Horseshoe crab factor b variant
A technology of factor B and amino acid, which is applied in the direction of using a carrier to introduce foreign genetic material, enzymes, and cells modified by introducing foreign genetic material.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0270] Preparation of Murasame-TFB
[0271] The expression vector of Limulus chinensis factor B mutant (Murasame-TFB) was prepared according to the following procedure.
[0272] (1) Production of Murasame-TFB expression vector
[0273]Using the above TFB / pCA7 as a template, an inverse PCR reaction using phosphorylated primers (primer 11 (SEQ ID NO: 32) and primer 12 (SEQ ID NO: 33)) was performed. The inverse PCR reaction was carried out using Tks Gflex DNA polymerase (manufactured by Takara Bio Co., Ltd.) according to the attached manual. Add restriction enzyme (Dpn I) to the above-mentioned PCR reaction solution to decompose the template, perform phenol / chloroform extraction and ethanol precipitation to separate and prepare DNA, and use DNA Ligation Kit to follow the attached instructions. A ligation reaction (self-ligation) is performed.
[0274] After Escherichia coli was transformed using the ligation reaction solution described above, the vector was amplified and pu...
reference example 3
[0279] Measurement of protease activity (specific activity) of TFB
[0280] A solution of 160 nM TFC, 3.2 μM LPS (derived from Salmonella minnesota R595, weight average molecular weight 1,700 Da, manufactured by List Biological Laboratories), 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), and 150 mM NaCl was prepared and statically incubated at 37° C. Leave for 20 minutes to activate TFC. Hereinafter, activated TFC is referred to as "α-TFC".
[0281] 20 μL of a solution of 50 nM TFB, 0.2 nM α-TFC, 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl, and 100 μg / mL BSA was prepared and allowed to stand at 37° C. for 1 hour. To this solution, 5 µL of 2 mM Boc-Leu-Thr-Arg-MCA (manufactured by Peptide Laboratories) dissolved in 20% DMF was added, and left to stand at 37° C. for 5 minutes. After adding 0.6 M acetic acid (75 µL) to complete the enzyme reaction, the amount of MCA released from the peptide (proportional to the protease activity (total activity) of activated TFB) was measured with a fluorescence detecto...
Embodiment 2
