Tin-based negative electrode sodium ion secondary battery
A secondary battery and sodium ion technology, applied in secondary batteries, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of tin electrode structure collapse, active material falling off, and loss of electrical contact, etc., so as to reduce the harm to the environment and improve Energy density, easy preparation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] This embodiment is the production of a pure tin sodium ion half-cell.
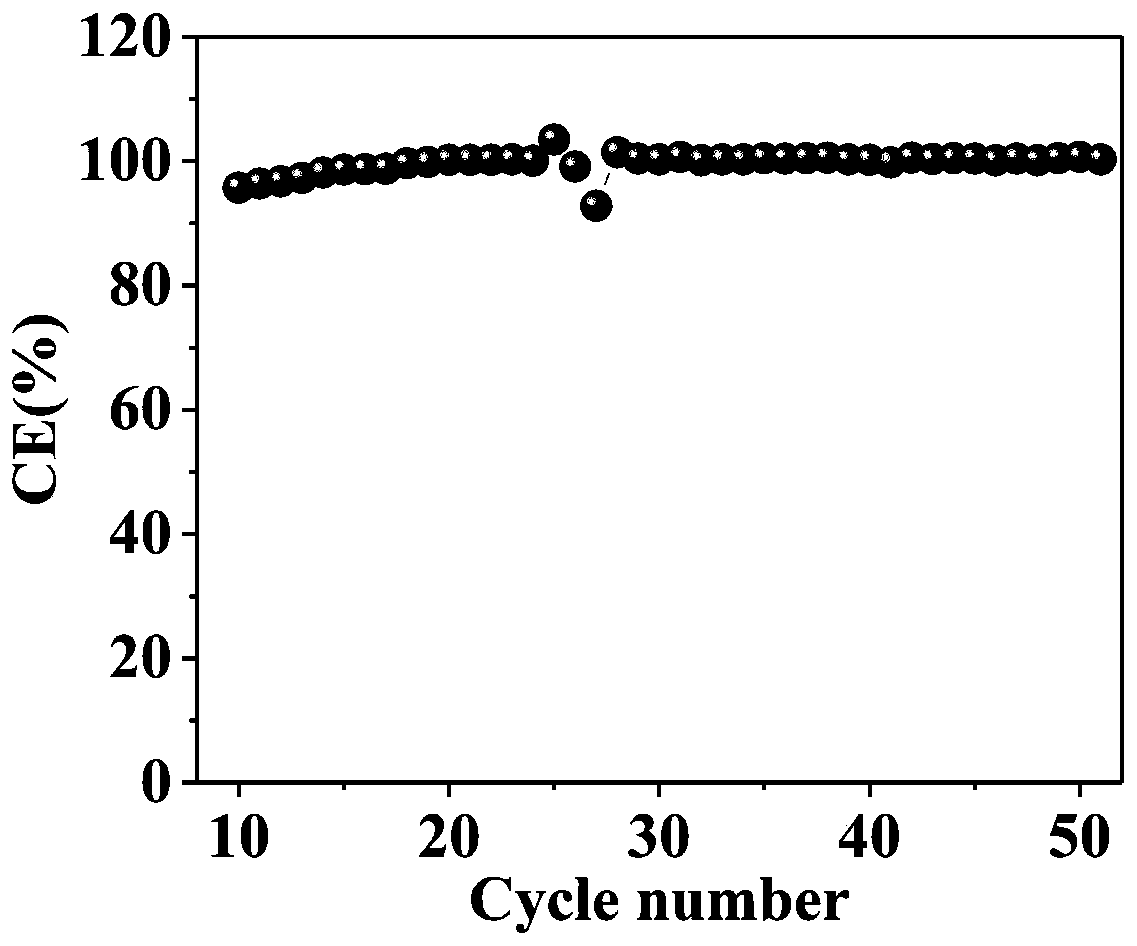
[0031] 100 μm tin foil and 100 μm sodium metal were cut into discs with a diameter of 12 mm as the negative electrode material of the half-cell, and assembled with sodium vanadium phosphate as the positive electrode to obtain a pure tin-sodium ion half-cell. Subsequently, the cycle test of the pure tin sodium ion half-cell was carried out, and the cycle coulombic efficiency was calculated. The test results are shown in figure 1 .
[0032] figure 1 It is a diagram of the cycle stability test results of the pure tin sodium ion half-cell in Example 1 of the present invention.
