A method for improving the biomineralization ability of silk fibroin
A technology of silk fibroin and biomineralization, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, peptide preparation methods, etc. The comprehensive properties of the material and the weak biomineralization function of silk fibroin have achieved the effects of excellent regulation of mineralization nucleation and growth, promotion of nucleation and rapid growth, excellent water solubility and biocompatibility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
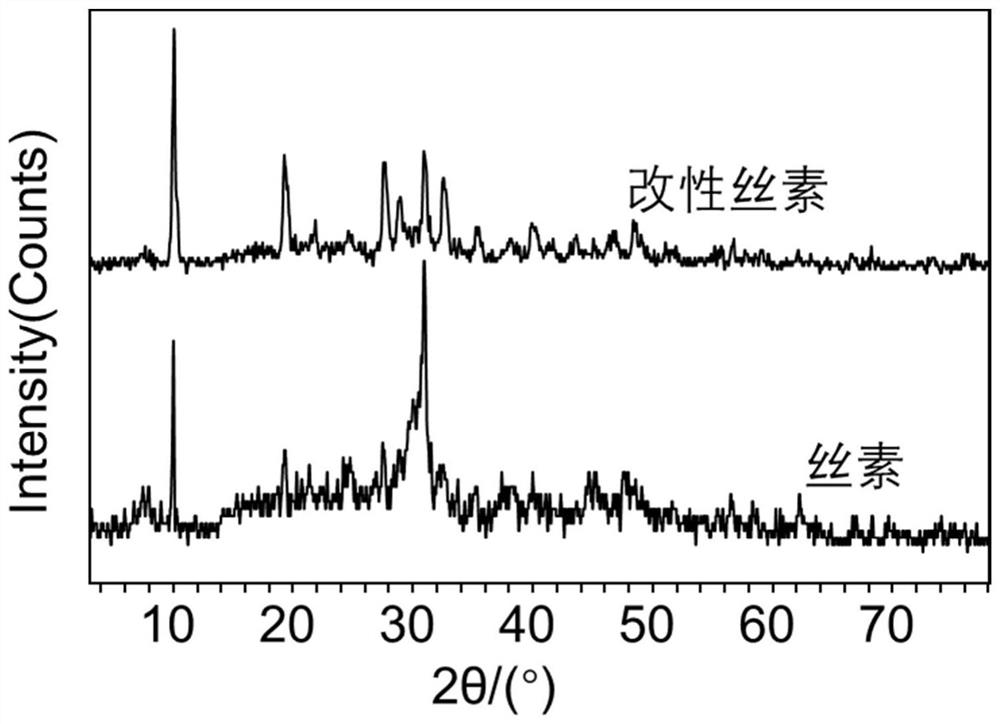
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] This embodiment includes the following steps in turn:
[0029] (1) Using phage display technology to display the amino acid sequence Thr-Lys-Arg-Glu-Glu-Val-Asp (such as SEQ ID NO.1) of the amelogenin core polypeptide fragment with the function of mineralization regulation on the P3 capsid of the phage On the protein surface, phage nanofibers exhibiting the function of inducing mineralization were prepared, called amelogenin-type phage;
[0030] (2) Add the amelogenin-type bacteriophage in step 1) and 10 mL of Escherichia coli expanded and shaken overnight into 500 mL of LB liquid medium and incubate at 37° C. for 24 hours. Then use 4500g high-speed centrifugation to collect the supernatant to remove Escherichia coli. Then use the PEG / NaCl mixed solution to precipitate the phage, spend 4 nights overnight, then centrifuge at 8000g to collect the precipitate to obtain the enriched amelogenin-type phage particles, repeat the precipitation-centrifugation step twice, so tha...
Embodiment 2
[0033] This embodiment includes the following steps in turn:
[0034] (1) Use phage display technology to display the amino acid sequence Glu-Glu–Glu-Glu-Glu-Glu-Glu-Glu-Glu (such as SEQ ID NO.2) of the mineralization-regulating dentin protein core polypeptide fragment on the P6 of the phage On the surface of the capsid protein, phage nanofibers exhibiting the function of inducing mineralization were prepared, called dentin-type phage;
[0035] (2) Add the dentin-type bacteriophage in step 1) and 5 mL of Escherichia coli expanded and shaken overnight into 100 mL of LB liquid medium and incubate at 37° C. for 12 hours. Then use 4500g high-speed centrifugation to collect the supernatant to remove Escherichia coli. Then use the PEG / NaCl mixed solution to precipitate the phage, spend 4 nights overnight, then centrifuge at 8000g to collect the precipitate to obtain the enriched dentin-type phage particles, repeat the precipitation-centrifugation step 2 times, so that the purity of...
Embodiment 3
[0038] This embodiment includes the following steps in turn:
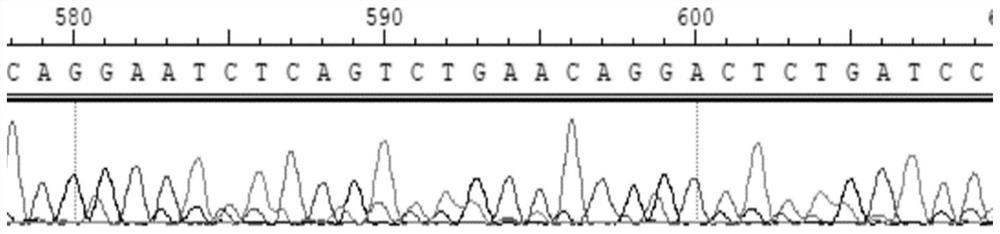
[0039] (1) Utilizing phage display technology to extract the amino acid base sequence Gln-Glu-Ser-Gln-Ser-Glu-Gln-Asp-Ser (such as SEQ ID NO.3, sequence For sequencing results, see image 3) was displayed on the surface of the P8 capsid protein of the phage, and a phage nanofiber exhibiting the function of inducing mineralization was prepared, which was called dentin matrix protein type 1 phage, and the sequencing results were as follows figure 1 shown;
[0040] (2) Add the dentin-type bacteriophage in step 1) and 4 mL of Escherichia coli expanded and shaken overnight into 100 mL of LB liquid medium and incubate at 37° C. for 16 hours. Then use 4500g high-speed centrifugation to collect the supernatant to remove Escherichia coli. Then use the PEG / NaCl mixed solution to precipitate the phage, spend 4 nights, and then centrifuge at 8000g to collect the precipitate to obtain the enriched dentin matrix protein type ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com