Construction and application of model for researching interaction between HBV cccDNA and host
A MC-HBV and model technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of low copy number of cccDNA, no direct labeling and detection of HBVcccDNA, low transfection rate, etc., and achieve the effect of a reliable detection method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
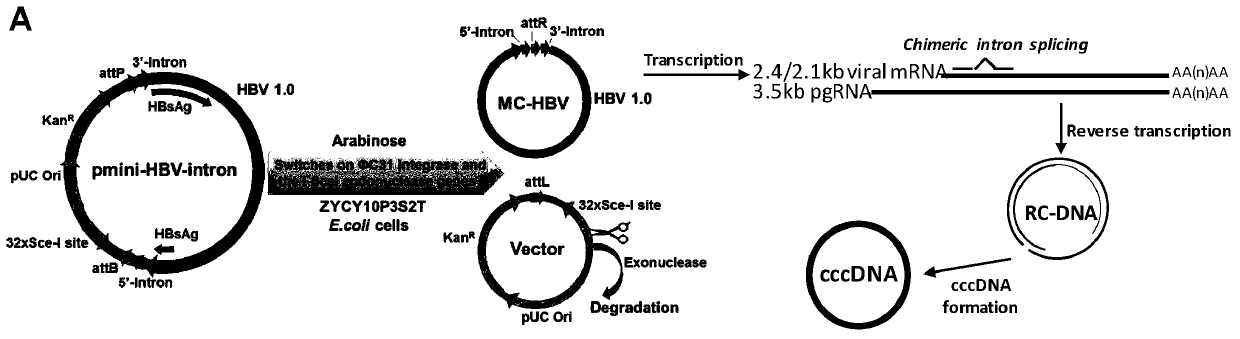
[0083] The construction of embodiment 1MC-HBV eukaryotic expression plasmid
[0084] 1. Using high-fidelity DNA polymerase to amplify the backbone fragments of HBV-Intron and MN0501 vectors;
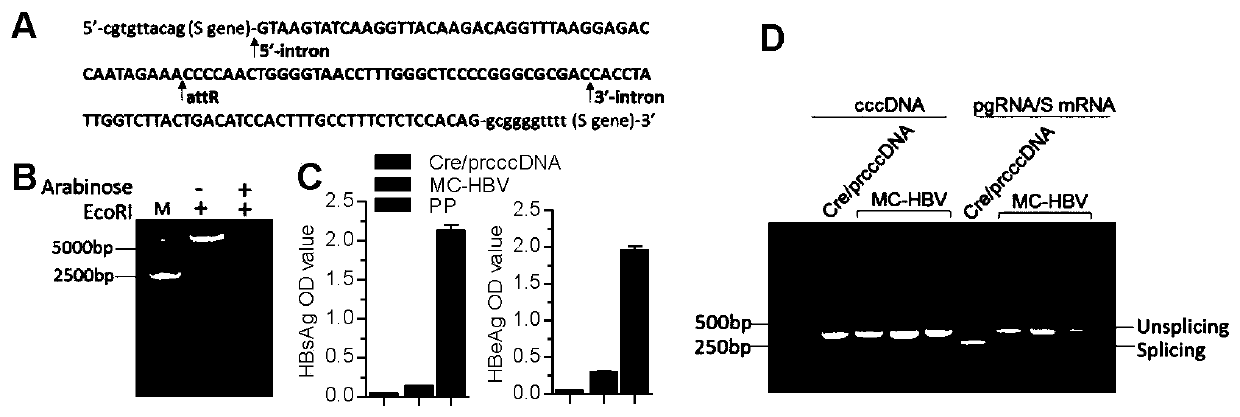
[0085] 1) HBV Intron-attR sequence:
[0086] 5'-cgtgtacag (S gene)-
[0087]
[0088] 2) High-fidelity DNA polymerase amplification system:
[0089]
[0090] PCR amplification conditions: pre-denaturation at 98°C for 3 min, followed by denaturation at 98°C for 10 s, annealing at 60°C for 15 s, extension at 72°C for 30 s and repeated 30 cycles, and finally extension at 72°C for 8 min.
[0091] 2. DNA gel electrophoresis, gel cutting recovery and quantification;
[0092]3. Infusion cloning technology connection, construction of eukaryotic expression plasmid pmini-MC-HBV-Intron
[0093]
[0094] Incubate at 50°C for 15 minutes;
[0095] 4. Transform DH5a competent, select and culture in Kan+ resistant LB culture plate;
[0096] 5. Pick a single clone, screen positive clones b...
