An organosilicon small molecule fluorescent probe for detecting hypochlorous acid
A technology for detecting hypochlorous acid and fluorescent probes, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of poor anti-interference, single recognition site, and difficult to obtain raw materials, and achieve the effects of rapid response, simple synthesis and strong specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The synthesis of embodiment 1 fluorescent probe BSi-1
[0032]
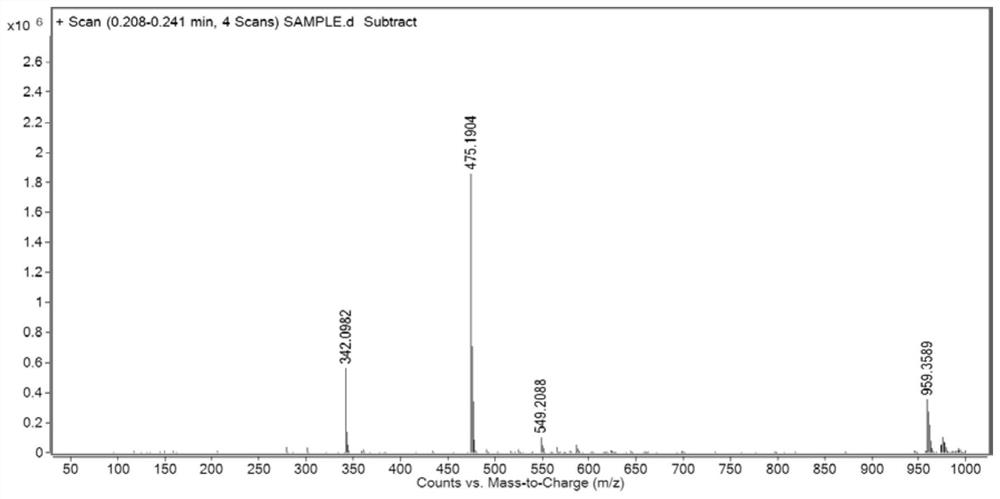
[0033] In a 250 mL round bottom flask, add 0.25 g of 1,3-bis(3-aminopropyl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyldisiloxane dissolved in 100 mL of ethanol, then add 0.49 g5 -Methylthio-1,8-naphthalene dicarboxylic anhydride, heated and stirred at reflux at 78 °C for 24 h, rotary evaporated, dried, using dichloromethane:methanol (V / V)=20:1 as the eluent, and obtained by column chromatography Compound BSi-1. That 1 H NMR spectrum such as figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2 Different concentrations of hypochlorous acid are detected by fluorescence titration of probe BSi-1
[0035] Prepare 10 mL of an aqueous solution with a concentration of 100 mM hypochlorous acid and a mother solution of the fluorescent probe BSi-1 obtained in Example 1 with a concentration of 1 mM as spares.
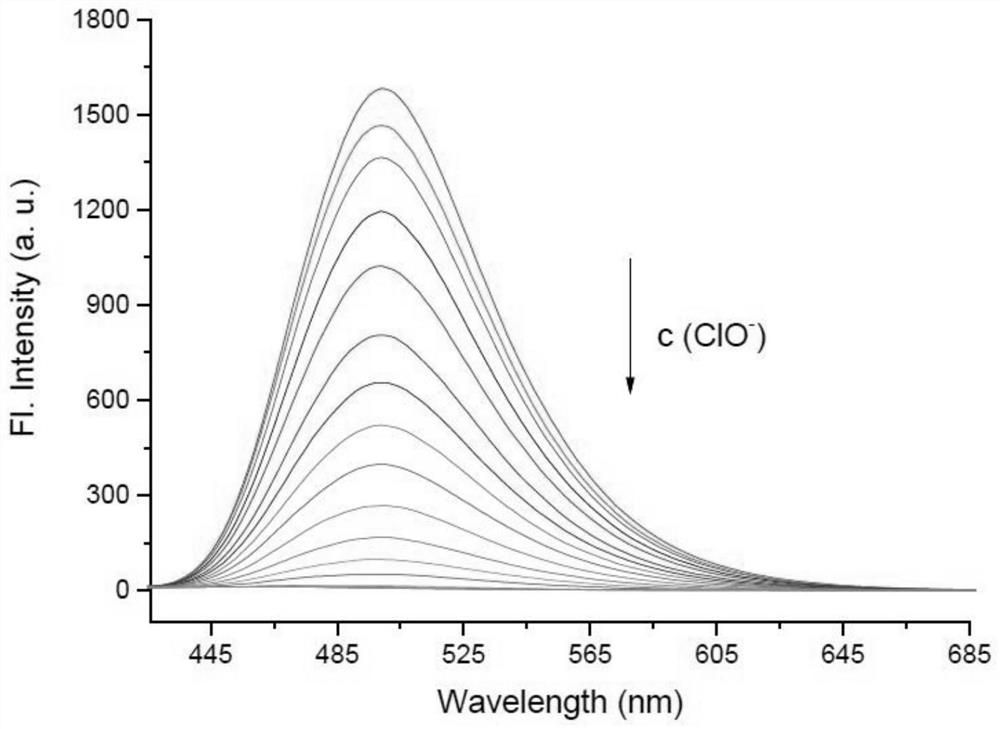
