Use of low ph active alpha-1,4/1,6-glycoside hydrolases as a feed additive for ruminants to enhance starch digestion
A ruminant, hydrolase technology, applied in the field of animal nutrition, can solve the problems of no raw starch binding domain, low efficiency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0293] Materials used in subsequent examples
[0294] Protein samples are listed in Table 1 and used in subsequent examples. Table 1 shows the enzyme type, the organism of origin of the samples (when known) and the internal or commercial source, and the patent reference for the sequence.
[0295] Table 1. List of enzyme components evaluated.
[0296]
example 2
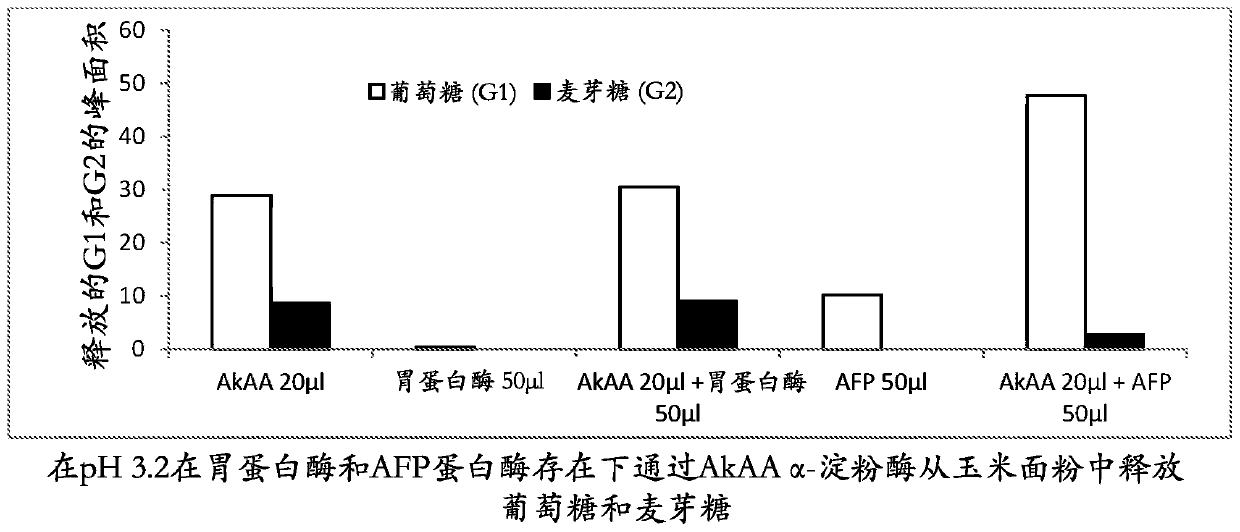
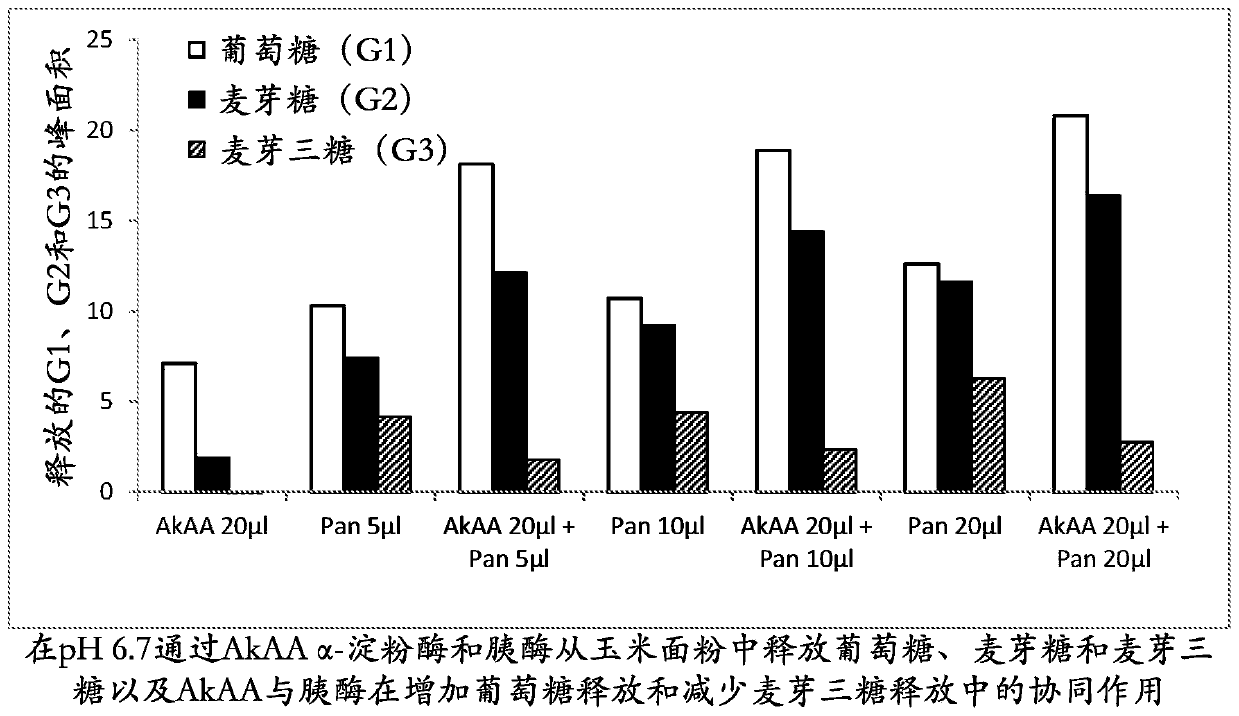
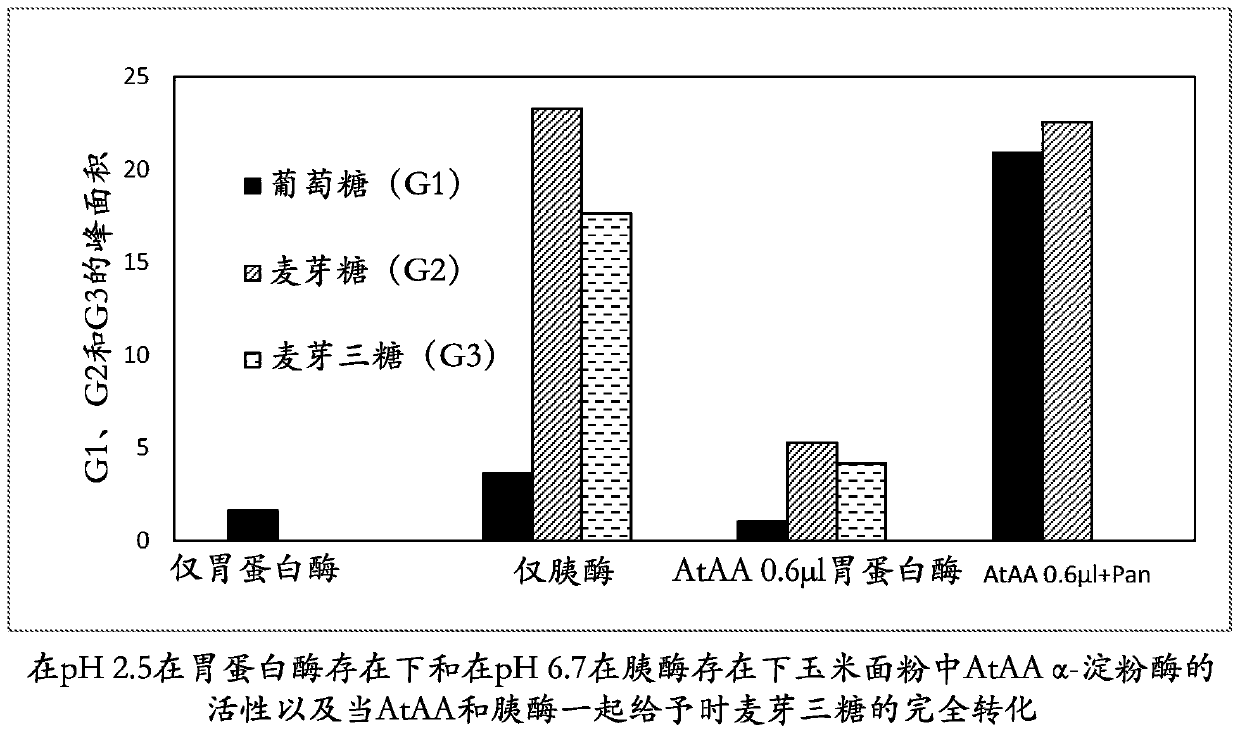
[0298] Hydrolysis of corn flour by AkAA amylase in the presence of acid aspartic protease porcine pepsin and Trichoderma reesei AFP
[0299] The reaction mixture contained 1 mL of corn flour slurry (20%, w / w, pH 3.2), 20 μL of AkAA (209 mg / mL), 50 μL of porcine pepsin (Sigma, P7000, 10000 U / mL in water), 50 μL of Trichoderma reesei (5 mg / mL) of 5 μL and 50 μL of AFP and water to a final volume of 1.07 mL. The reaction was carried out at 40 °C for 5 h with shaking at 200 rpm. At the end of the reaction, 30 μL of the reaction supernatant was mixed with 0.23 mL of water and filtered through a 0.22 μm membrane filter. The