Embodiment 2
[0102] Embodiment 2 MC-HBV alternative splicing ability and supporting HBV replication ability analysis
[0103] HuH7 cells were digested to make a concentration of 2×10 5 cells / ml of cell suspension, seeded into cell culture plates or dishes as needed. After culturing overnight for 16h-24h, the MC-HBV, PP and pCMV-Cre / prcccDNA plasmids were transfected into HuH7 cells for 48h, respectively. ELISA was used to detect HBsAg and HBeAg in the culture supernatant, and the pgRNA was detected by RT-PCR and PCR amplification using P1P2 primers. Whether alternative splicing occurs, whether the offspring cccDNA can be produced.
[0104] 1. ELISA detection of HBsAg in the supernatant
[0105] 1) Add 20 μl sample diluent to each well;
[0106] 2) Add 100 μl of negative and positive control serum or supernatant to be tested in corresponding wells respectively, and react at 37°C for 1 hour;
[0107] 3) Add 50ul of HRP enzyme-labeled antibody, and continue to react at 37°C for 30min;
...
Embodiment 3I
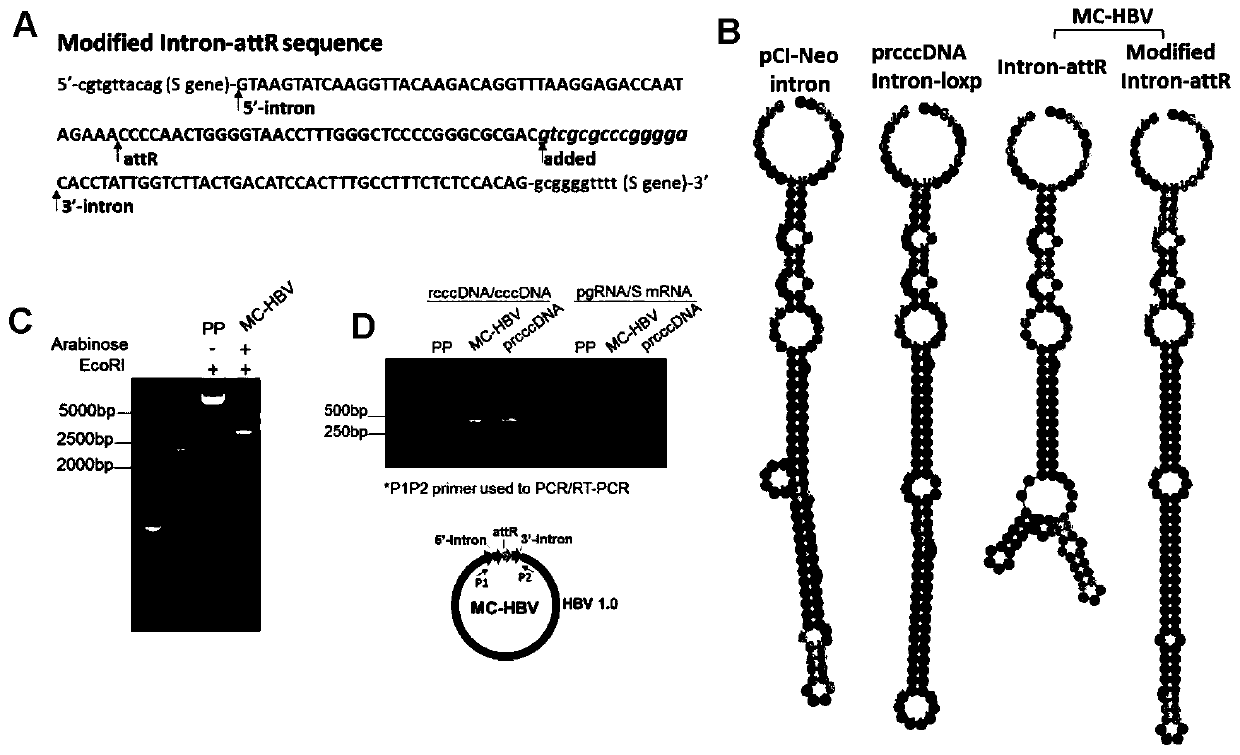
[0144] Example 3 Intron-attR sequence optimization restores pgRNA alternative splicing ability
[0145] The RNA secondary structure has an important influence on the efficiency of pre-mRNA alternative splicing. In Example 2, the 5'Intron-attR-3'Intron structure has more stem-loop structures, and the secondary structure changes from a single rod structure to two hairpins structure, and may be the main reason for the inhibition of RNA alternative splicing. According to the principle of complementary base pairing, add gtcgcgcccgggga sequence, changing its structure to a single rod-like structure similar to the intron of the 5'Intron-loxp-3'Intron and pCI-Neo vectors. Subsequent verification steps are the same as in Example 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com