[0036] Prepare the probe at a concentration of 10 μM, interact with different concentrations of hypochlorous acid (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 μM), and Perform fluorescence detection (λ ex =405 nm, λ em =485 nm), calculate the fluorescence intensity in each system, and establish a standard curve of fluorescence intensity and hypochlorous acid concentration, such as figure 2 . Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that as the concentration of hypochlorous acid increases, the fluorescence intensity of the reaction system decreases rapidly, and when the concentration of hypochlorous acid reaches 20 μM, the fluorescence of the reactio...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3 Kinetic test of interaction between probe BSi-1 and hypochlorous acid
[0038] Prepare 10 mL of an aqueous solution with a concentration of 100 mM hypochlorous acid and a mother solution of the fluorescent probe BSi-1 obtained in Example 1 with a concentration of 1 mM as spares.
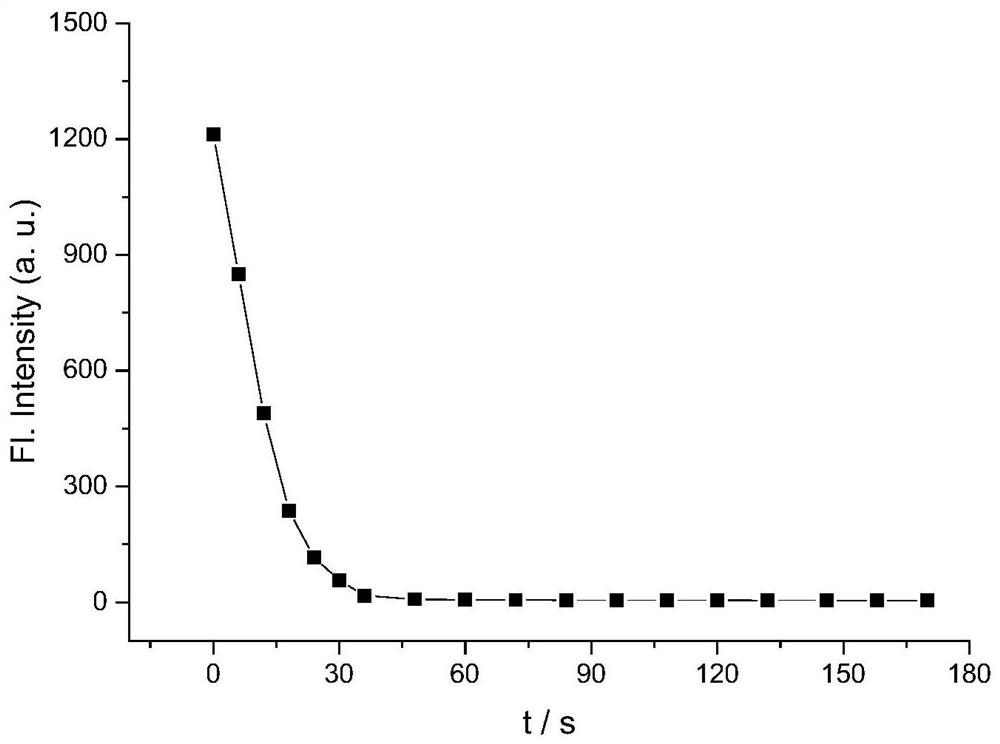
[0039] The solutions of probe BSi-1 and hypochlorous acid were prepared, the concentration of which was 10 μM of the probe; the concentration of hypochlorous acid was 20 μM. Perform fluorescence detection (λ ex =405 nm, λ em =485 nm), in the first 30s, test every 5s; after that, test every 10s, about 3 minutes. Calculate the fluorescence intensity changing with time in each system, and establish a standard curve of fluorescence intensity and action time, such as image 3 shown. Depend on image 3 It can be seen that the fluorescence of the reaction system is basically quenched after 30 s of reaction.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com