[0283] Determination of protease activity (specific activity) of Murasame-TFB
[0284] Using Murasame-TFB instead of TFB, the same operation as the above was carried out, and the protease activity of Murasame-TFB was measured.
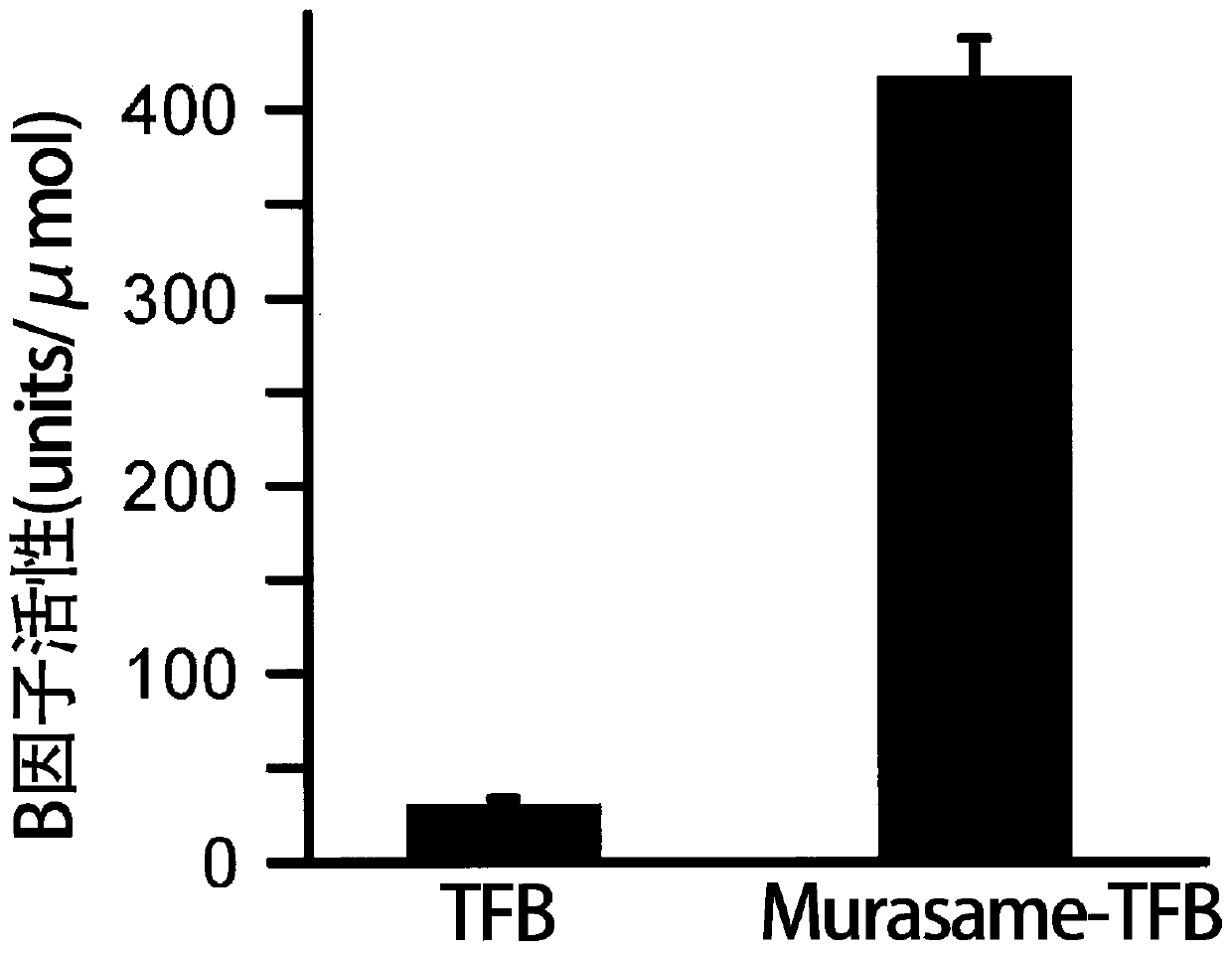
[0285] As a result of the above test, the protease activity (specific activity) of Murasame-TFB was 416.87±20.50 units / μmol.
[0286] The results of and are shown in figure 1 . The results of the above experiments show that Murasame-TFB has 13.4 times higher protease activity (specific activity) than TFB.
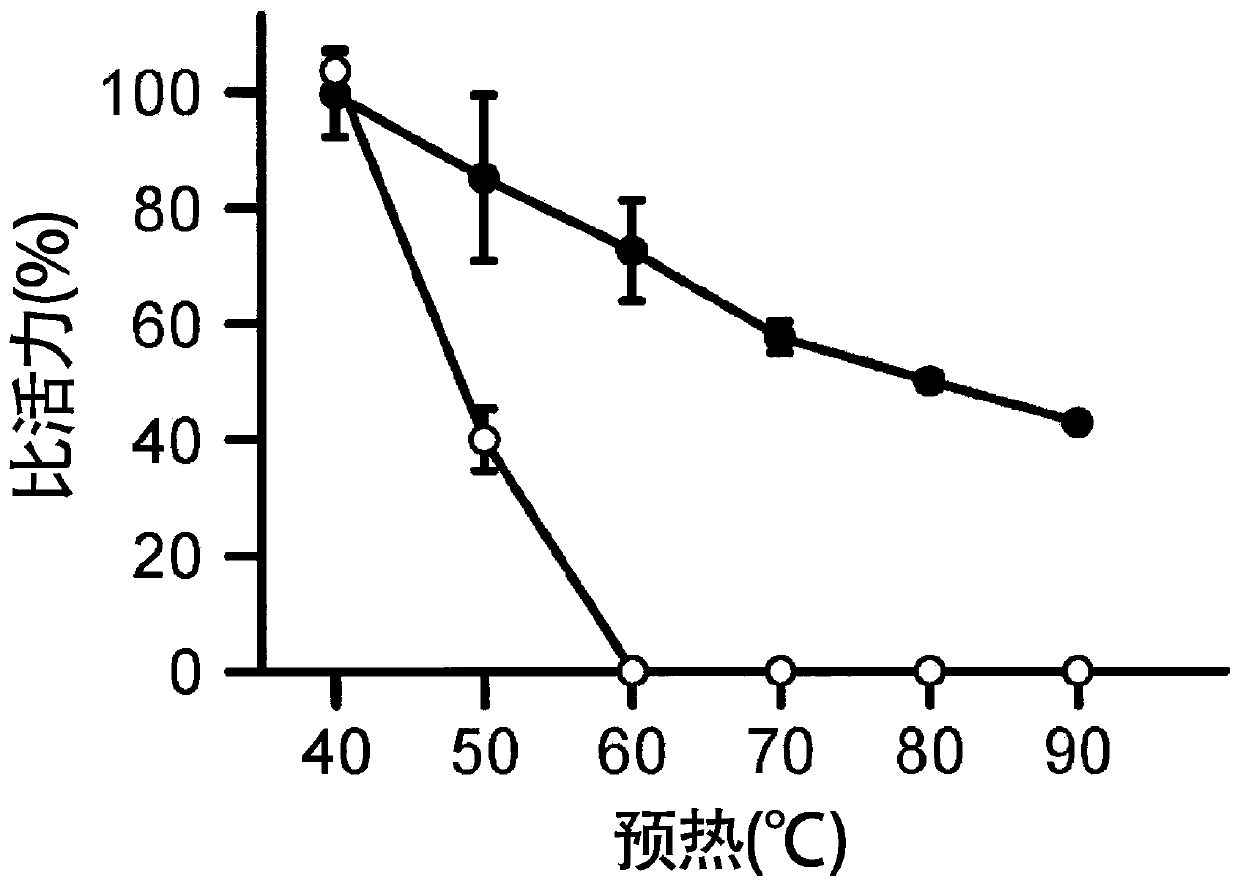
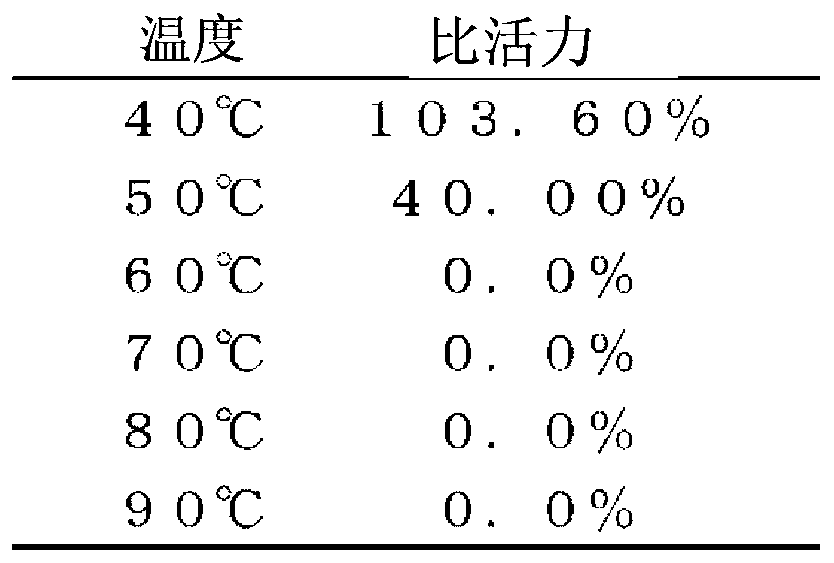
[0287] Evaluation of thermal stability of TFB
[0288] Prepare 10 μL of a solution of 100 nM TFB, 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH8.0), 150 mM NaCl, 100 μg / mL BSA at a given temperature (40 °C, 50 °C, 60 °C, 70 °C, 80 °C, or 90 °C) Let stand for 2 minutes. Thereafter, 10 μL of a solution of 0.4 nM α-TFC, 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl, and 100 μg / mL BSA was added to this solution, and the mixture was left to stand at 37° C. for 1 hour. Thereafter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com