Intermediate factor BnMED16 gene to regulate Sclerotinia stem rot resistance in Brassica napus and application thereof
A technology for sclerotinia sclerotiorum and genetics of rapeseed, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions to achieve the effect of improving resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: BnMED16 gene isolation clone
[0031](1) Isolation and cloning of BnMED16 gene
[0032] The Brassica napus westar variety (provided by the Rapeseed Research Laboratory of Huazhong Agricultural University) was used as the experimental material. Super Total RNA Extraction Kit (purchased from Promega, U.S.) was used to extract the total RNA from leaves of Brassica napus westar variety. After the RNA extraction was completed, it was treated with DNaseI (purchased from Promega’s kit), and the RNA integrity passed 1.2% (w / v) Agarose gel (EtBr) electrophoresis detection (5V / cm). The determination of nucleic acid concentration was carried out on an IMPLENNanoPhotometer-N50 series ultra-micro ultraviolet spectrophotometer (Germany). The RNA 260 / 280 ratio is between 1.9 and 2.1, the 260 / 230 ratio is greater than 2.0, and the RNA with a concentration greater than 500ng / μL is used for the next analysis. cDNA was synthesized using IIQ RT SuperMix for qRNA (+gDNA...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: the acquisition of overexpression BnMED16 transgenic rape plant
[0037] (1) Construction of plant overexpression vector
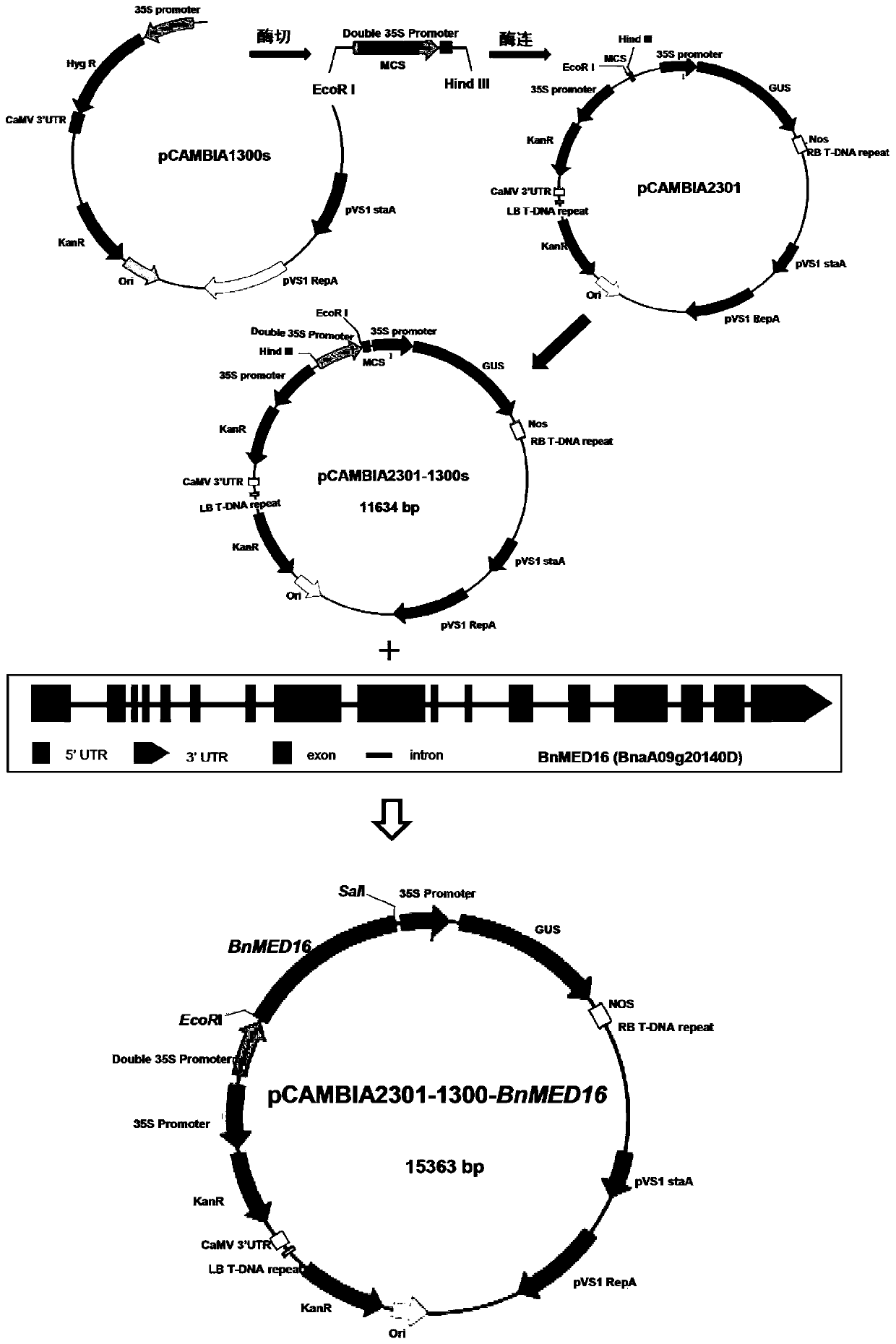
[0038] According to the CaMV 35S sequence (Gene ID: AJ007626) information published on NCBI, use Primer Premier5.0 software to design the following primers:
[0039] 5′-GAATTCTTAATTAAGAGCTCGCATGCC-3′ and
[0040] 5'-GGTACCGTCCCCCGTGTTTCTCCAA-3', the Double CaMV 35S fragment was amplified from the pCAMBIA1300s vector (purchased in Beijing Dingguo Changsheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) by PCR method, and then connected to the pCAMBIA2301 vector (Mr. Wang Jing, Huazhong Agricultural University Kindly donated) EcoRI / HidIII restriction site, and finally the final vector pCAMBIA2301-1300s (11634bp) was obtained.
[0041] EcoRI and SalI restriction sites and corresponding protective bases were added to the two ends of the BnMED16TA cloning amplification primers respectively, and the primers were named OE-BnMED16-F (5'CGGAATTCTTGCTCTCTCGCTCGACA...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Example 3: Evaluation of BnMED16 Overexpression Transgenic Rapeseed Against Sclerotinia
[0075] (1) Immune response of BnMED16 overexpression strain to S. sclerotiorum
[0076] The in vitro inoculation treatment of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (sclerotias clerotiorum, the pathogen of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum was preserved by the Laboratory of Life Science College of Huazhong Agricultural University and activated by the laboratory) was carried out on the second leaf of rapeseed seedlings (at the stage of four leaves and one heart). For the second leaf of the positive line with significantly increased expression in Example 2, the leaves were cut and placed in a transparent square box. The leaves of each transgenic plant were placed side by side with the non-transgenic control in a box, and several layers of filter paper were laid under the leaves. sheets and damp gauze, freshly prepared Mycelium block, with the side of mycelium facing down, was inoculated at the position s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com