Slow/controlled-release fertilizer having water retention function and preparation method of slow/controlled-release fertilizer
A technology of controlled-release fertilizers and functions, which is applied in the field of slow- and controlled-release fertilizers with water-retaining functions and its preparation, and can solve problems such as easy loopholes in the coating layer, uneven nutrient slow-release performance, and poor degradability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] The preparation of embodiment 1 coated slow-release fertilizer
[0048] The present embodiment provides a kind of preparation method of slow and controlled release fertilizer, comprising the following steps:
[0049] S1. Prepare material A; mix and stir the prepared material A in the reactor for 5-10 minutes, and heat to 80°C;
[0050] S2. Configuration B material: mix one or more of toluene diisocyanate, lysine diisocyanate, and polymethylene polyphenyl polyisocyanate according to the proportion, add additives and heat to 65-75°C, stir for 1 -2min, get material B;
[0051] S3. Coating: Put the fertilizer core into a horizontally rotating drum and roll it at a speed of 40r / min to polish the surface to make it smooth. At the same time, blow hot air at 98°C into the drum to make the fertilizer core temperature reach 55- 80°C, the optimal temperature is 70-75°C; after the surface of the fertilizer core is smooth, add material A and material B, and after curing for a peri...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2 Comparison of film-forming characteristics, controlled-release effect and water retention performance of coated slow- and controlled-release fertilizers
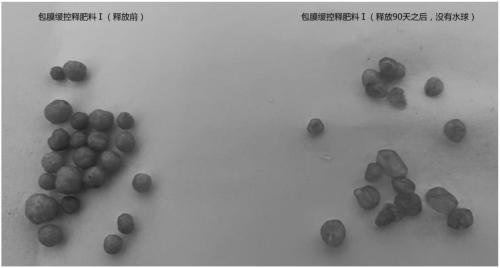
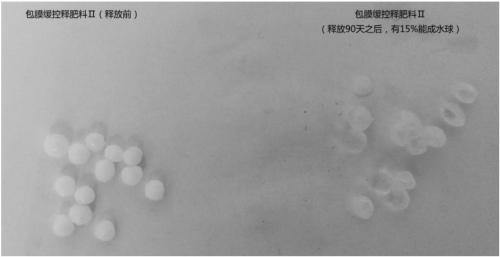
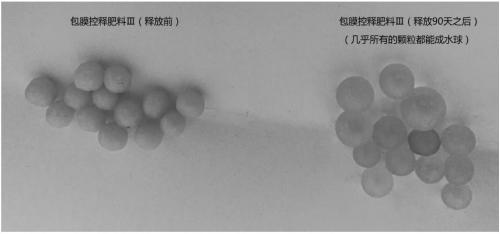
[0062] This example provides a comparison of film-forming characteristics, controlled-release effects, and water-retaining properties of different film-coated slow- and controlled-release fertilizers. Wherein, the detection method of the controlled release effect of the slow and controlled release fertilizer is carried out according to the method specified in the HG / T4215-2011 standard, and the present invention will not repeat them.
[0063] The test results are shown in Table 2. In fertilizer Ⅰ, material A and material B polyurethane reacted faster, and soon formed a film on the surface of the fertilizer core, which made it difficult to control the production process. The release rate of the fertilizer was determined according to the HG / T4215-2011 standard Finally, it was found that the fertilizer release ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Embodiment 3 Coated slow-release fertilizer degradation performance comparison
[0069] This example provides a comparison of the degradation properties of a group of different coated slow-release fertilizers. Wherein, the detection method for the biodegradability of the slow and controlled release fertilizer is carried out according to the method specified in the GB / T19277-2003 standard, and will not be described in detail in the present invention.
[0070]The test results are shown in Table 3. The biodegradation rate of Fertilizer III is much higher than that of Fertilizer I and Fertilizer II. Combined with the comparative test data in Example 2, it shows that Fertilizer III not only has strong biodegradability, but also has a higher biodegradability. In the case of low degradation rate, due to its good flexibility and film-forming performance, it can still maintain good water retention performance.
[0071] Table 3 Biodegradation data table of different fertilizers ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hydroxyl value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com