filtrate (40 μL) was subjected to HPLC analysis on an Aminex HPX-87N HPLC column (Bio-Rad) at a flow rate of 0.6 mL / min at 78° C. using water as eluent for 15 min. Glucose and maltose peaks were detected using an in-line RI (refractive index) detector and peak areas were integrated using Chromeleon software (Dionex) according to the manufacturer's instructions....
example 3
[0305] Stability of AkAA amylase in the presence of rumen fluid
[0306] For an animal feed enzyme additive to be effective in ruminants, it is important that the enzyme have considerable stability in rumen fluid and rumen conditions. The data in Table 2 show that AkAA is stable when incubated at 40 °C for 4.5 h in the presence of cell-free rumen fluid, as the release of glucose and maltose was not significantly affected by increased rumen fluid volume.
[0307] The AkAA used had a total protein concentration of 209 mg / mL and rice starch granules (Sigma S7260) were prepared as an 8% (w / w) slurry in water with the pH adjusted to 3.2. After mixing with the pre-incubation mixture, the pH changed to pH 5.3. Cell-free rumen fluid had a pH of 6.1 collected from cows fed grass (41.66%), whole barley (14.79%), maize (16.78%), dried beet pulp and beet residue cake (3.02 %), Milled Barley (6.66%), Rapeseed Meal (4.88%), Soy Meal (4.46%), Komix (Vitamin and Mineral Mixture, 0.2%), Roed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com