[0033] Such as figure 1 As shown, the abscissa represents the cycle number of the pure tin sodium ion half-cell, and the ordinate represents the coulombic efficiency of the pure tin sodium ion half cell, by figure 1 It can be seen that after the tin metal negative electrode has been activated for several initial cycles (abou...
Embodiment 2
[0035] This embodiment is the manufacture of a tin-silver-copper alloy sodium ion secondary full battery.
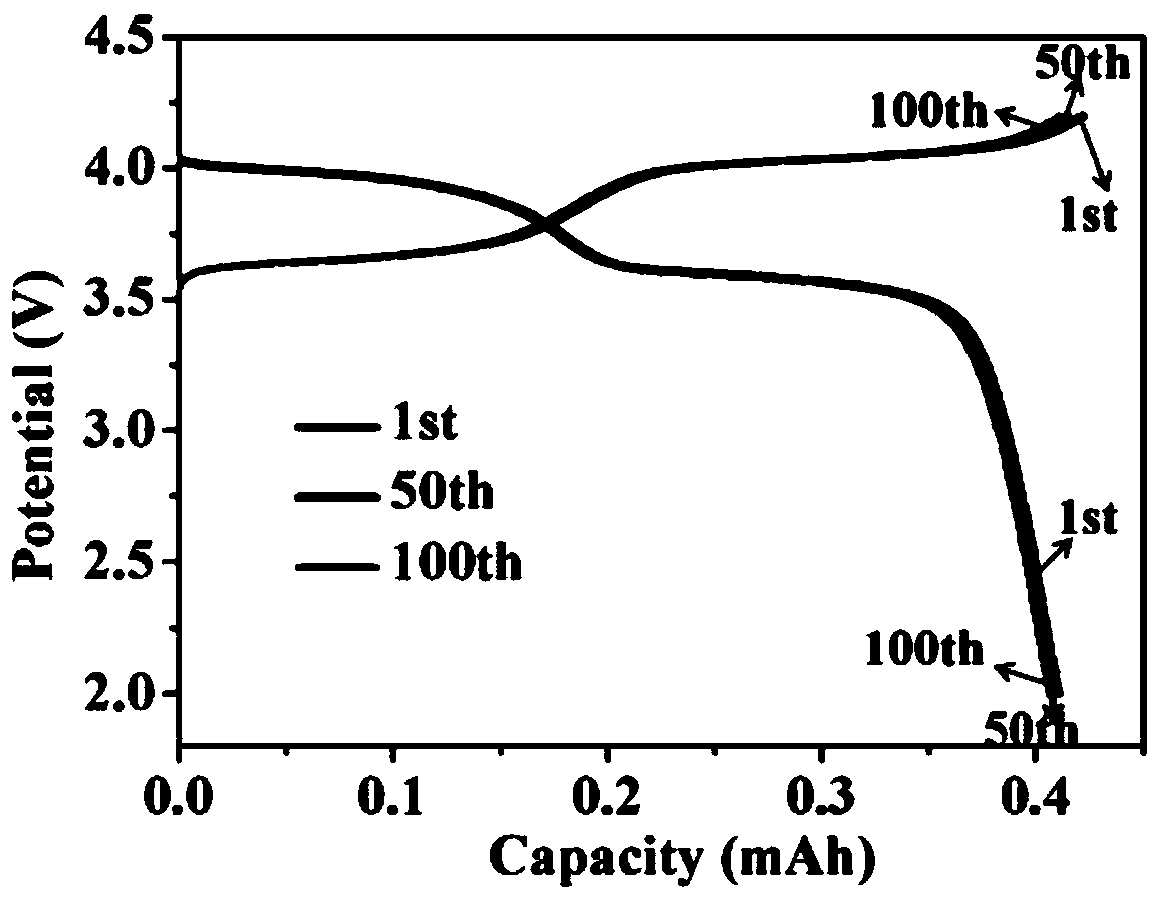
[0036] A tin-silver-copper alloy foil of 70 μm was selected as the negative electrode material, cut into a disc with a diameter of 12 mm, and a tin-silver-copper alloy sodium ion secondary full battery was assembled with the sodium vanadium phosphate positive electrode. Subsequently, the full battery was subjected to a cycle charge and discharge test, and the test results are shown in figure 2 . Wherein, the silver content in the tin-silver-copper alloy foil is 3wt%, the copper content is 0.5wt%, and the balance is tin.
[0037] figure 2 It is the capacity-voltage graph of the tin-based negative electrode sodium-ion full battery in Example 2 of the present invention.
