassium carbonate / ether mixed solution and stir for 1 hour, then add HCl to adjust the pH of the solution to 3, and then wash the mixture with ether to remove organic phase, and vacuum evaporated the remaining ether, then adjusted the pH of the solution to neutral with NaOH solution, and freeze-dried the mixture;
[0042] (4) washing the mixture obtained in step (3) three times with a methanol / etha...
Embodiment 1
[0055] This embodiment is used to illustrate a lithium ion battery disclosed in the present invention and its preparation method.
[0056] 1) Preparation of electrolyte
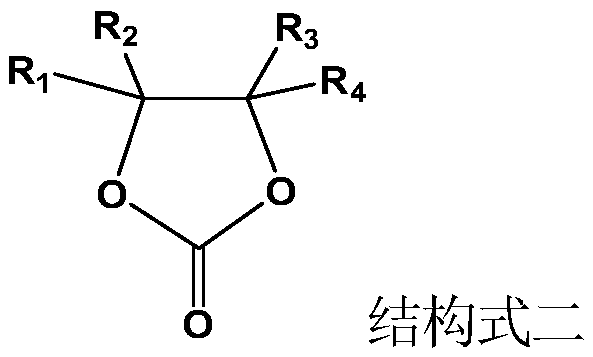
[0057] Mix ethylene carbonate (EC), diethyl carbonate (DEC) and ethyl methyl carbonate (EMC) according to the mass ratio of EC:DEC:EMC=1:1:1, and then add lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF 6 ), its concentration is 1mol / L, then add the fluorinated cyclic carbonate shown in structural formula three by 5% of the total mass of the electrolyte.
[0058] 2) Preparation of positive electrode
[0059] Mix the positive electrode active material lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide LiNi according to the mass ratio of 93:4:3 0.5 co 0.2 mn 0.3 o 2 , conductive carbon black Super-P and binder polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), and then disperse them in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) to obtain positive electrode slurry. The positive electrode slurry was uniformly coated on the aluminum foil, dried, calendered and vacuum...
Embodiment 2~12
[0067] Examples 2 to 12 are used to illustrate the lithium-ion battery disclosed in the present invention and its preparation method, including most of the operating steps in Example 1, the difference is that: the total amount of the negative active material, conductive agent and binder The mass percentage is 100%, the mass percentage of the conductive agent is fixed at 1%, and the mass percentage of the negative electrode active material changes with the ratio of the binder. The mass percentage and molecular weight of the binder are shown in Table 1. In addition, the fluorinated cyclic carbonate and mass percentage in the electrolyte are listed in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com