[0038] Such as figure 2 As shown, the abscissa represents the battery charge and discharge capacity, and the ordinate represents the charge and discharge voltage. Depend on figure 2 It can be see...
Embodiment 3
[0040] This embodiment is the fabrication of a tin-antimony alloy sodium ion secondary full battery.
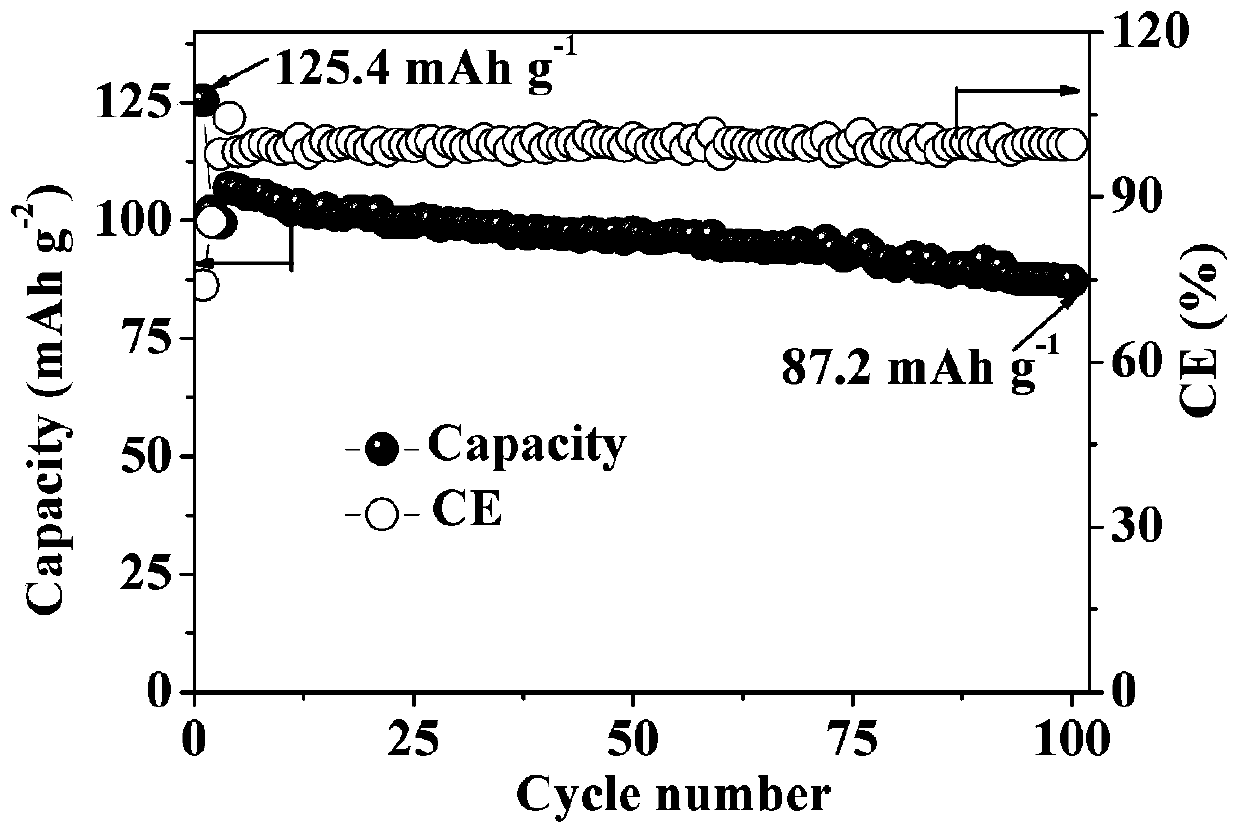
[0041] A tin-antimony alloy foil of 70 μm was selected as the negative electrode material, cut into discs with a diameter of 12 mm and assembled with a sodium vanadium phosphate positive electrode to obtain a tin-antimony alloy sodium ion secondary full battery, and the full battery was charged and discharged. The test results are shown in image 3 . Wherein, the antimony content in the tin-antimony alloy foil is 5wt%, and the balance is tin.
[0042] image 3 It is a graph showing the charge and discharge results of the tin-antimony alloy sodium ion secondary full battery in Example 3 of the present invention.
[0043] Such as image 3 As shown, the abscissa represents the number of cycles, the ordinate represents the discharge specific capacity, and the right ordinate represents the Coulomb efficiency. Depend on image 3 It can be seen that the initial discharge capaci...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com